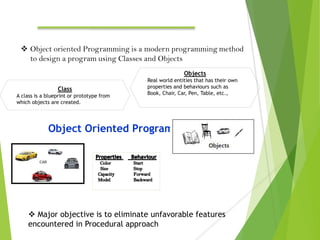
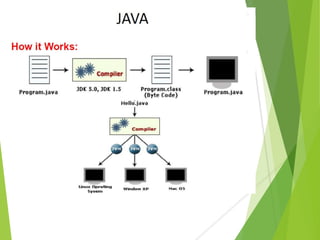
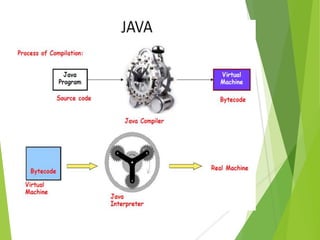
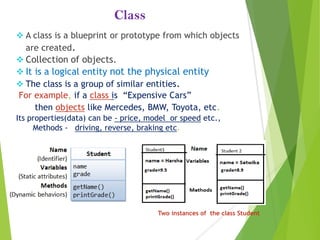
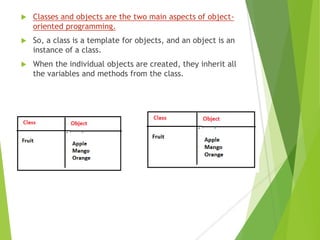
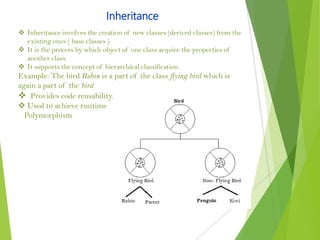
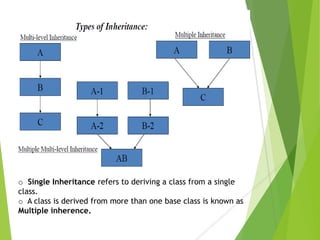
The document provides an overview of Java Object-Oriented Programming (OOP) concepts, highlighting its development by James Gosling in 1995 and key principles such as abstraction, encapsulation, inheritance, and polymorphism. It contrasts OOP with procedural programming, emphasizing the advantages of OOP, including better data management and code reusability. The document also outlines specific attributes of Java as a class-based and concurrent programming language, along with its applications in various fields.