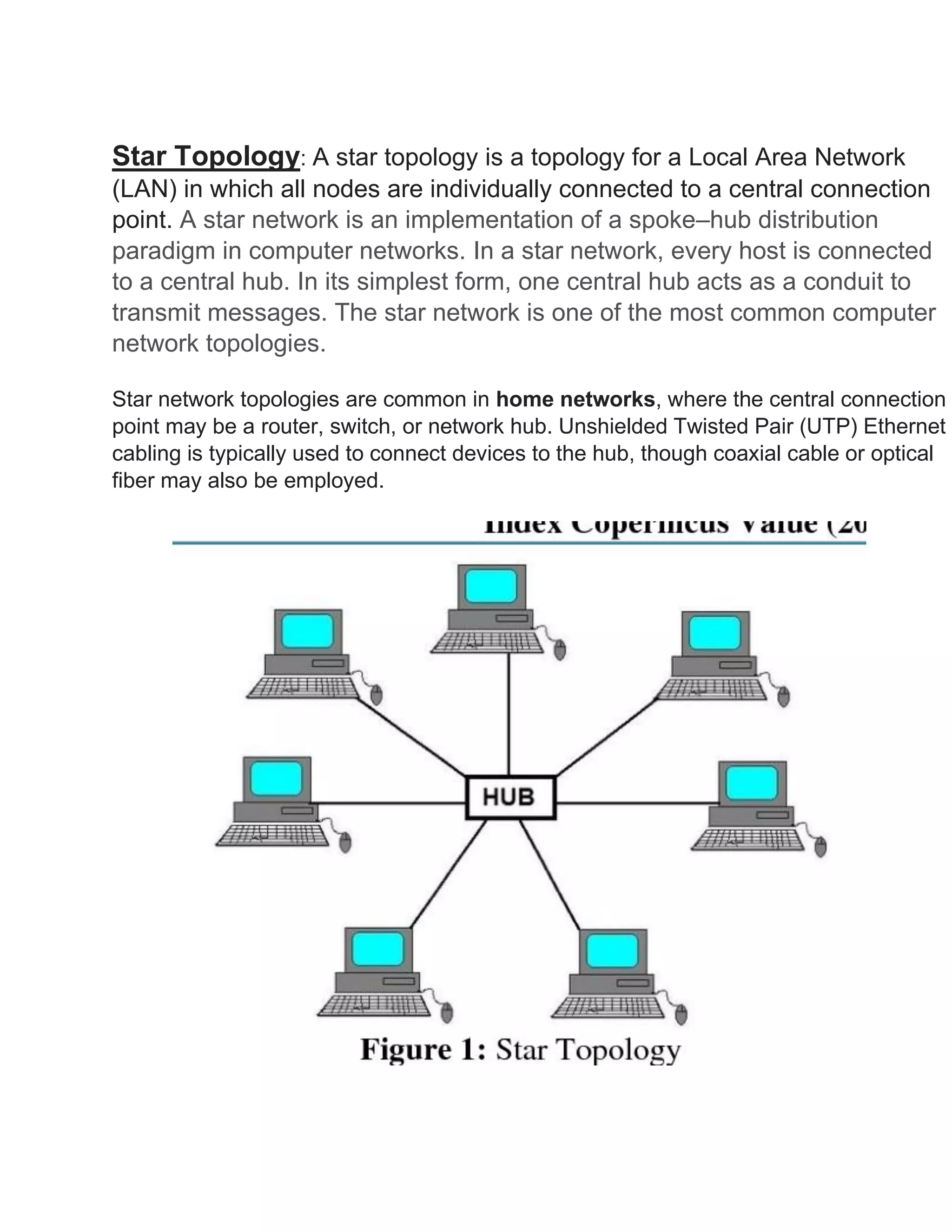
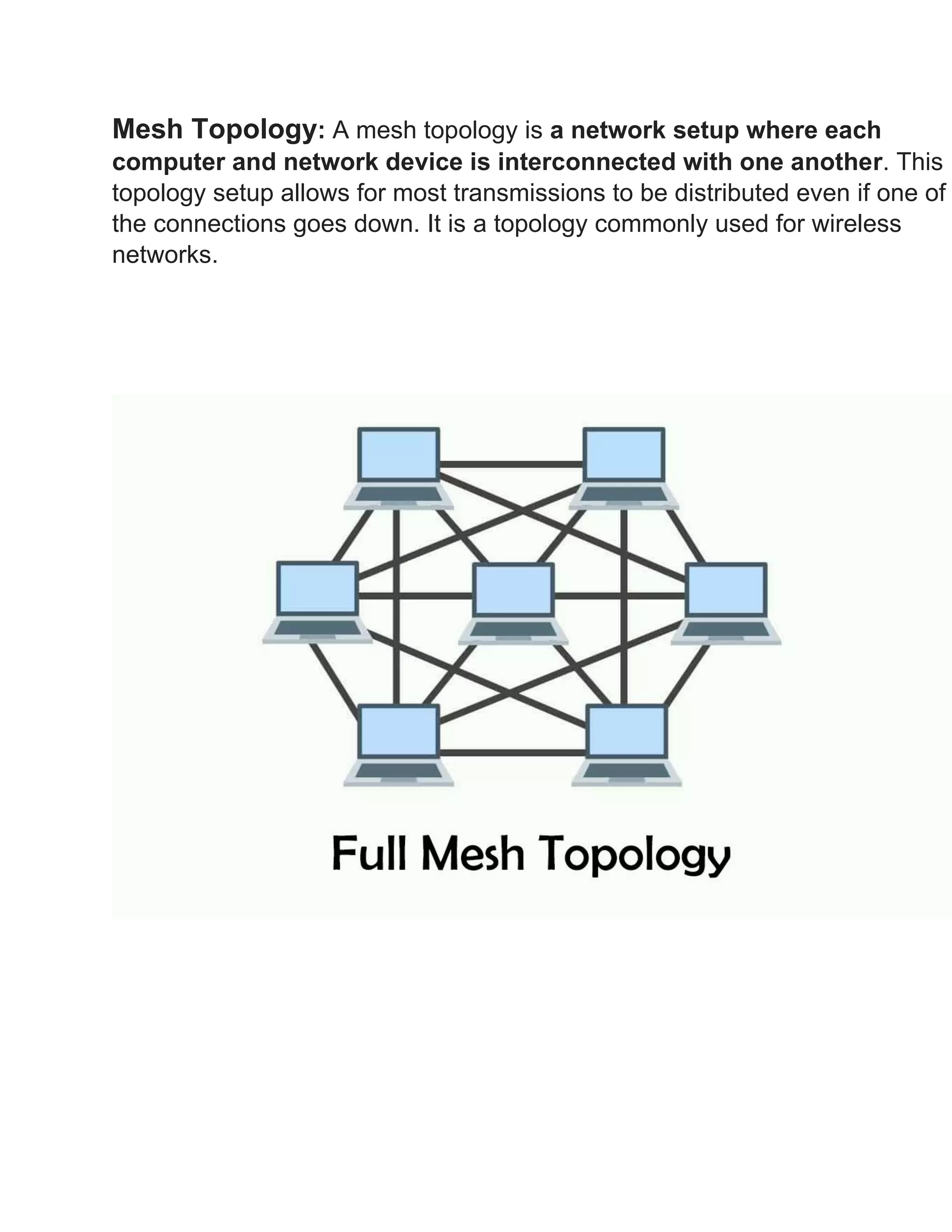
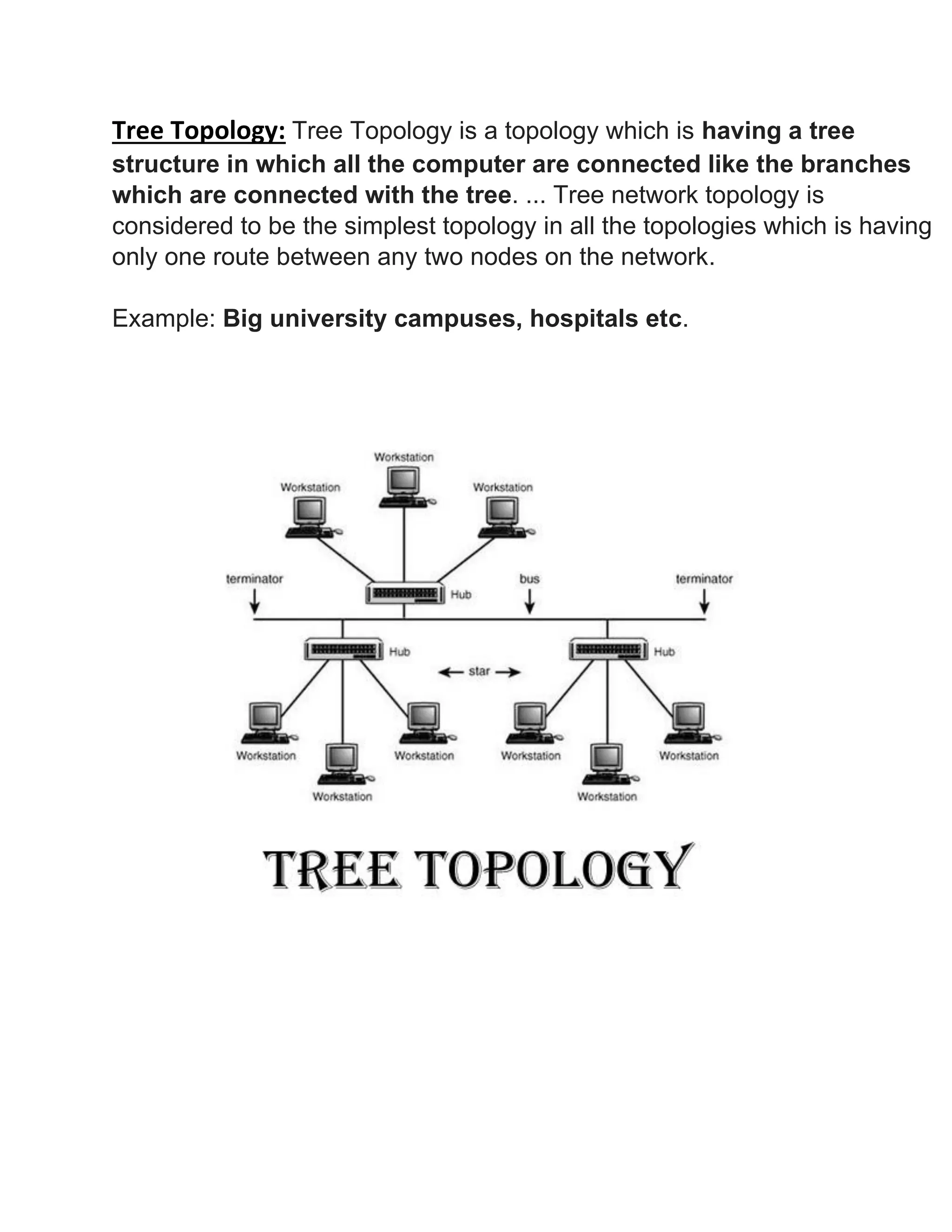
This document discusses different types of network topologies. It defines network topology as the arrangement of links and nodes in a network and provides examples of physical topologies including star, mesh, tree, ring, point-to-point, circular and hybrid. The document then proceeds to describe the characteristics of several common network topologies - bus, ring, star, mesh, tree and hybrid - in one to three sentences for each.