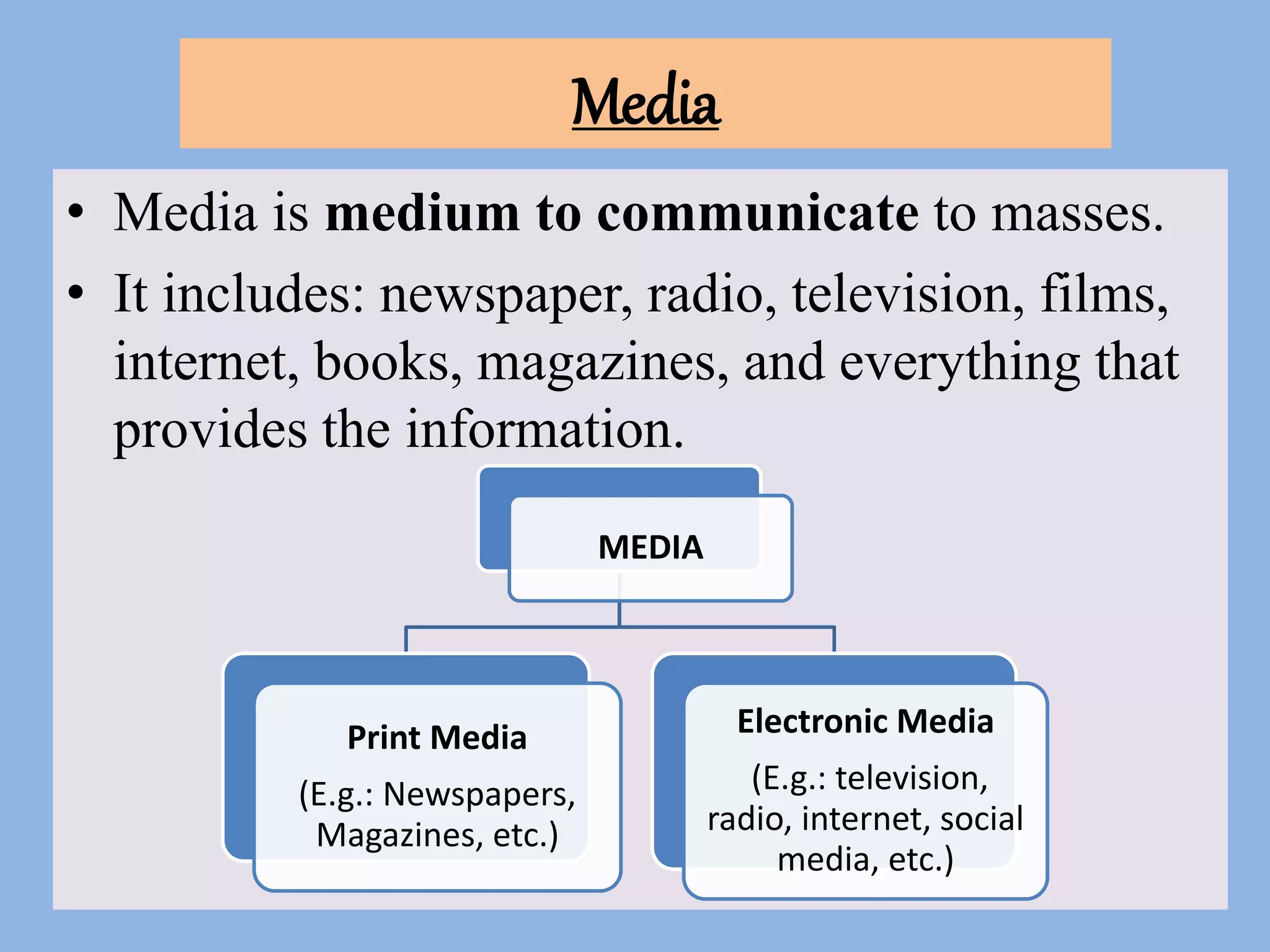
This document discusses media ownership patterns in India. It notes that both public and private entities own parts of the Indian media. For newspapers and magazines, around 70% are privately owned by individuals, partnerships, trusts or companies. The government owns some media organizations that disseminate information but does not own newspapers directly. Films are mostly privately owned by producers and distributed through private distributors and exhibitors. Radio includes both private FM channels and public organizations like All India Radio. In conclusion, the media landscape involves a mix of public and private ownership with some government oversight.