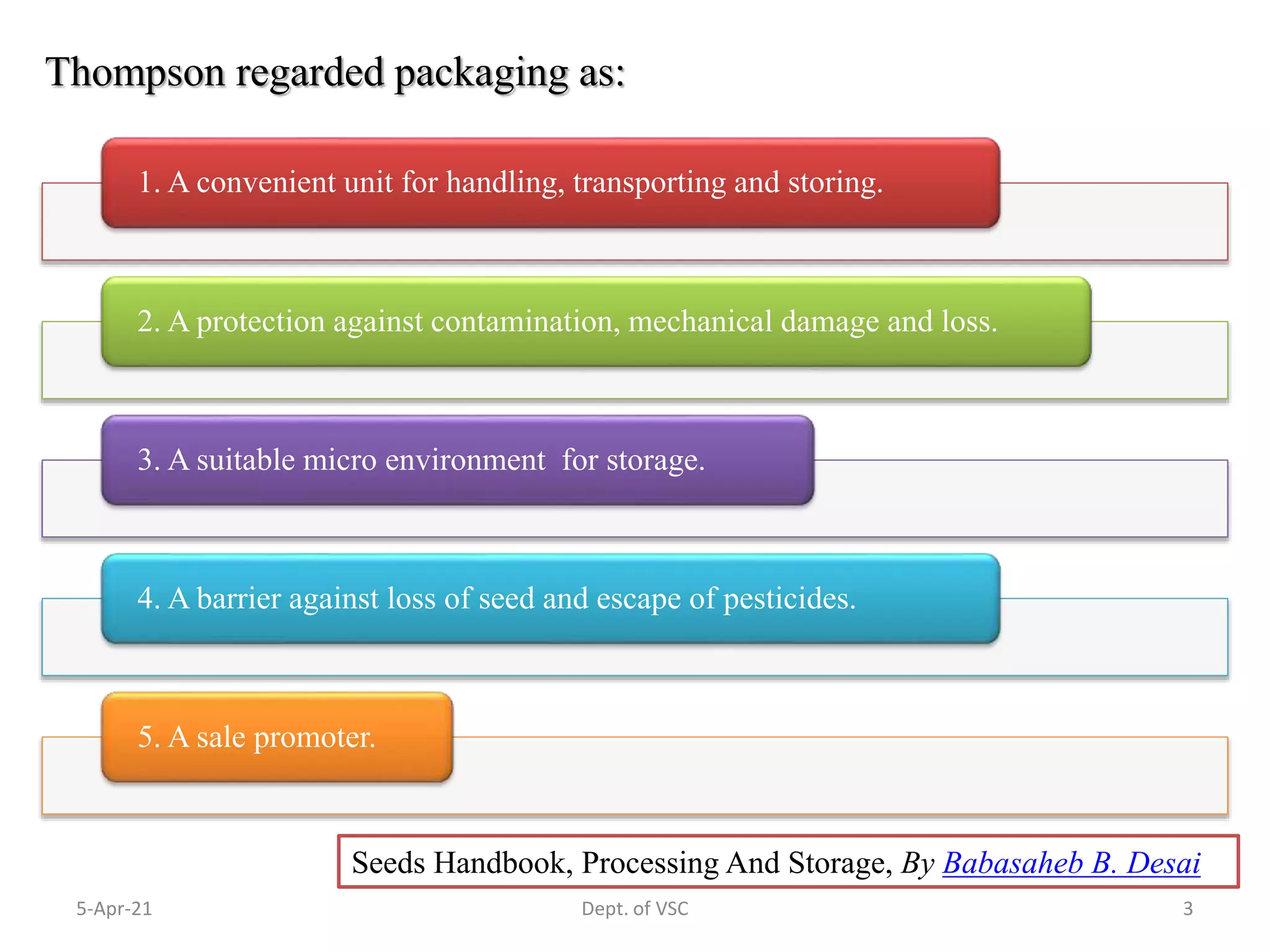
The document discusses seed packaging, labeling, and storage. It describes the different types of containers used for packaging seeds, including moisture-proof and hermetically sealed containers for long-term storage. The key steps in seed packaging include preparing and weighing seeds, filling labeled containers, sealing containers to maintain moisture content, and recording packaging information. Quality control checks ensure containers are sealed properly and don't leak. Labels contain important information about the seed accession for identification and tracking.