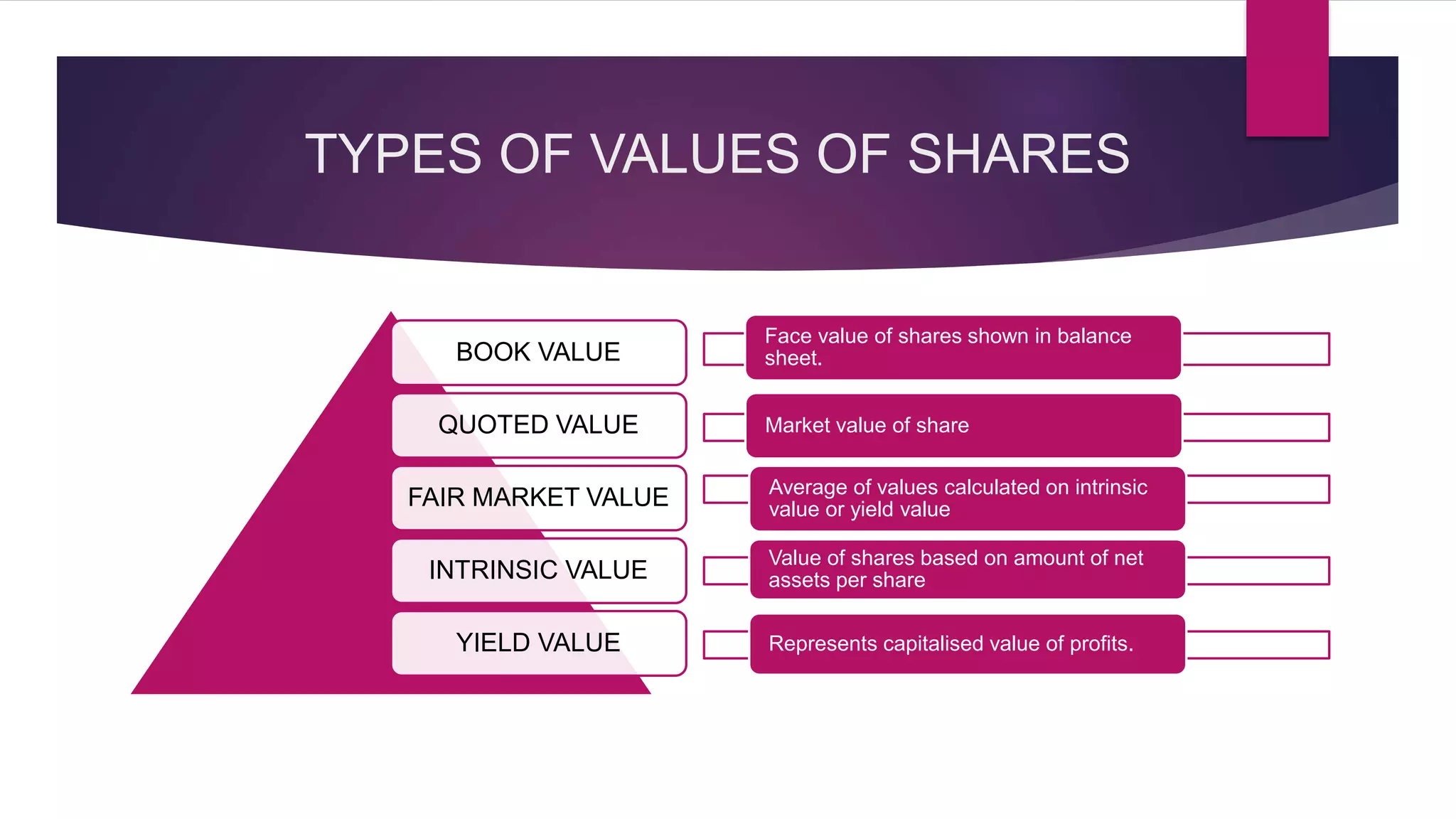
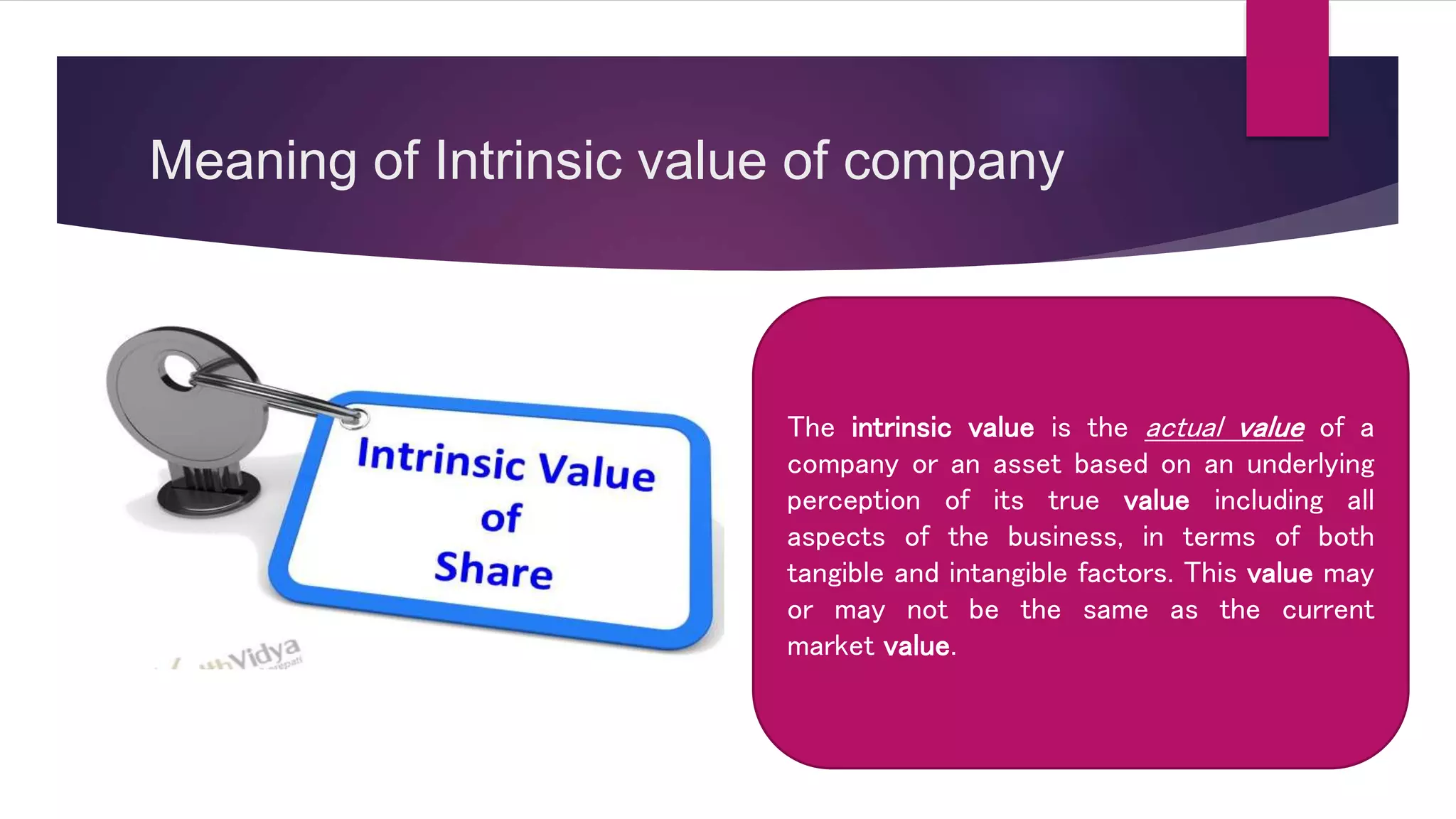
