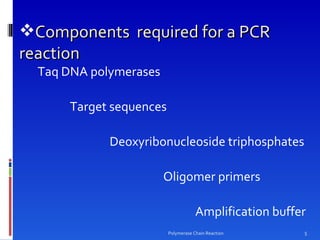
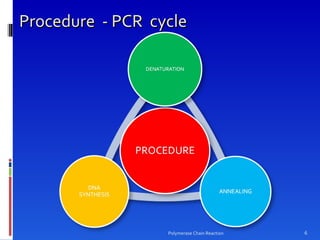
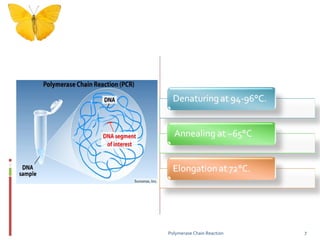
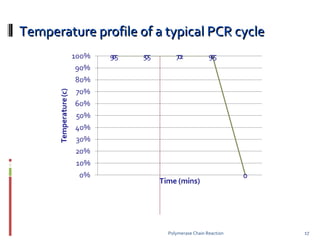
Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is a technique used to amplify DNA sequences. It was developed in 1984 by Kary Mullis, who won the Nobel Prize in 1993 for this work. PCR uses thermal cycling to amplify a target DNA sequence, allowing for its detection and analysis. It has applications in DNA cloning, sequencing, phylogeny, gene function analysis, diagnosis of hereditary diseases, genetic fingerprinting, paternity testing, and detection of infectious diseases.