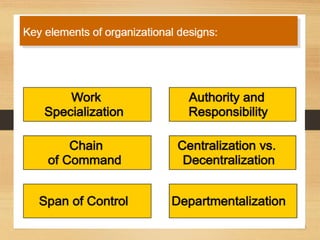
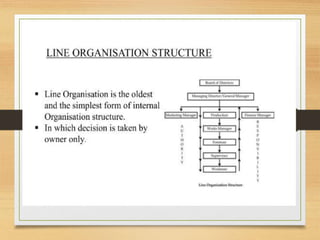
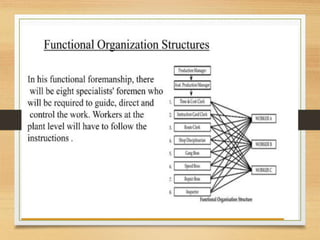
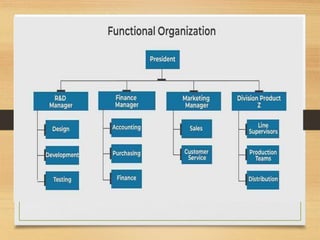
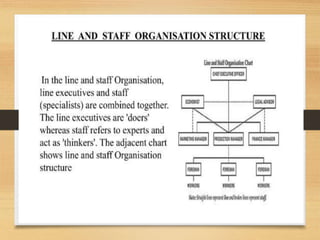
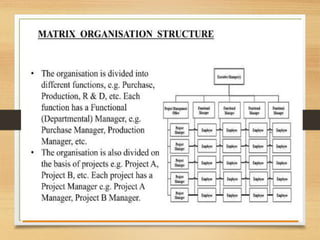
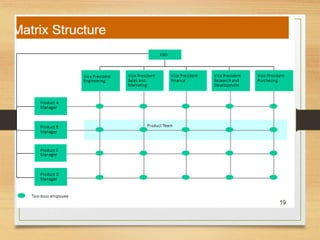
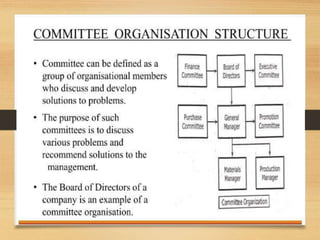
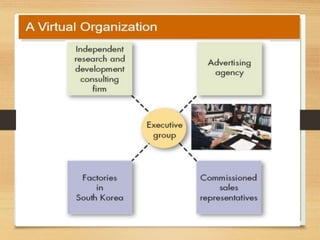
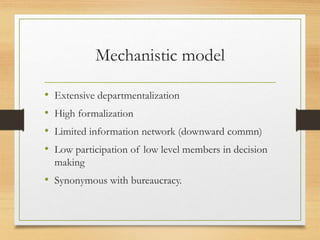
The document discusses factors that influence organizational structure and design, including the environment, strategy, size, life cycle, and technology. It describes two common models of organizational design: the mechanistic model, which is highly departmentalized and bureaucratic, and the organic model, which is flatter and more collaborative with cross-functional teams and participation in decision making across levels. Functional and divisional structures are also mentioned as ways to group employees.