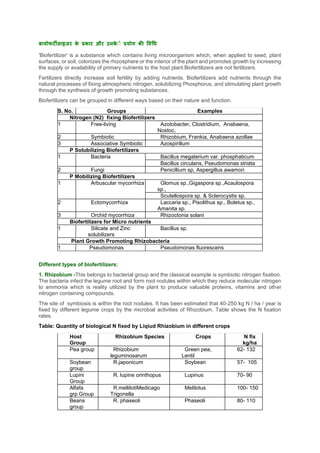
1. Biofertilizers are living microorganisms that help plants grow by increasing the supply of nutrients through natural processes like nitrogen fixation and phosphorus solubilization. They can be classified based on their function into nitrogen fixers, phosphorus solubilizers, and plant growth promoters.
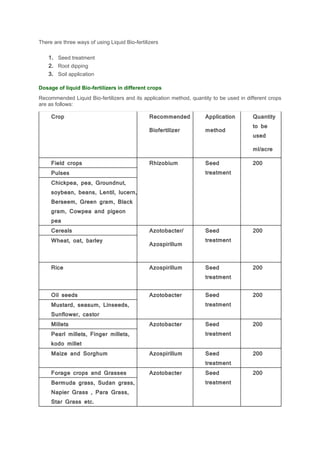
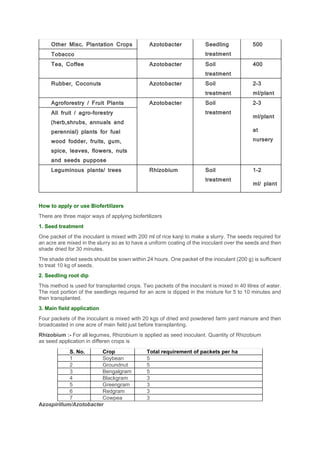
2. Common biofertilizers include Rhizobium for legumes, Azotobacter and Azospirillum for cereals, and mycorrhizal fungi. Liquid formulations have longer shelf lives and are easier for farmers to use than carrier-based biofertilizers. Proper application methods and dosages depend on the crop.
3. While biofertilizers provide ecological benefits over chemical