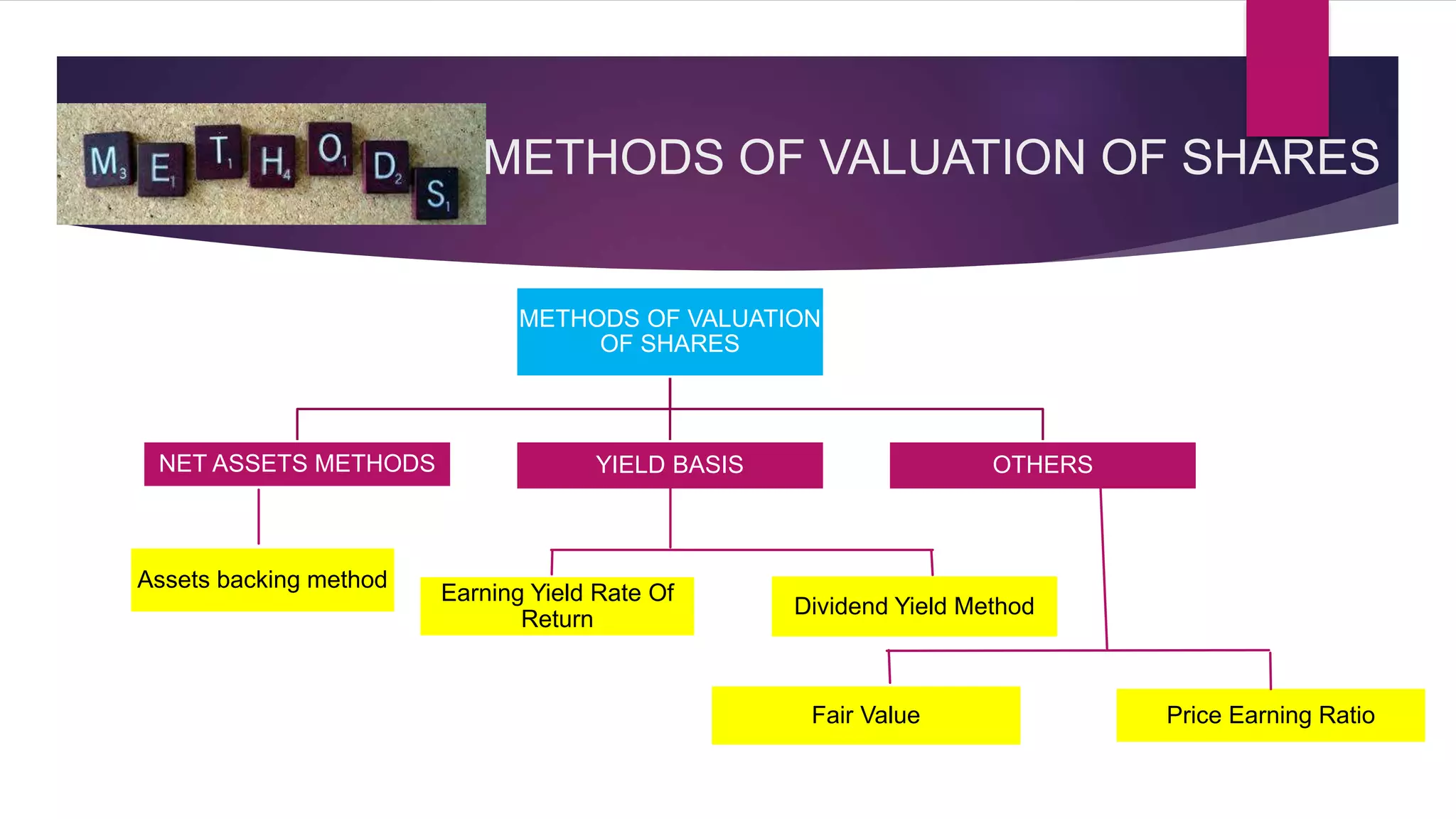
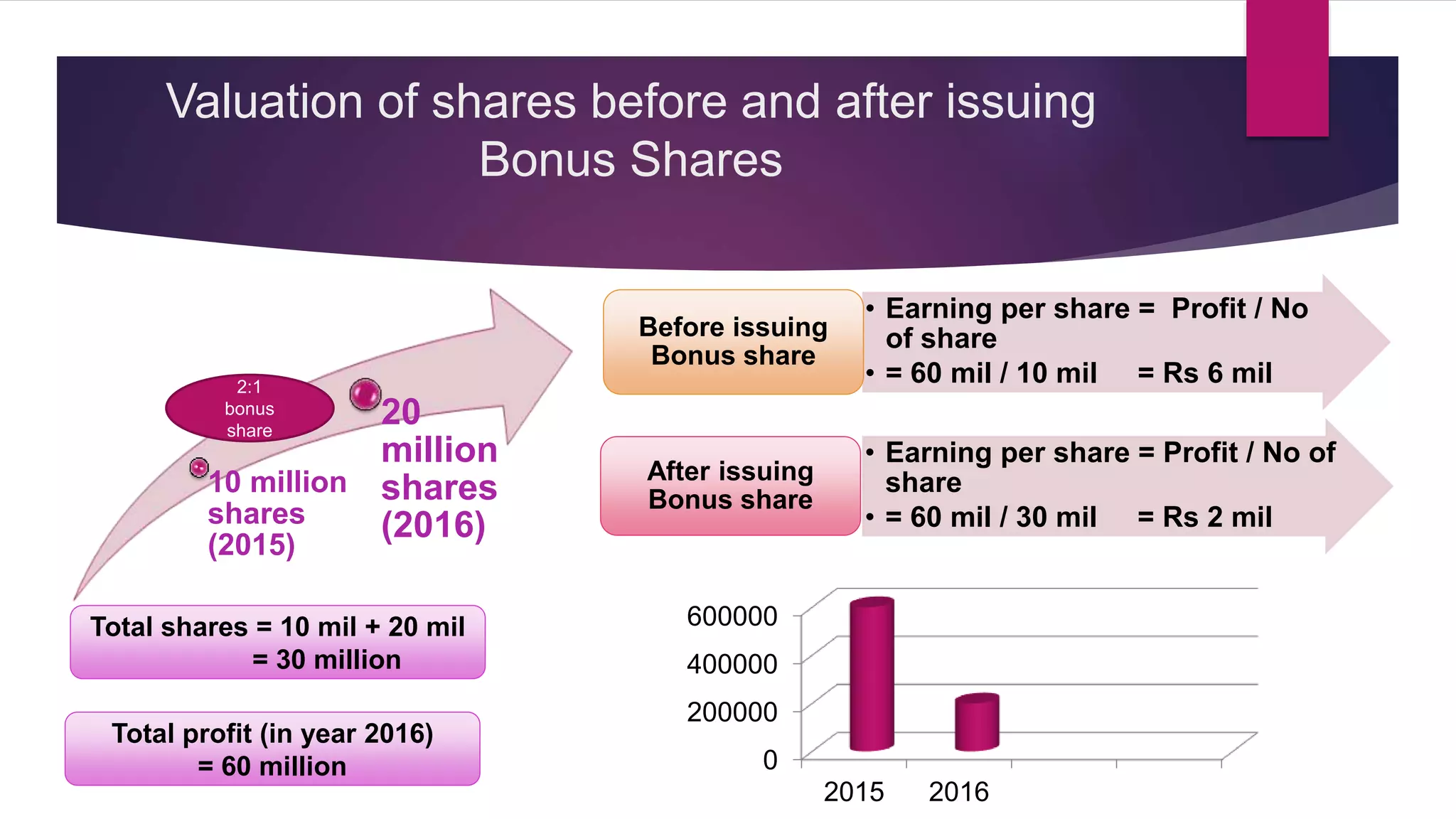
