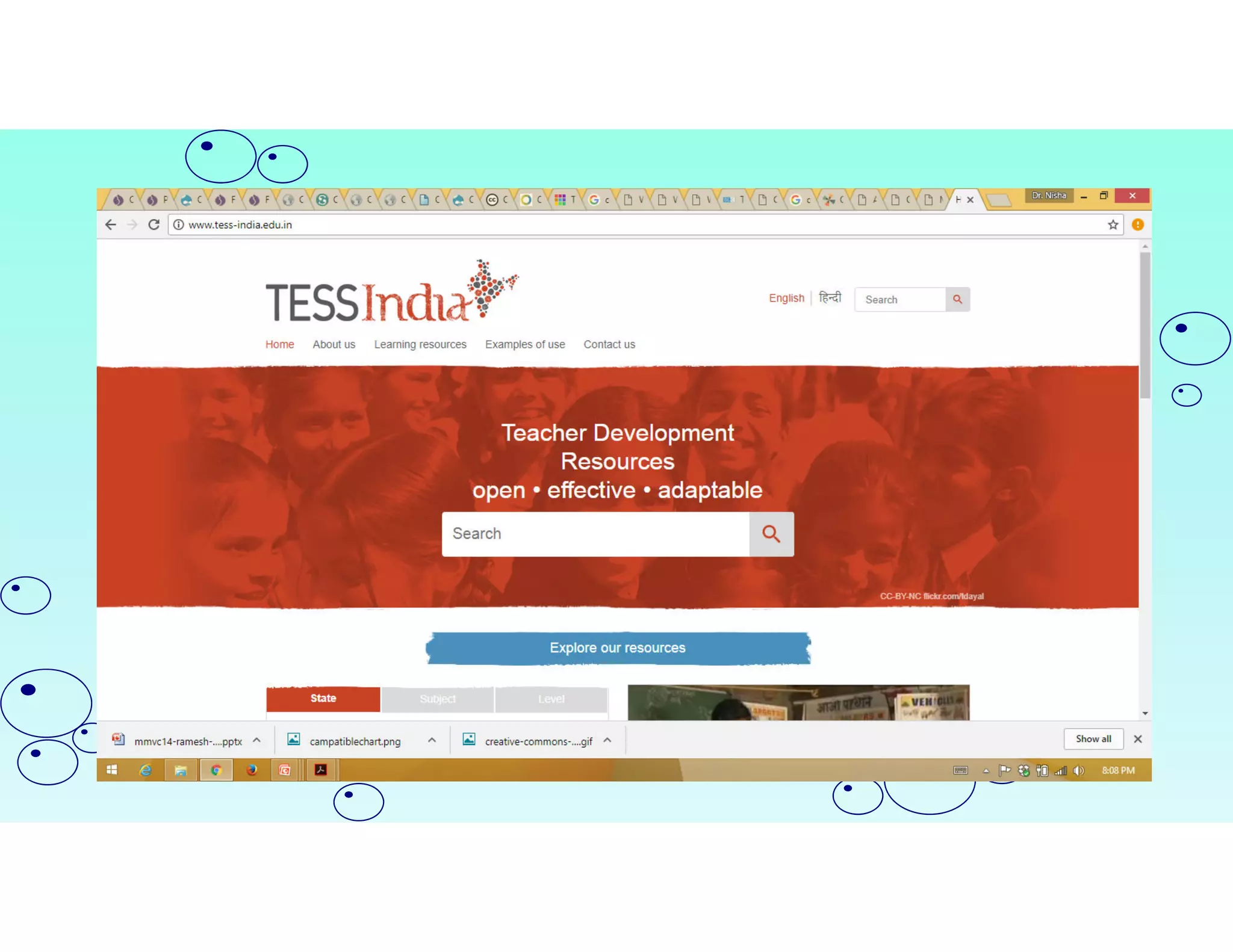
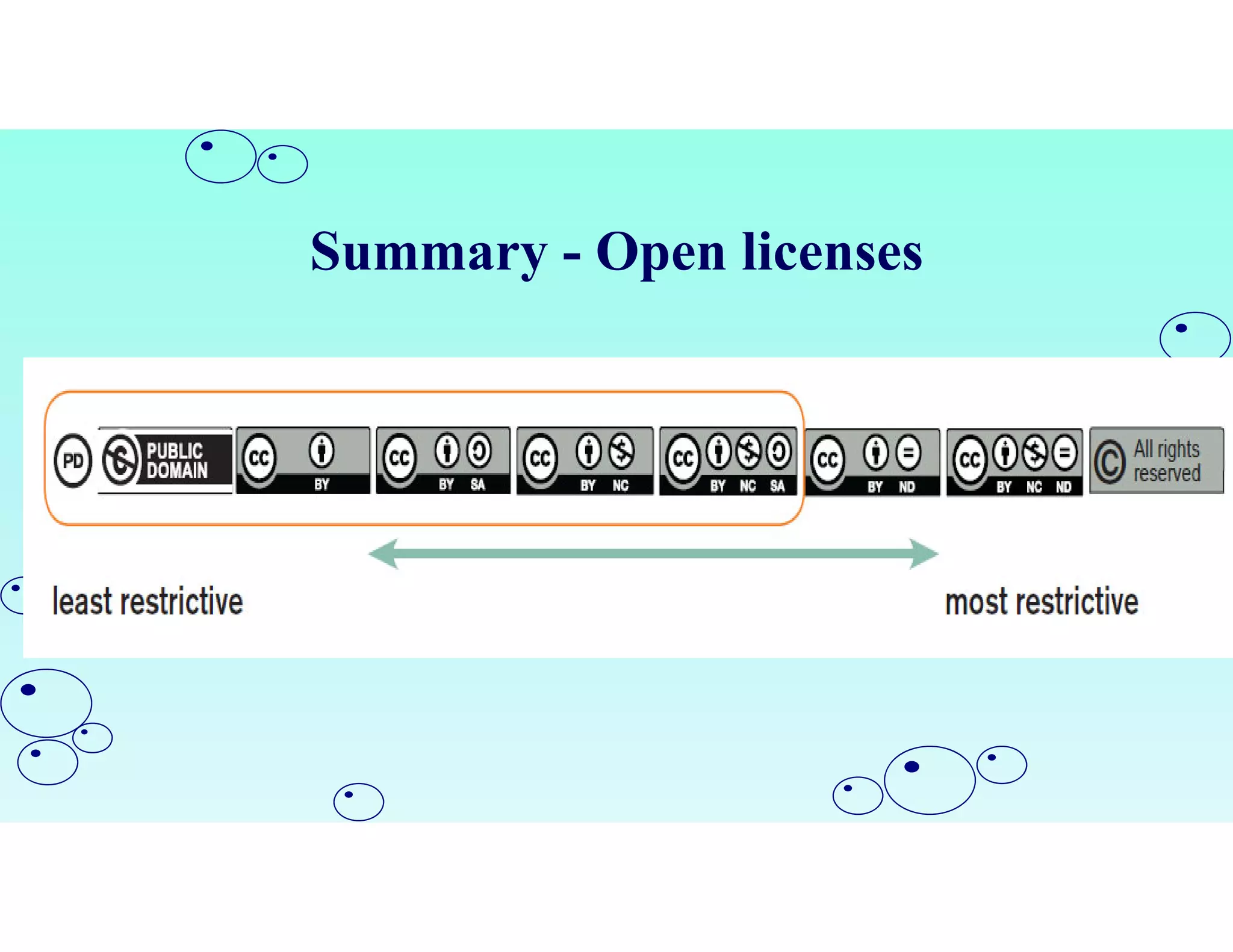
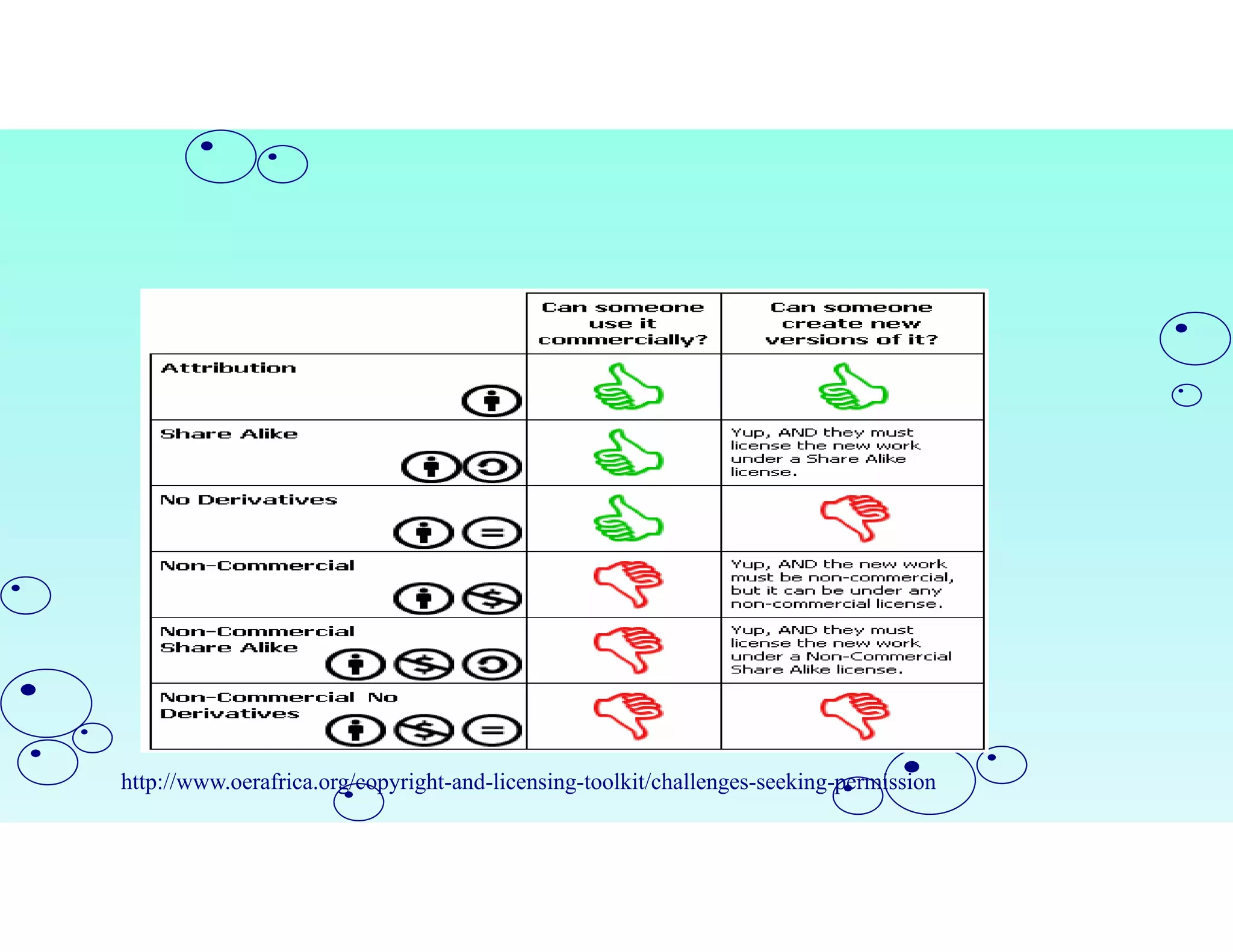
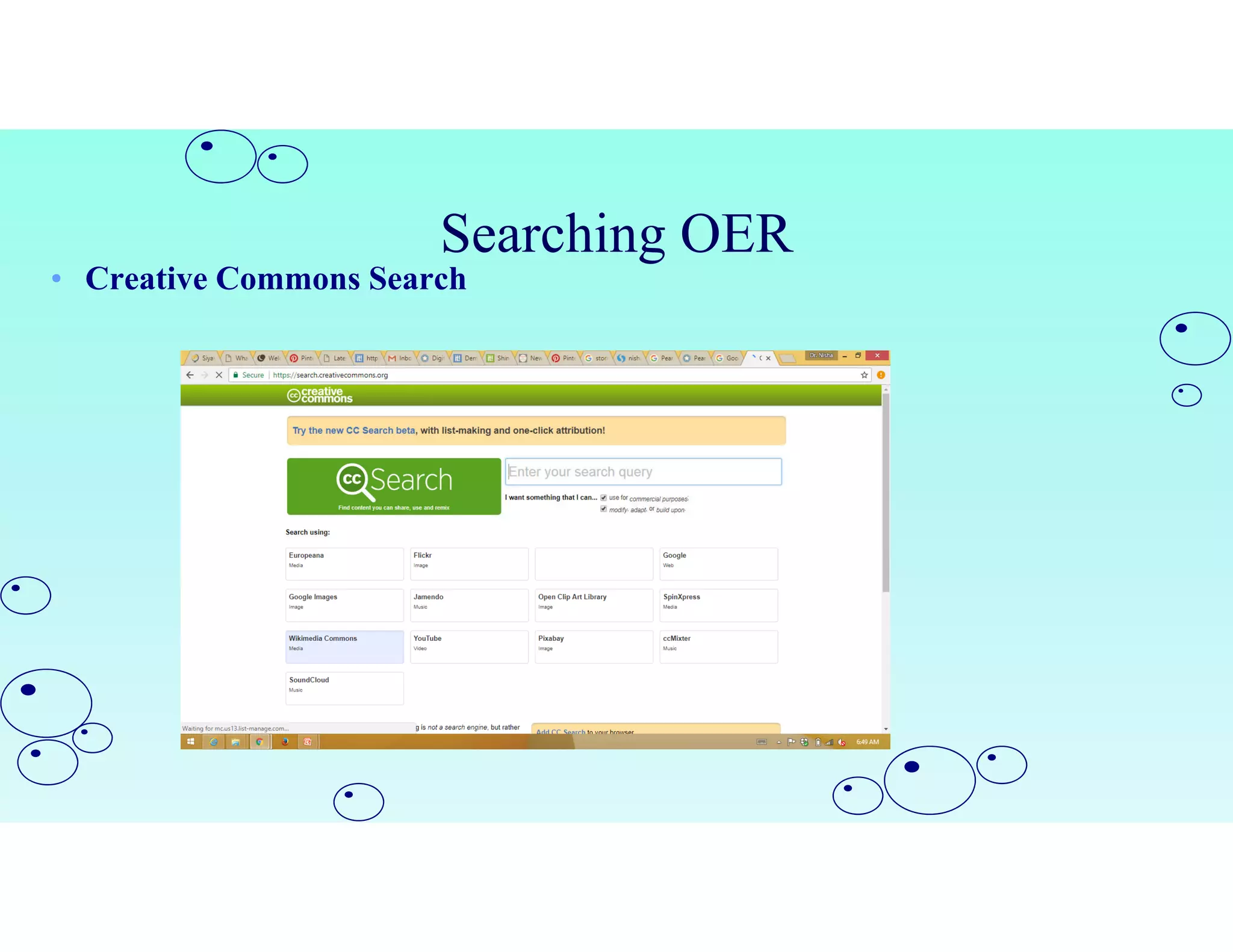
