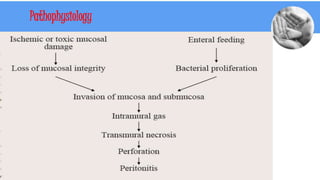
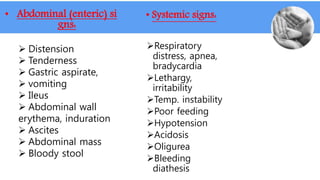
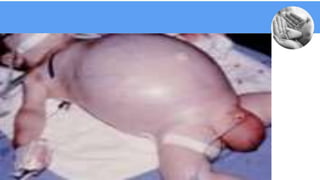
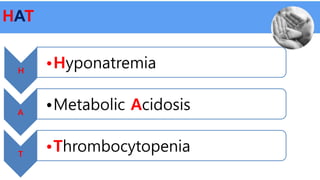
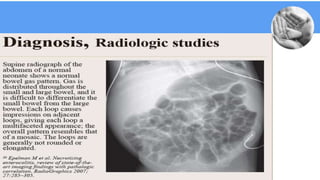
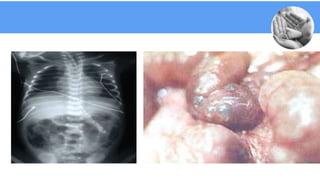
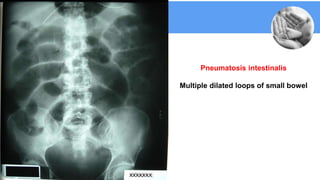
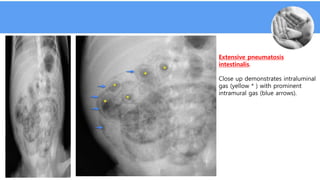
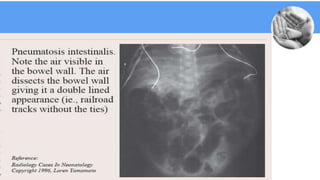
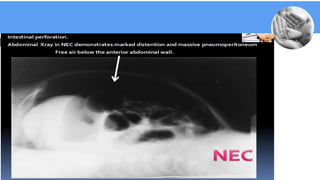
Necrotizing enterocolitis (NEC) is a common gastrointestinal emergency in neonates, especially preterm infants. It involves necrosis of the intestinal mucosa associated with inflammation and infection. Risk factors include prematurity, enteral feeding, and intestinal ischemia. Clinically, NEC presents with abdominal and systemic signs. Diagnosis is based on clinical features and radiographic findings like pneumatosis intestinalis. Treatment involves cessation of feeding, antibiotics, and possible surgery for perforation or failure to improve. Prognosis depends on gestational age and severity of disease. Prevention focuses on exclusive breastfeeding when possible.