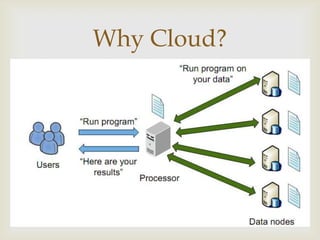
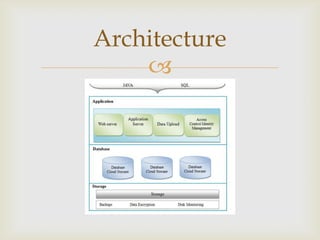
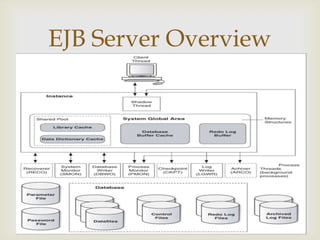
This document discusses database management systems (DBMS) in the cloud. It outlines limitations of traditional DBMS including costs, and benefits of cloud DBMS including lower costs, scalability, and moving operational burdens to service providers. It proposes an architecture for a cloud DBMS and discusses challenges including multi-tenancy, elastic scalability, and privacy. Requirements are outlined for users, public clouds, and providers. Screenshots show example features of a cloud DBMS including login/signup, database creation, table creation, and data entry/deletion. Future work and references are also included.