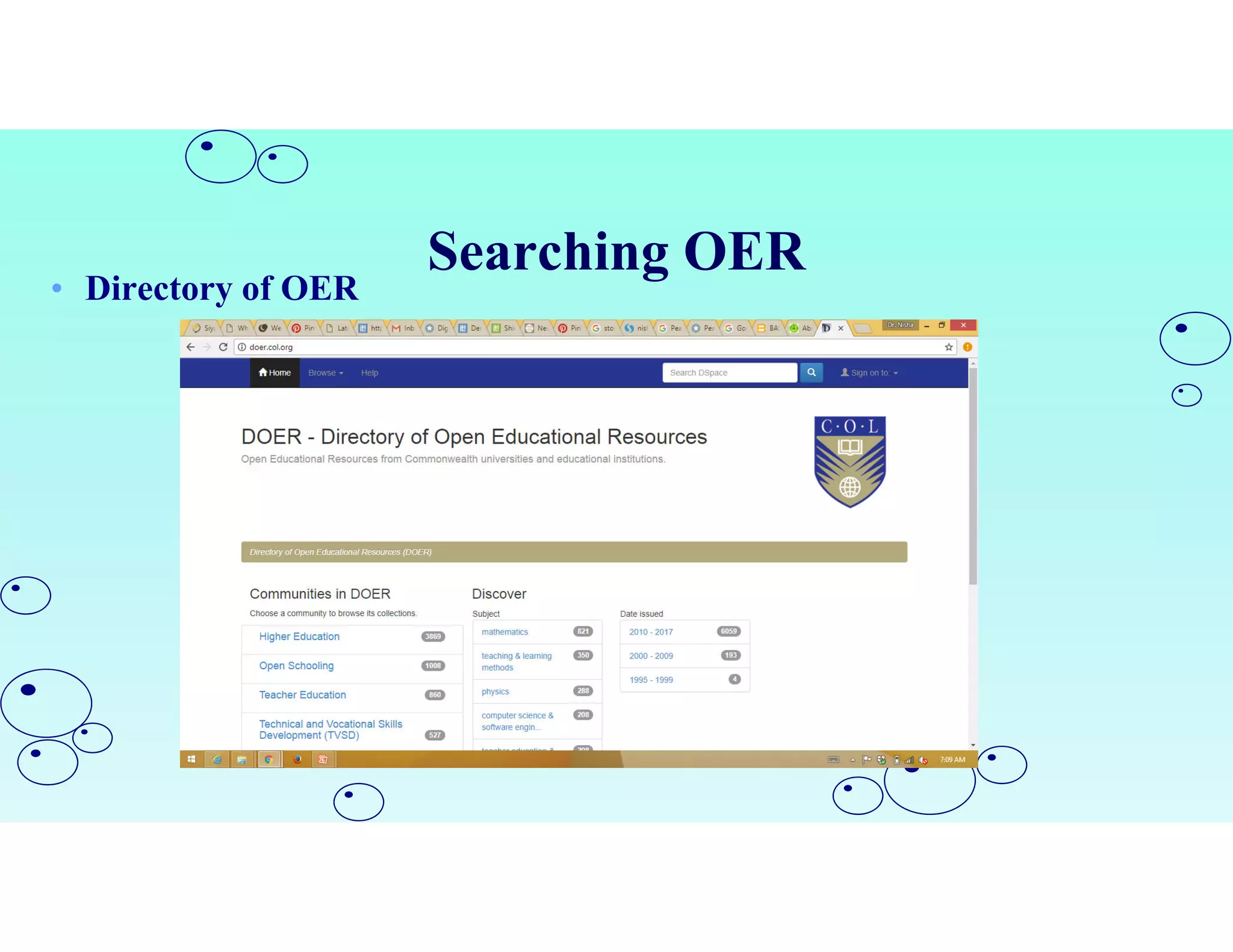
Open Educational Resources (OER) are teaching and learning materials that can be freely used and adapted. OER include materials like textbooks, videos, tests, software and any other resources used to support education. Some key characteristics of OER include free access, use, adaptation and sharing. OER are typically licensed under open licenses like Creative Commons licenses which allow for free use while requiring attribution. Major repositories of OER include sites like OER Commons, MERLOT and repositories from initiatives in India like NPTEL and NROER. OER are created and shared to achieve goals like expanding access to education and supporting open knowledge.