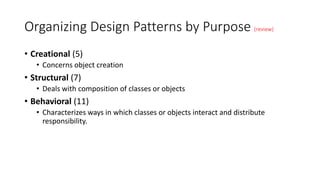
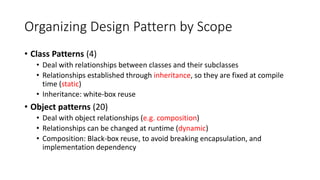
The document discusses different ways to organize design patterns. It describes categorizing patterns by purpose into creational, structural, and behavioral patterns. Patterns can also be organized by scope into class patterns, which deal with inheritance relationships that are fixed at compile time, and object patterns, which deal with dynamic object relationships through composition. The document provides a catalog of 23 design patterns organized by scope and purpose. It also describes six types of design patterns based on how they use inheritance and composition. Finally, it discusses relationships between patterns in how they can be used together, provide alternatives, or have similar designs with different intents.