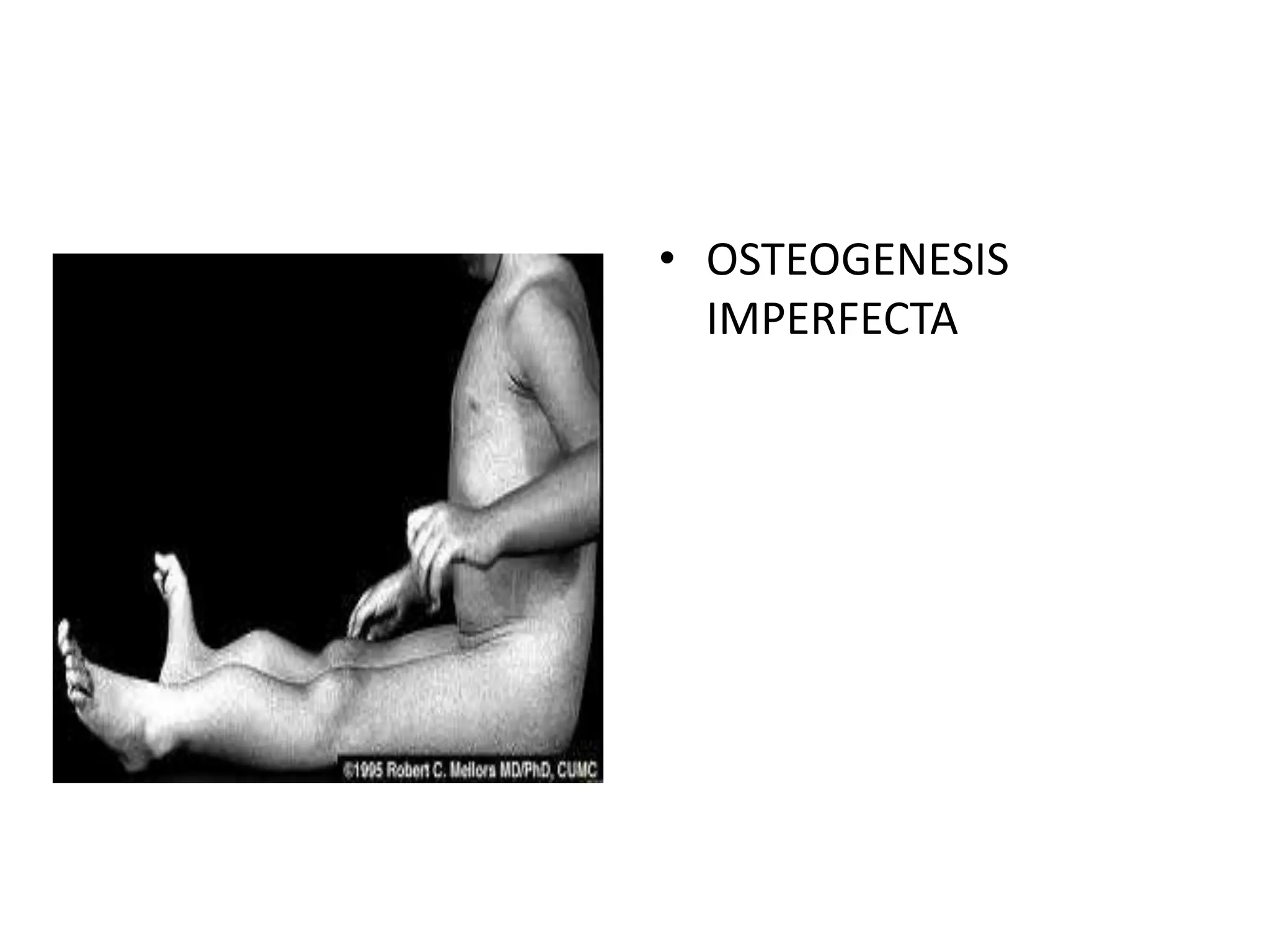
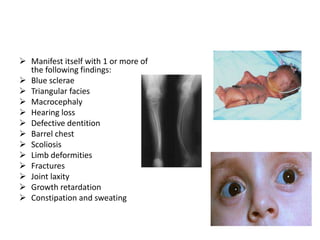
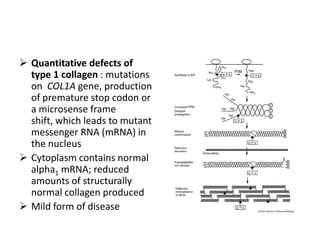
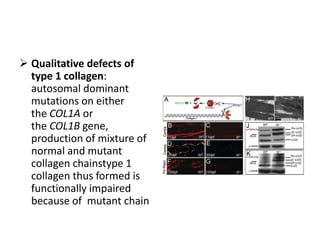
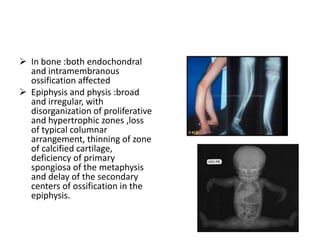
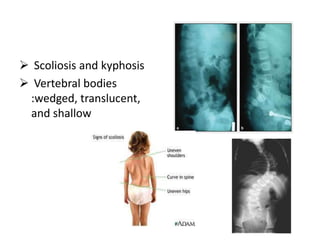
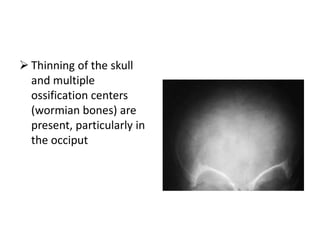
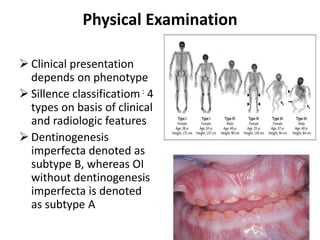
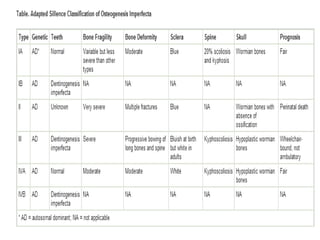
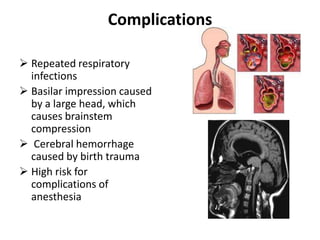
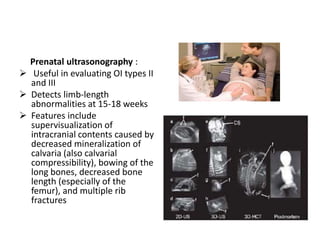
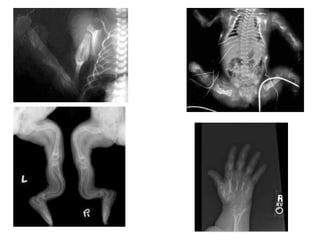
Osteogenesis imperfecta (OI), also known as brittle bone disease, is a genetic disorder characterized by bones that break easily. It is caused by mutations in genes that produce type 1 collagen, which is important for bone strength. Symptoms can include bone fractures, skeletal deformities, weak bones, hearing loss, and blue sclera. Treatment focuses on surgery to repair bones, bracing to prevent deformities, and bisphosphonates to increase bone density and reduce fractures.