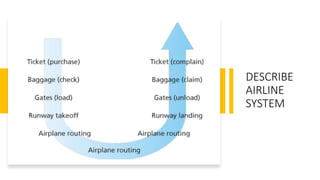
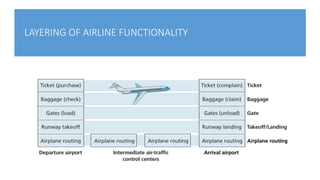
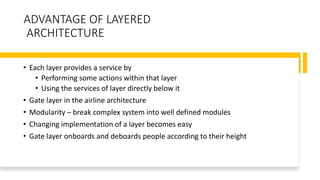
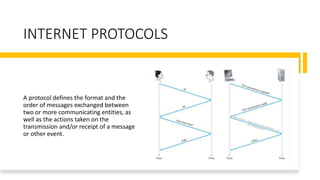
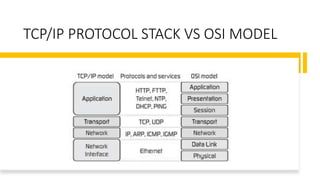
The document discusses the layered architecture of internet protocols and how communication occurs between devices on the internet, using an analogy of an airline system. It outlines the roles of various layers: application, transport, network, data link, and physical, highlighting the respective protocols and functions of each layer. Additionally, it raises questions about the implementation and physical location of these layers within networked devices.