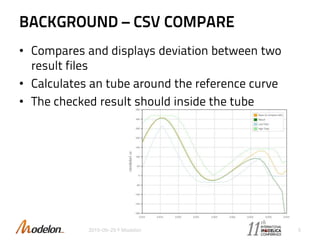
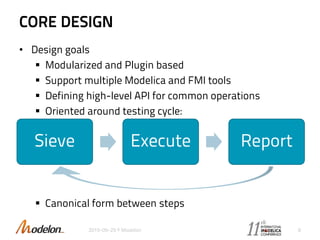
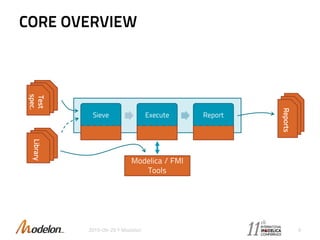
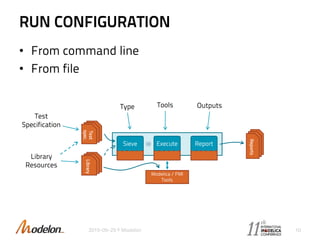
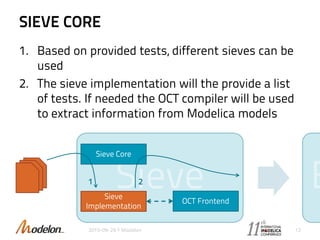
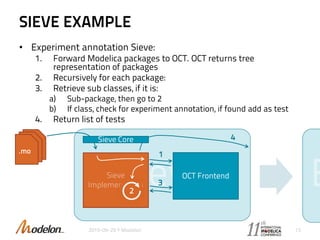
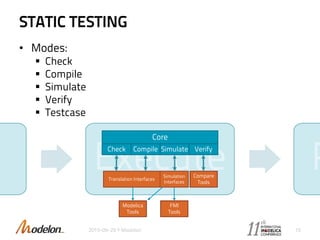
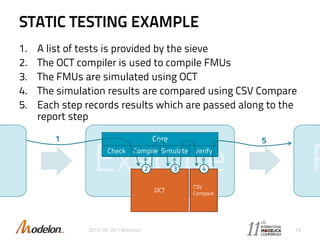
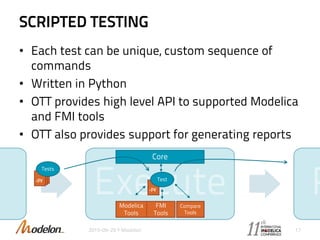
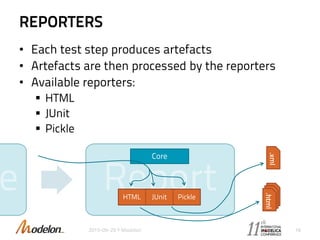
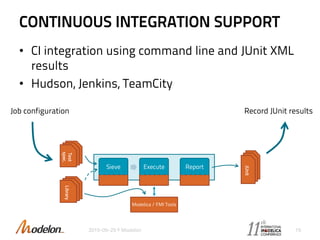
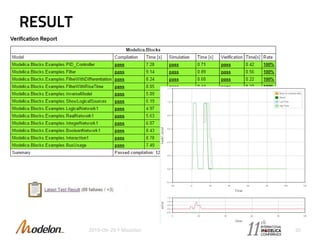
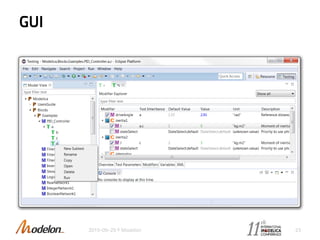
The document introduces the Optimica Testing Toolkit, which provides a framework for testing Modelica models across different tools. It allows flexible test authoring and automated test execution with reporting. The core runs tests through a sieve to extract them, executes them, and reports the results. Tests can be run statically through predefined sequences or dynamically through scripting. The goal is a cross-tool testing platform to ensure consistent functionality over time.