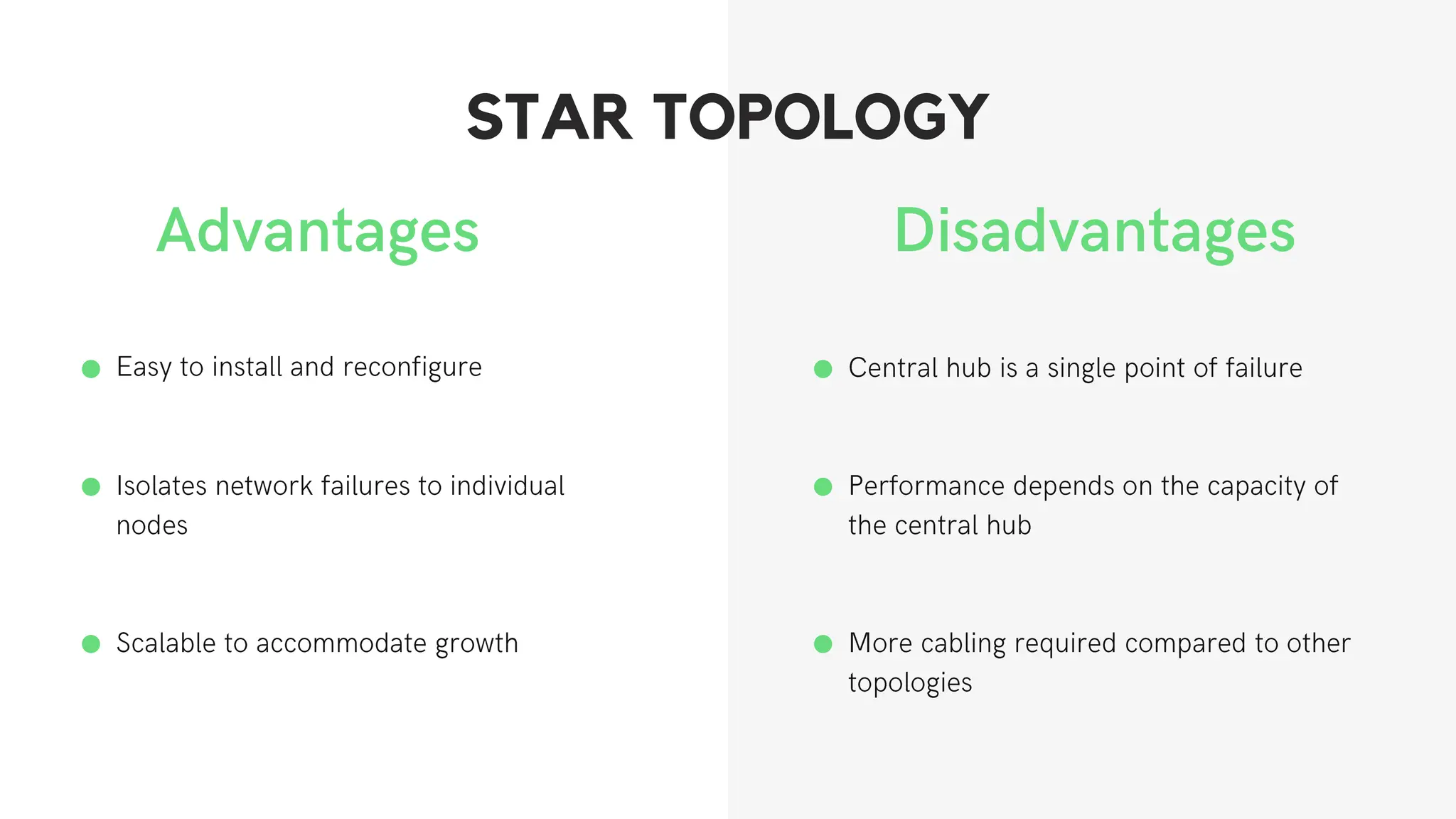
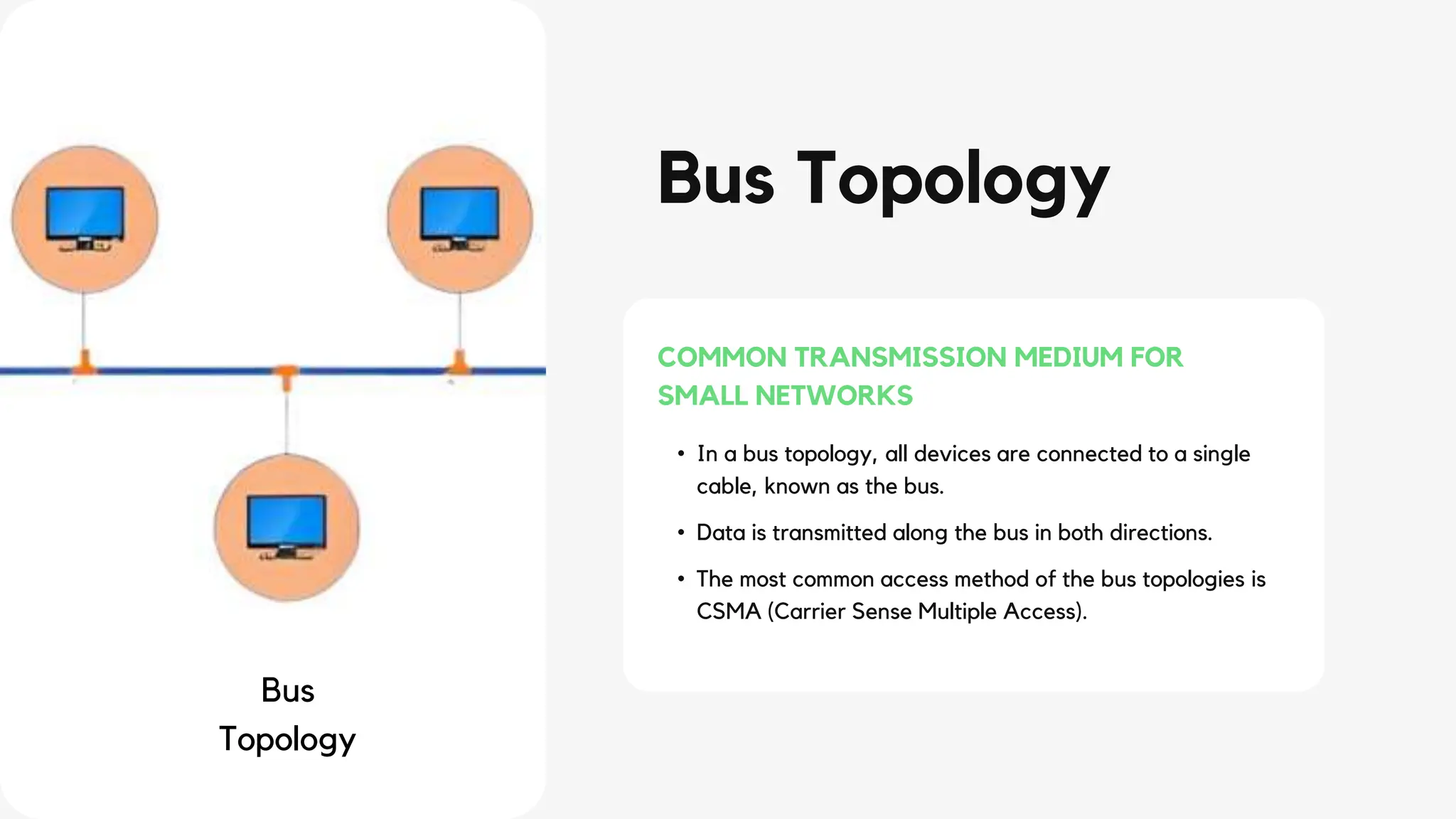
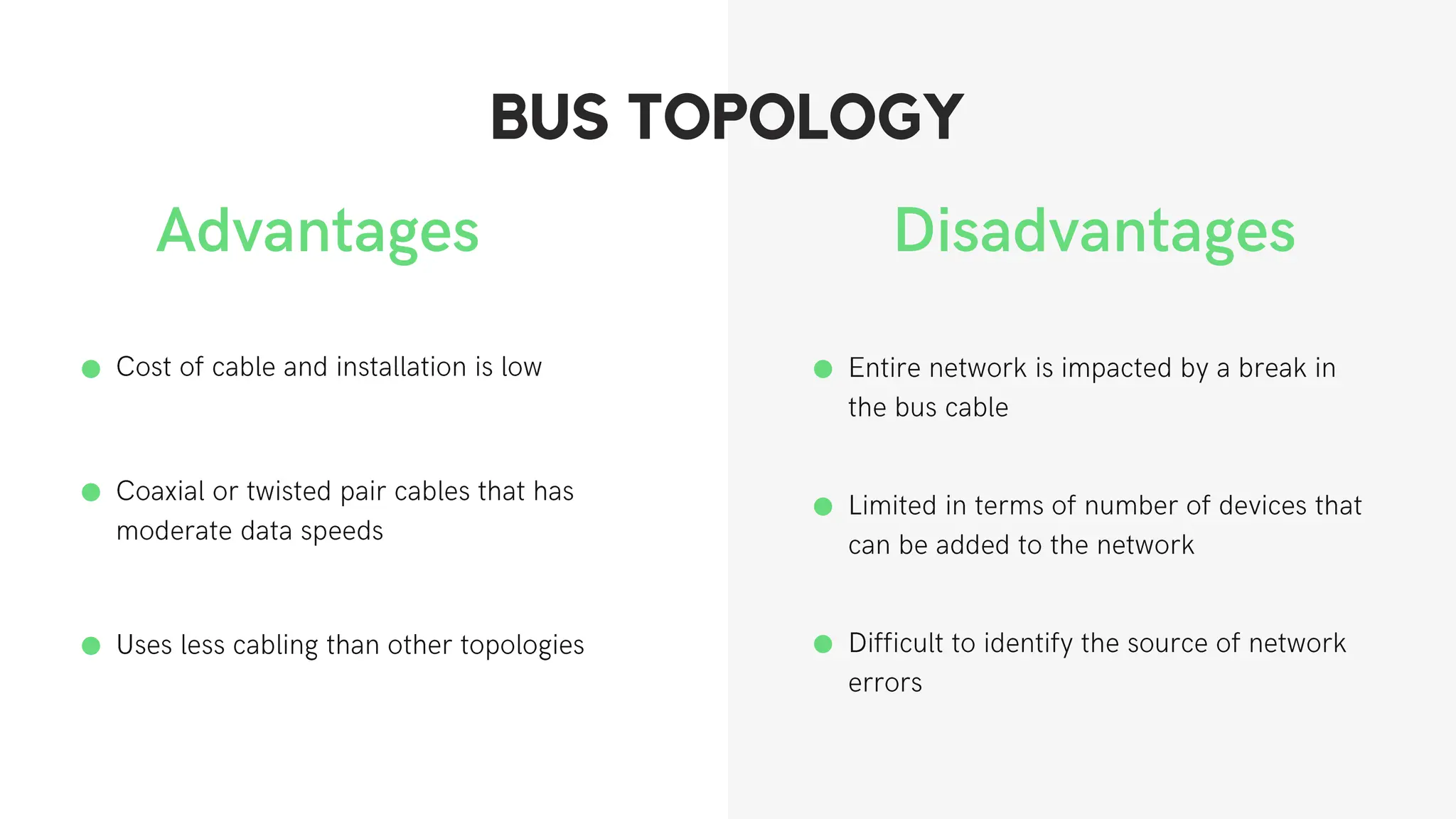
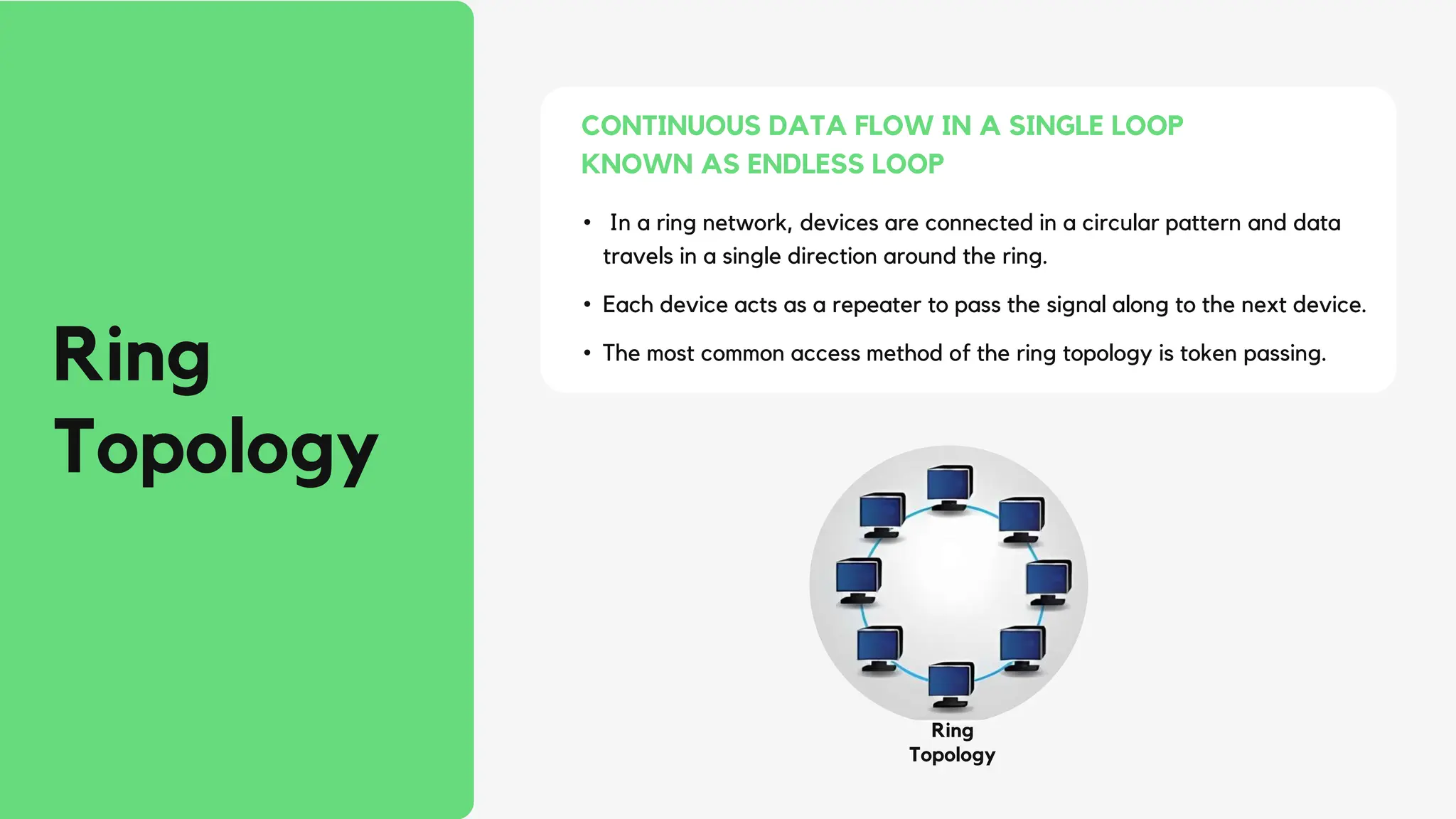
