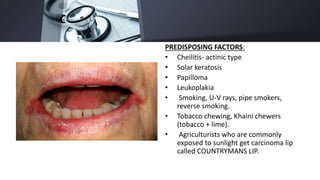
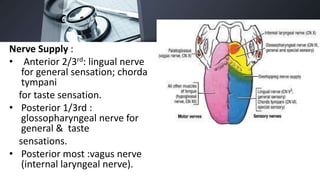
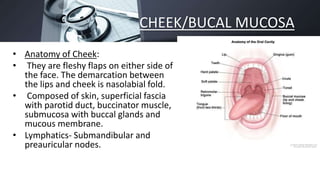
1. Carcinoma of the oral cavity most commonly arises from the lips, tongue, floor of mouth, cheek and retromolar trigone. Major risk factors include smoking, alcohol, betel nut chewing and HPV infection.
2. Early lesions are typically treated with wide local excision or radiotherapy. More advanced tumors involving surrounding bone or lymph nodes may require surgery such as partial glossectomy or mandibulectomy combined with neck dissection followed by postoperative radiotherapy.
3. Prognosis depends on tumor size, location and extent of spread - tumors of the posterior tongue or those invading surrounding structures carry a worse prognosis.



![Epidemiology:
• Oral ca tightly associated with exposure to causative tobacco
carcinogens.
• HPV-associated with oropharyngeal &nasopharyngeal ca.
• EBV-responsible for subset of nasopharyngeal ca.
• Male predominance due to more males consume tobacco but
in recent years ratio is decreasing because increased incidence
of female smokers.
• HPV associated head and neck SCC has 4:1 male
predominance.
• SCC is MC head and neck tumour[88.9%].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/oralmalignanciesm-230731122132-49add7cf/85/ORAL-MALIGNANCIES-M-pptx-4-320.jpg)