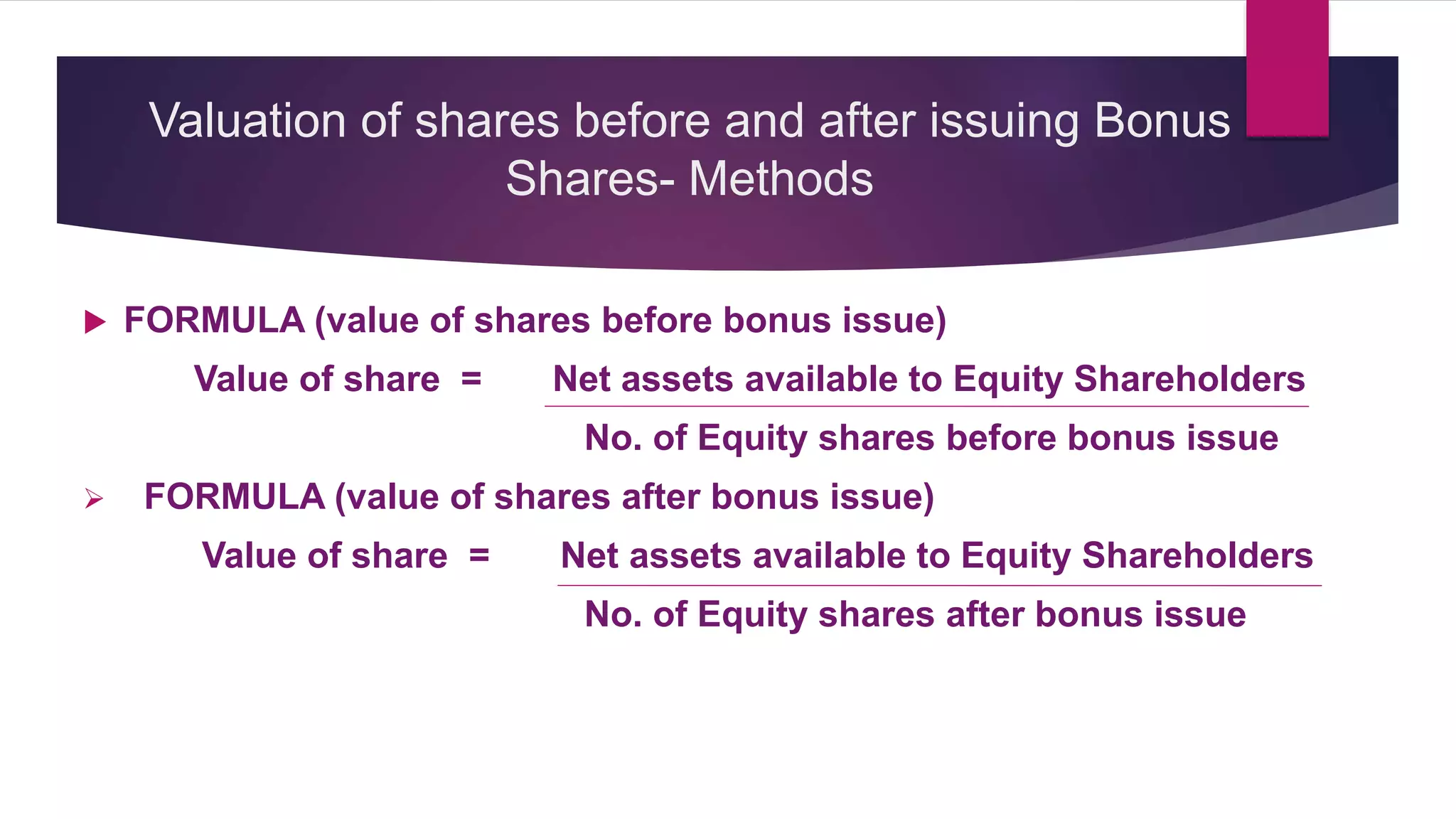
This document discusses various methods for valuing company shares, including book value, quoted value, fair market value, intrinsic value, and yield value. It describes the net assets method and yield method in more detail.