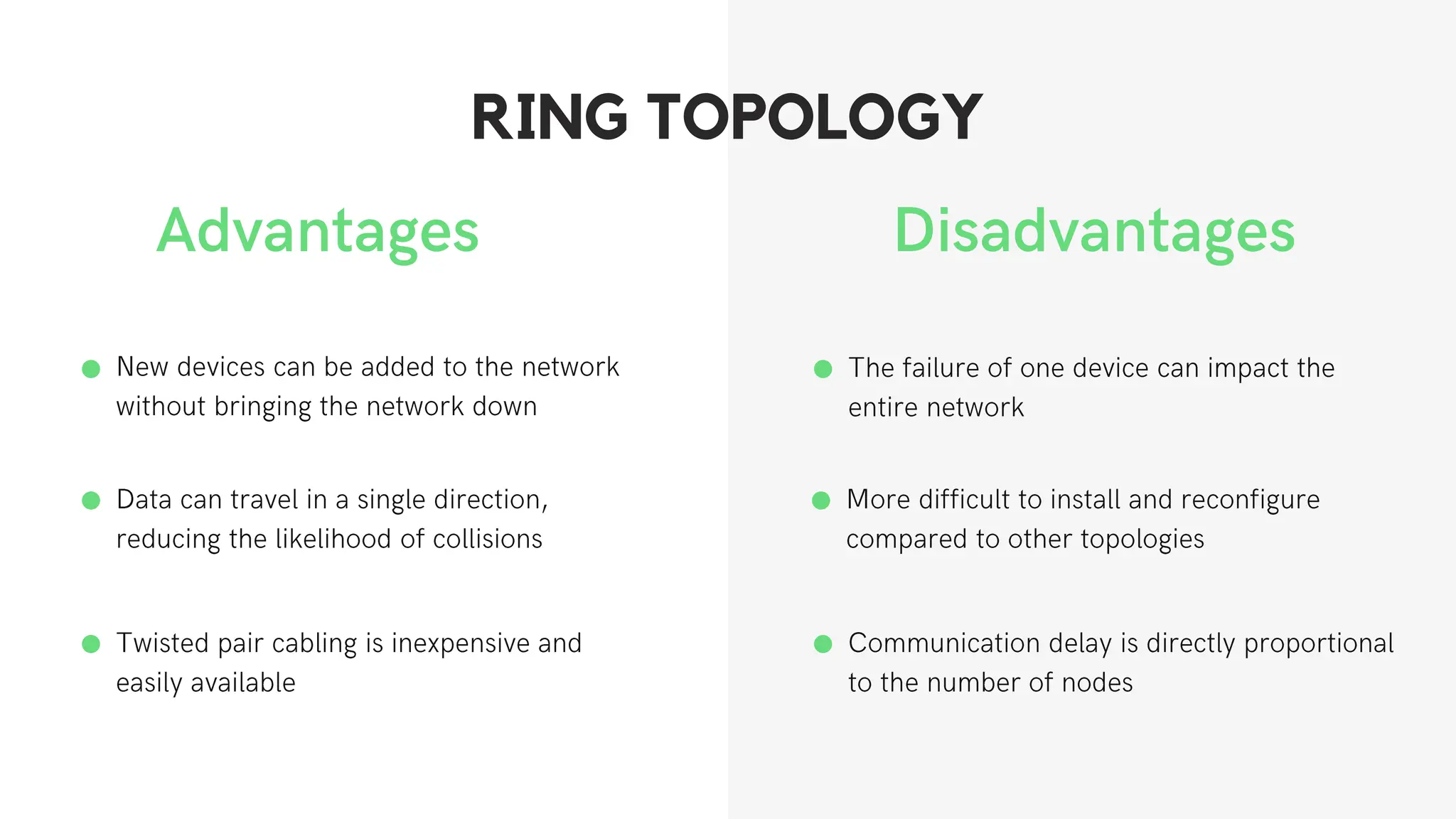
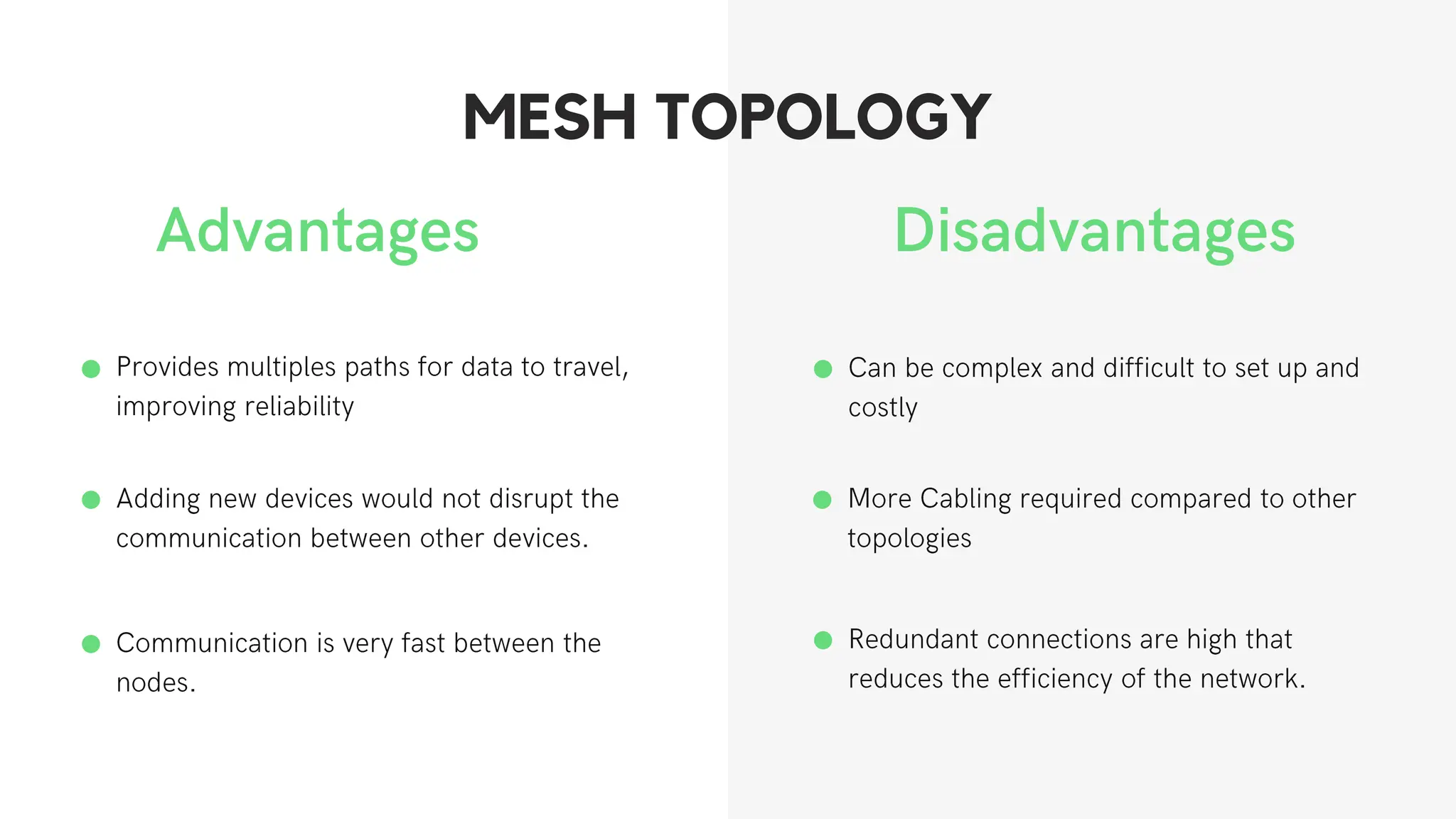
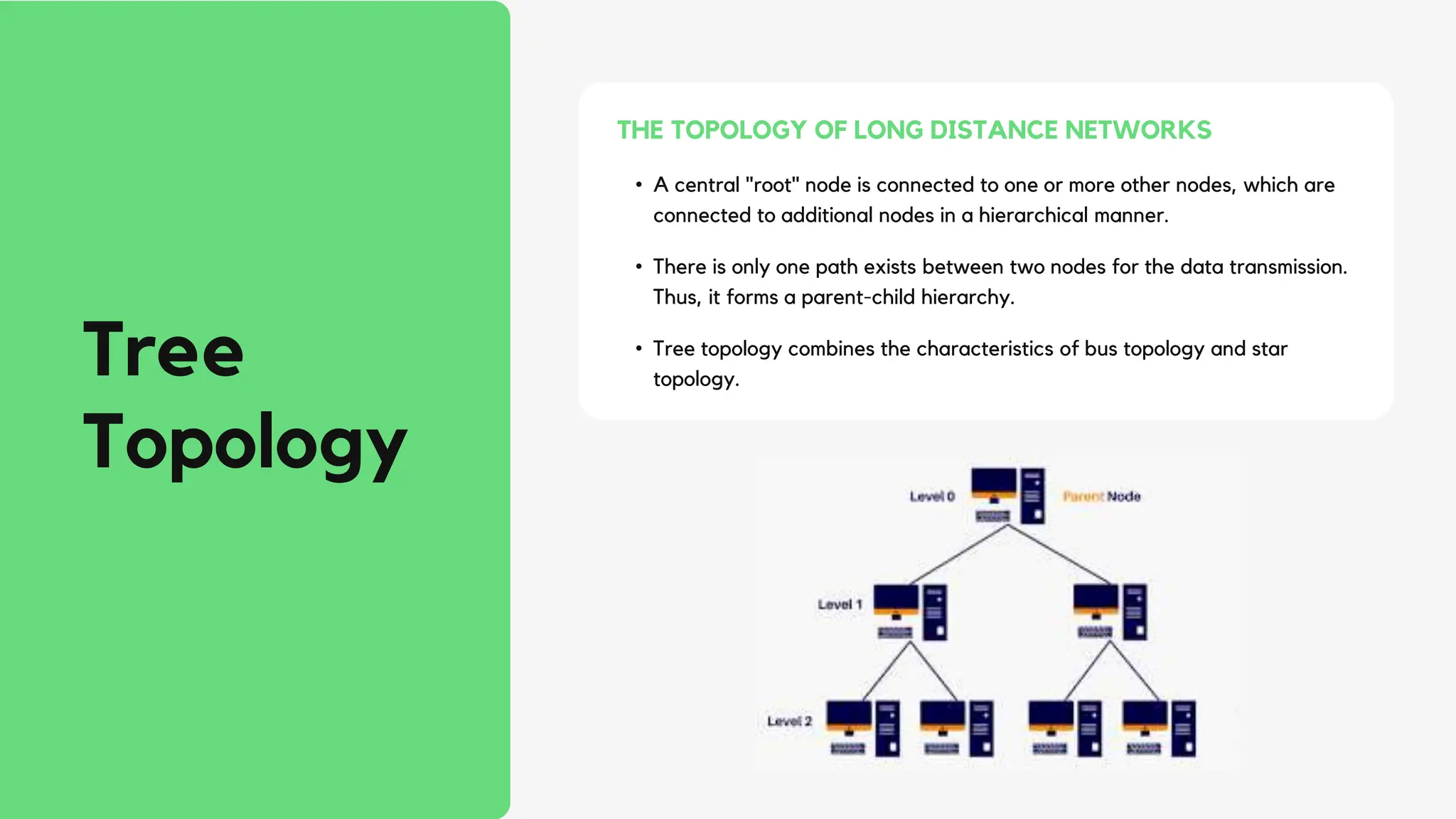
