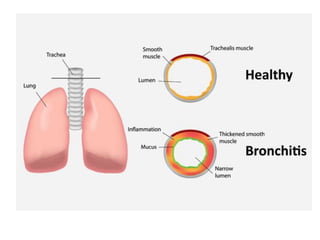
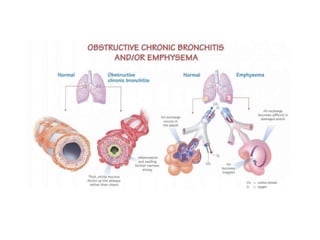
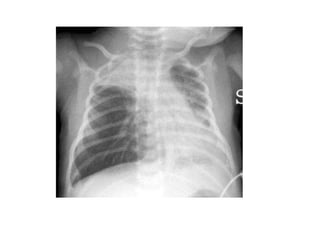
The document discusses obstructive bronchitis in children. It defines bronchitis as an inflammation of the bronchial mucosa that can affect the upper respiratory tract. The main causes of obstructive bronchitis in children are viruses, bacteria, hypothermia, poor air quality, and contact with sick children. The symptoms of obstructive bronchitis include a heavy cough, cyanosis, wheezing, and shortness of breath. Treatment involves reducing bronchial obstruction through pulmonary medications, humidified oxygen, and bronchodilators.