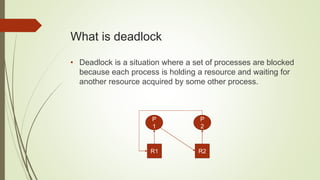
Deadlock occurs when a set of processes are blocked because each process is holding a resource and waiting for another resource held by another process. There are four necessary conditions for deadlock: mutual exclusion, hold and wait, no preemption, and circular wait. There are four approaches to handling deadlock: ignore, avoid, prevent, and detect and recover. Deadlock avoidance algorithms aim to keep the system in a safe state by considering available and allocated resources. Banker's algorithm is a deadlock avoidance technique that maintains a safe sequence of pending processes.