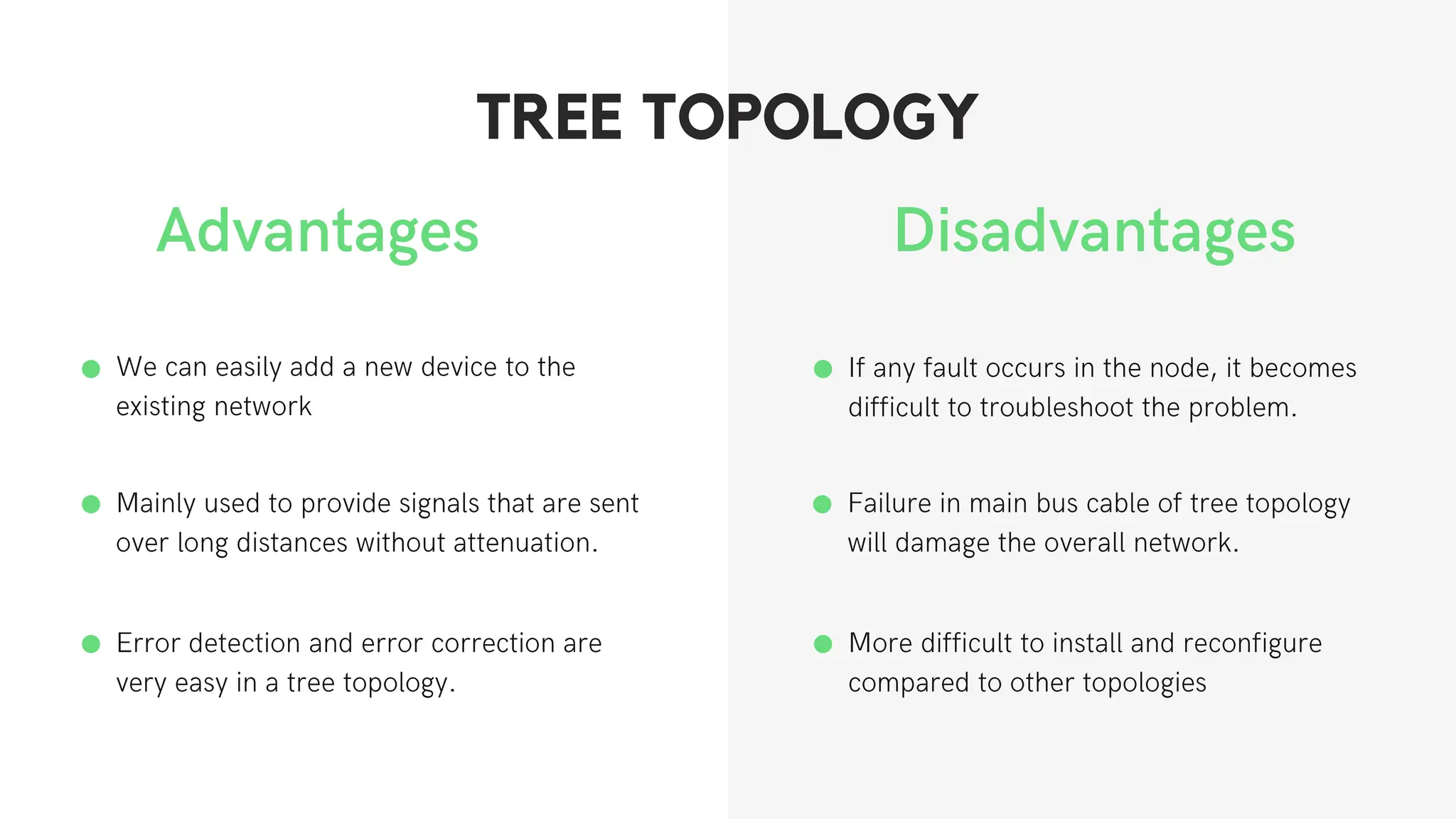
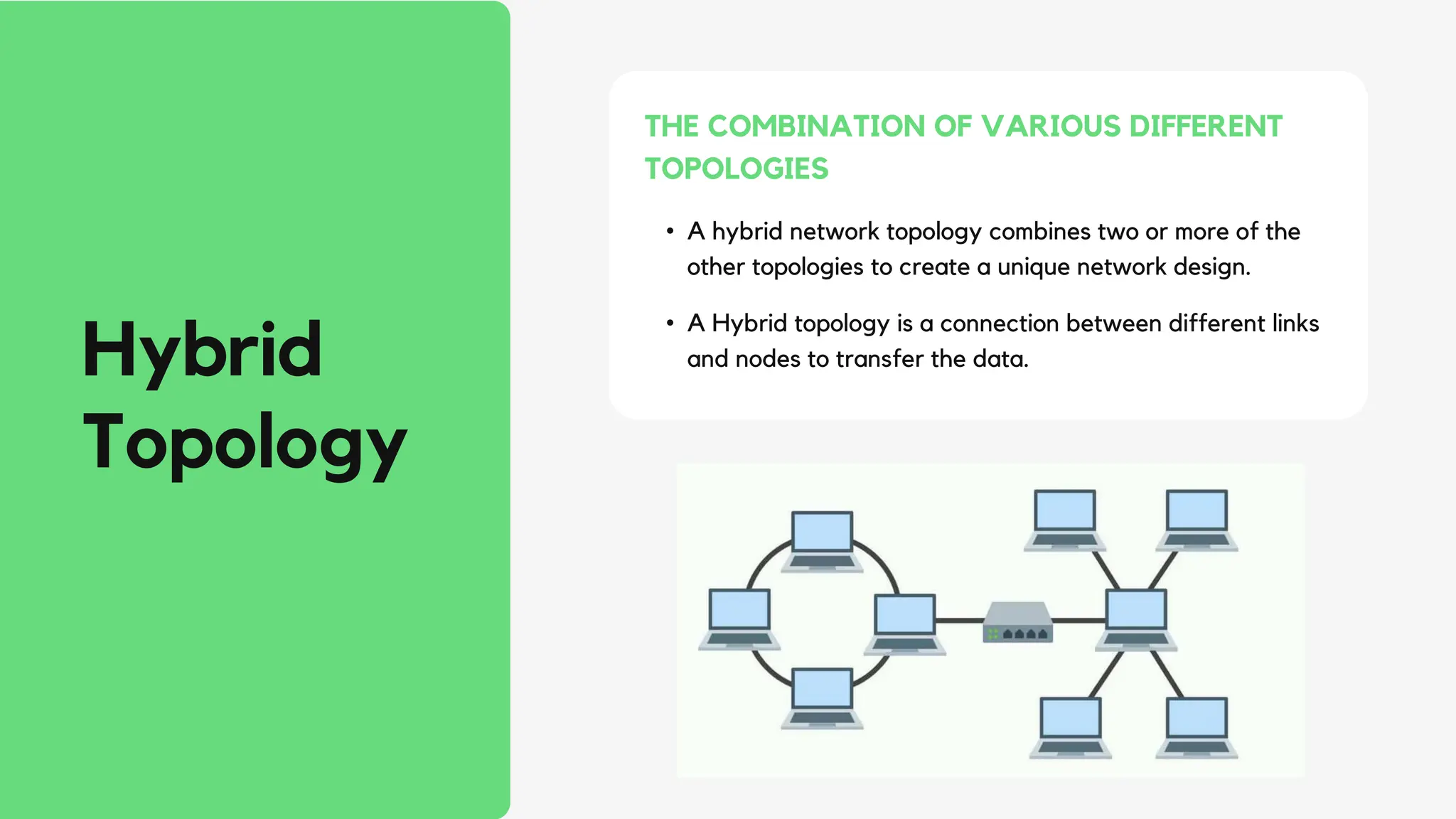
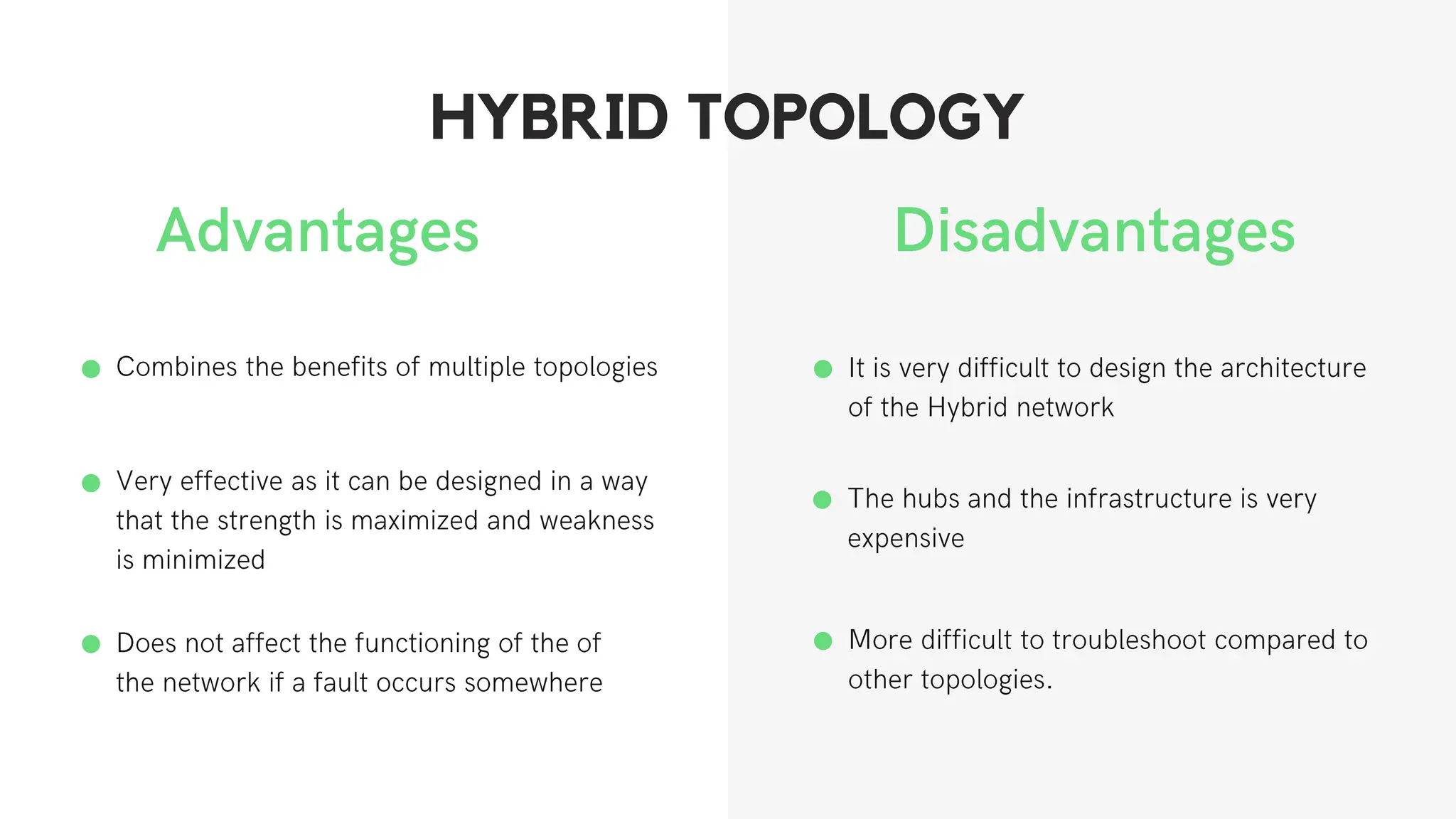
This document discusses different network topologies including star, bus, ring, mesh, tree, and hybrid topologies. It defines network topology as the physical and logical layout of nodes and connections in a network. Each topology is described, including how devices connect and how data flows. A star topology connects all devices to a central hub. A bus topology uses a common cable to connect all devices. A ring topology connects devices in a closed loop with single direction data flow. A mesh topology connects every device to every other device. A tree topology uses a root node and branches in a hierarchical structure. A hybrid topology combines two or more topologies. Network topology is important for network performance, troubleshooting, and resource allocation.