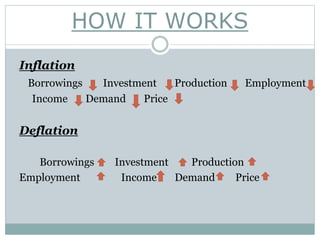
Monetary policy refers to the measures taken by a central bank to control money supply and credit conditions in an economy. The objectives of monetary policy include price stability, economic growth, and full employment. Quantitative monetary policy tools include open market operations, bank rate policy, cash reserve ratio, and statutory liquidity ratio. Qualitative tools include moral suasion, direct action, and discriminatory interest rates. Open market operations involve the central bank buying and selling government securities to influence money supply and control inflation or deflation. Evidence shows that India's monetary policy has been effective in achieving economic growth while reining in inflation and ensuring financial stability.