Embed presentation
Download to read offline


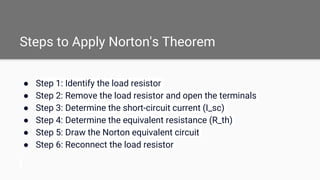


Norton's theorem states that any linear circuit, no matter how complex, can be simplified into an equivalent circuit with a single current source in parallel with a resistance connected to a load. The theorem involves identifying the load resistor, determining the short-circuit current and equivalent resistance, and drawing the Norton equivalent circuit. It can be used to simplify complex circuits, design and analyze electronic circuits, and troubleshoot electrical networks, but is limited to linear DC circuits.





