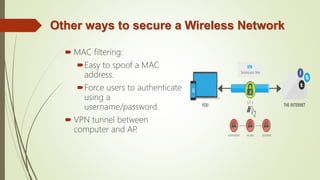
Network security involves implementing physical and software measures to protect a network from unauthorized access and enable authorized access. It aims to maintain confidentiality of data, integrity of data, availability of resources, and privacy of personal data. Key aspects of network security include encryption to scramble data, firewalls to control access to networks, and securing wireless networks through standards like WPA2. Common security processes also involve backing up data regularly, using access controls like passwords, and encrypting data during storage and transmission.