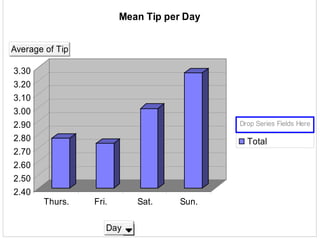
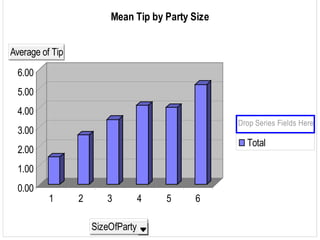
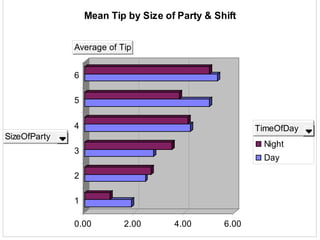
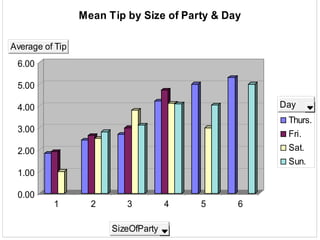
The document outlines the general procedure for hypothesis testing, including defining the null and alternative hypotheses, calculating the test statistic, and making a decision based on significance levels and critical values. It then provides an example case study analyzing factors that may influence food servers' tips, such as day of week, party size, gender, and time of shift. Two hypothesis tests are conducted. The first finds Saturday and Sunday are the best days for tips. The second finds that larger parties tip better than smaller parties, on average. Based on the results, the recommendation is to schedule food servers on a rotating basis across days and shifts to ensure fair treatment.