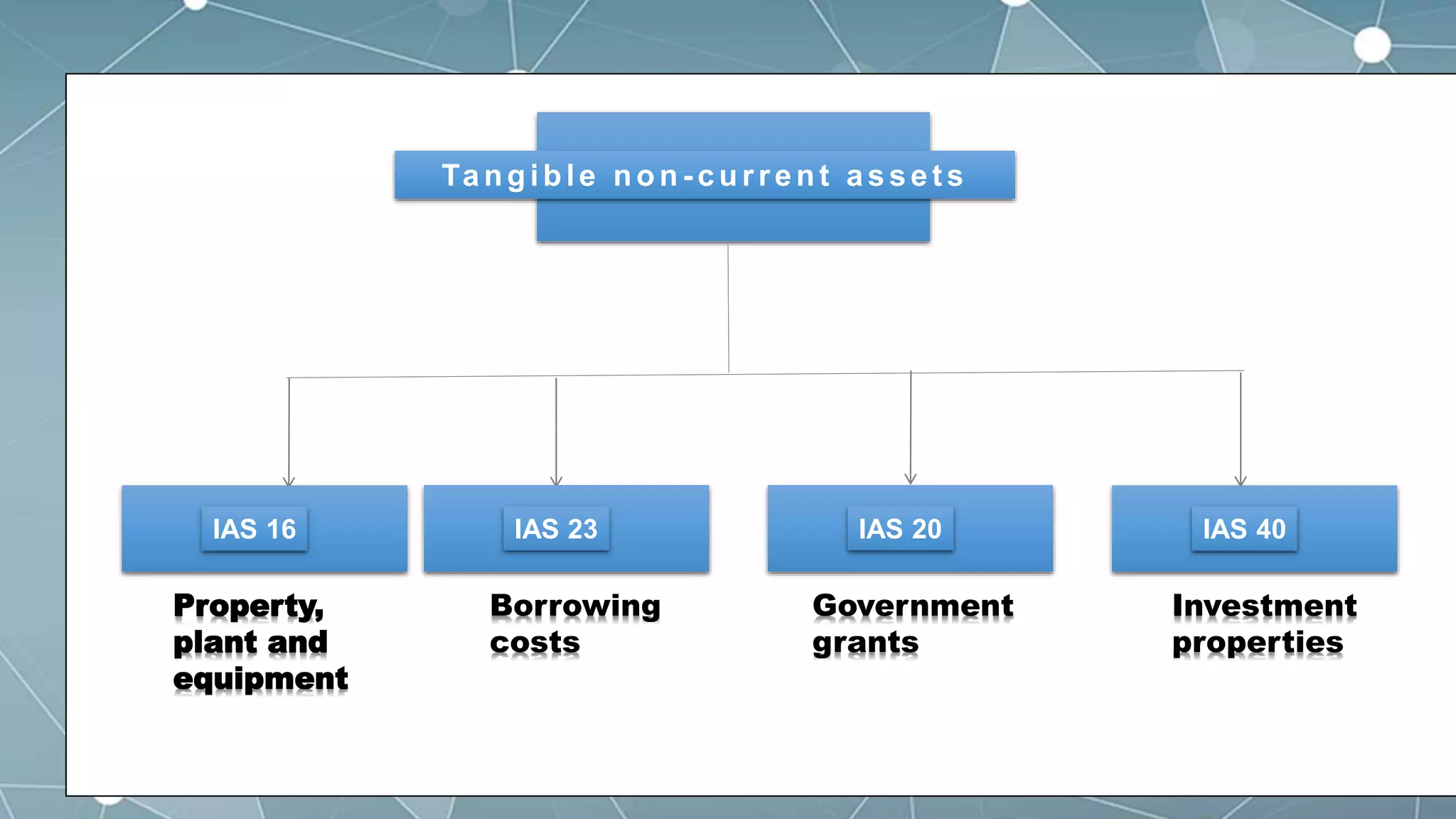
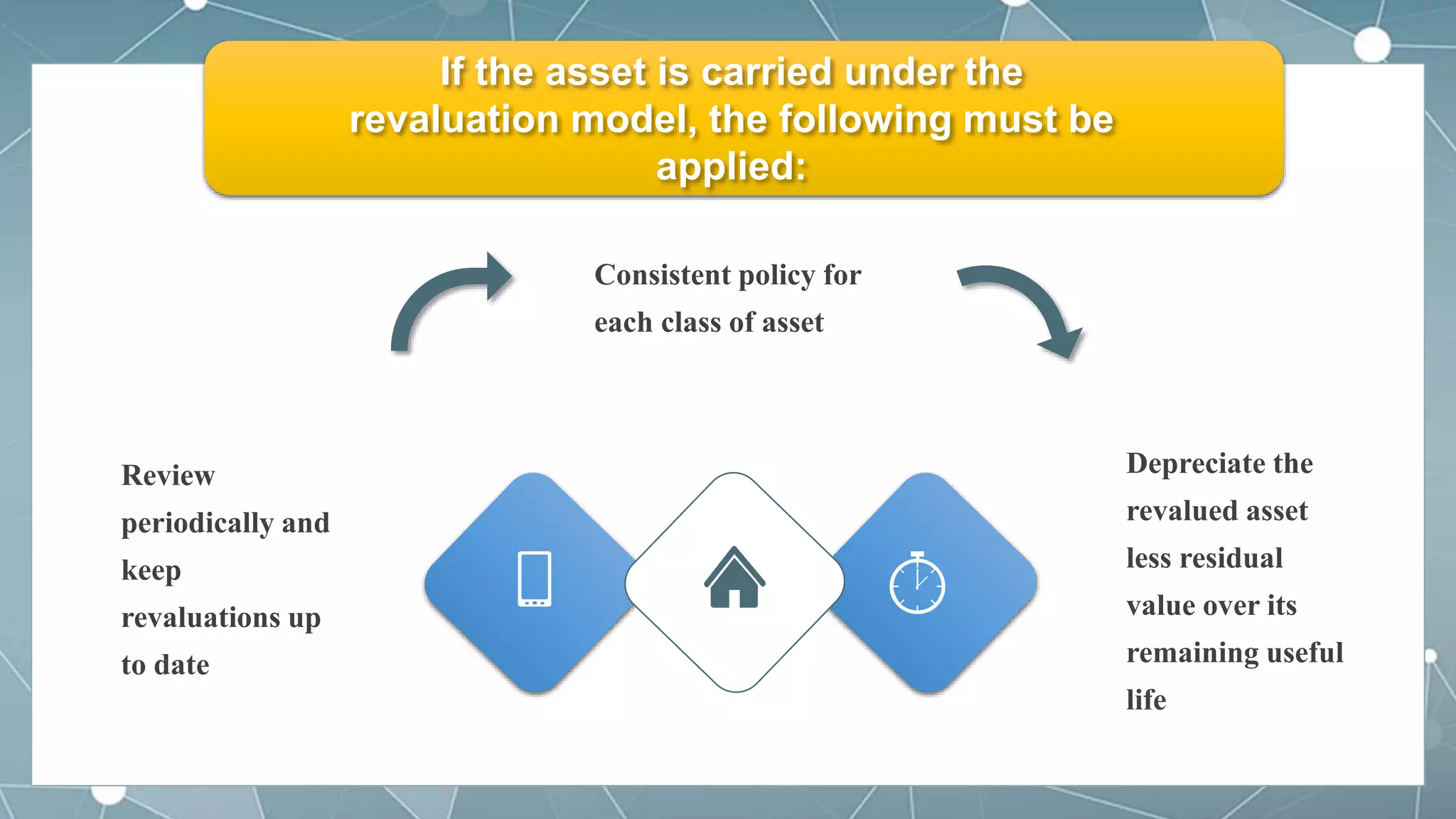
This document discusses accounting for tangible non-current assets under IAS 16, IAS 23, IAS 20 and IAS 40. It covers measurement of property, plant and equipment at cost or using revaluation model. It discusses capitalization of borrowing costs, treatment of government grants, and classification and measurement of investment properties using cost or fair value model. The document provides accounting policies, requirements and examples for non-current tangible assets in accordance with International Financial Reporting Standards.