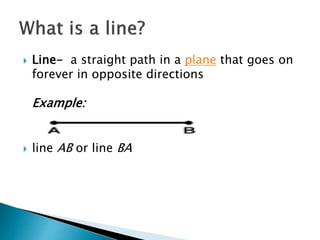
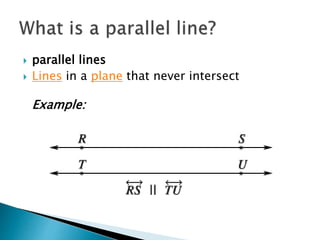
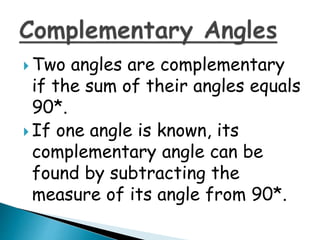
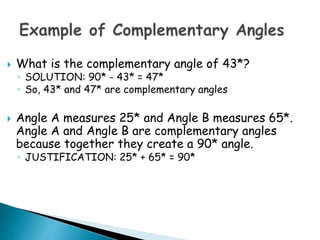
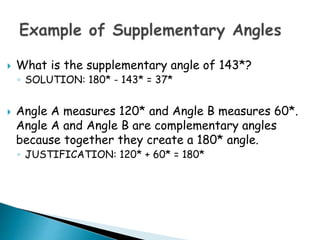
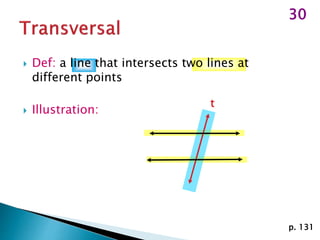
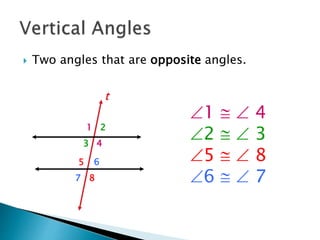
This document defines and provides examples of geometric terms including: lines, line segments, points, parallel lines, complementary angles, supplementary angles, transversal lines, and vertical angles. Complementary angles sum to 90 degrees, while supplementary angles sum to 180 degrees. Vertical angles are opposite and equal.