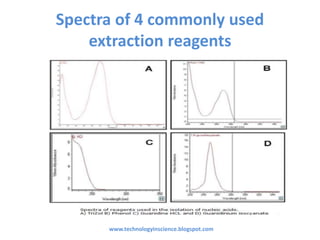
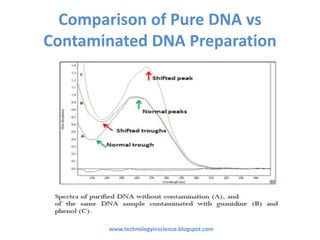
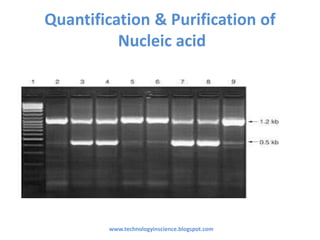
Nucleic acid quantification is essential for assessing the concentration and purity of DNA/RNA, which is critical for applications like PCR and restriction digestion. Two primary methods for quantification are the spectrophotometric method using NanoDrop and agarose gel electrophoresis, each having distinct advantages for measuring sample purity and concentration. The document outlines how to interpret spectrophotometric readings and the separation of nucleic acids in agarose gel, including the identification of contaminants.