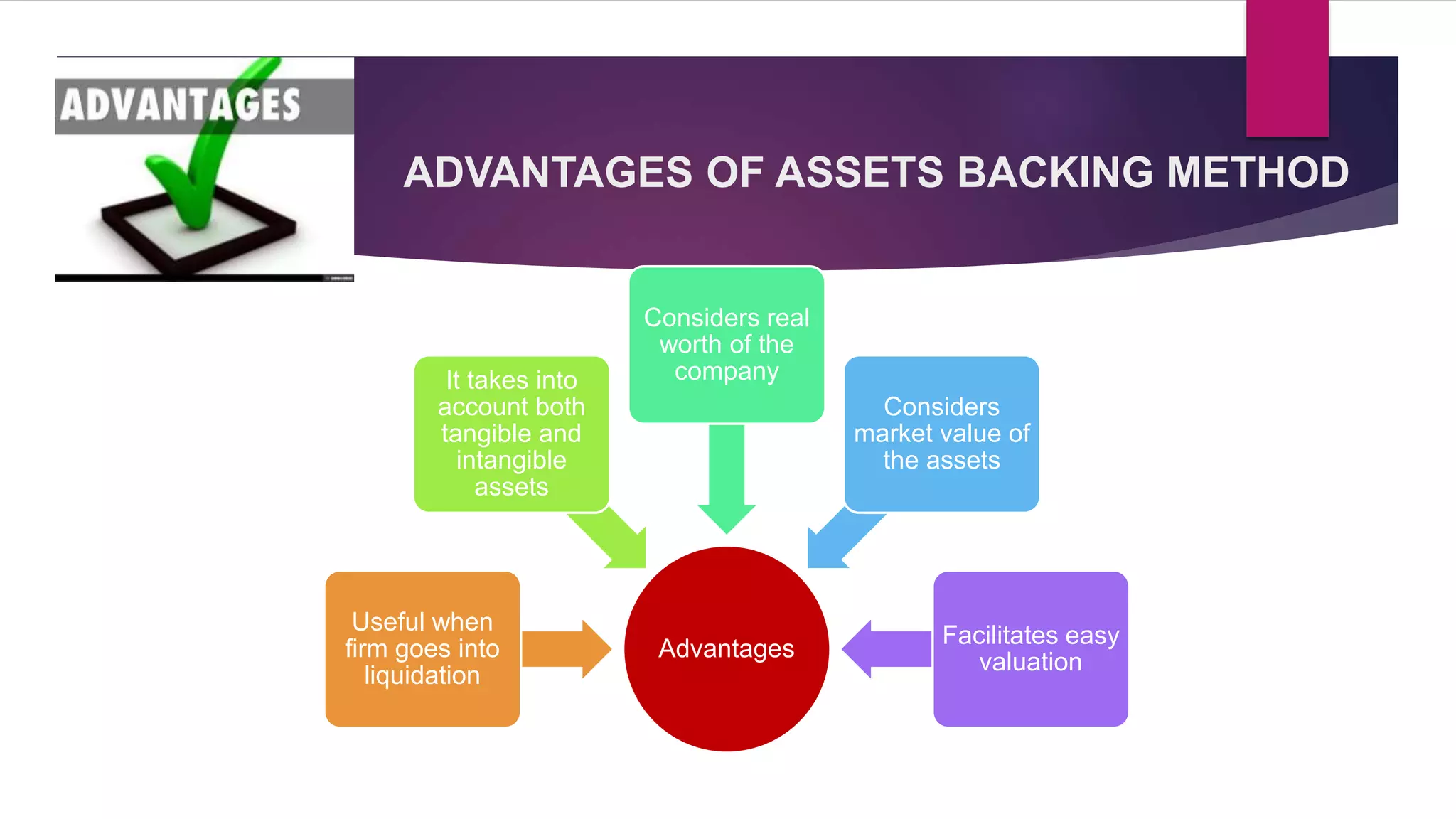
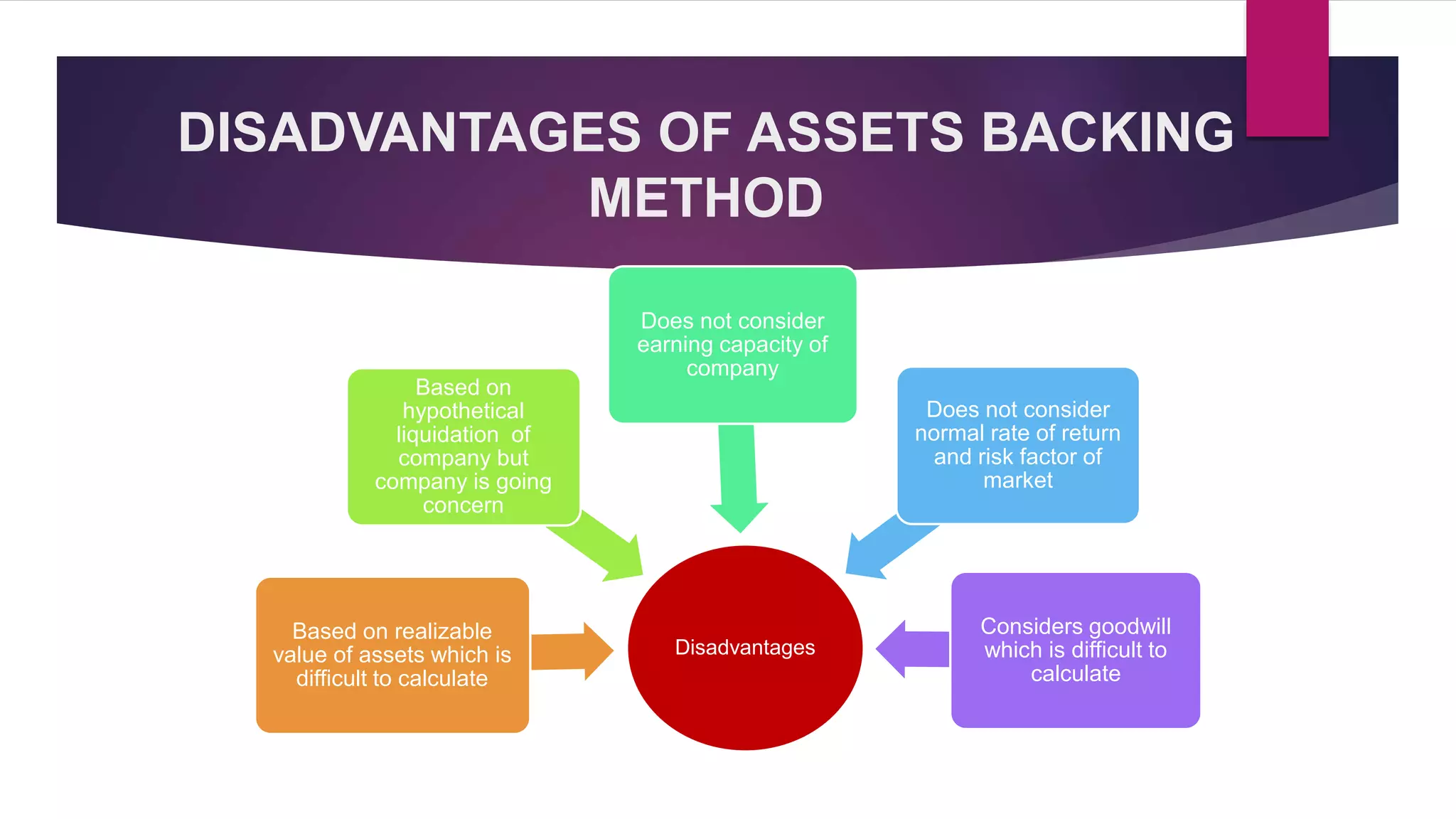
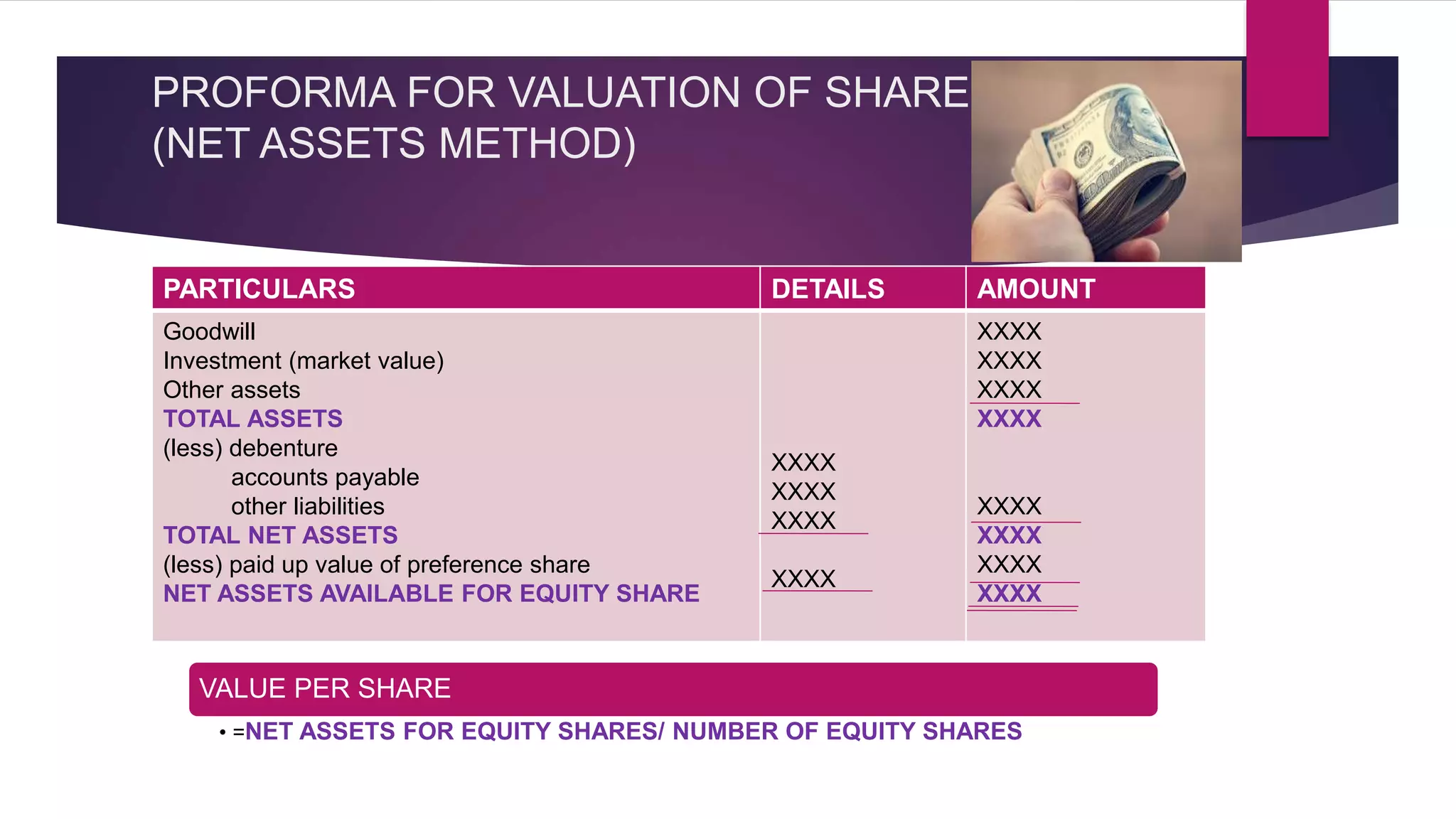
The net assets method values shares based on a company's net assets per share. This considers tangible and intangible assets. The yield method values shares based on earnings yield or dividend yield by capitalizing profits.
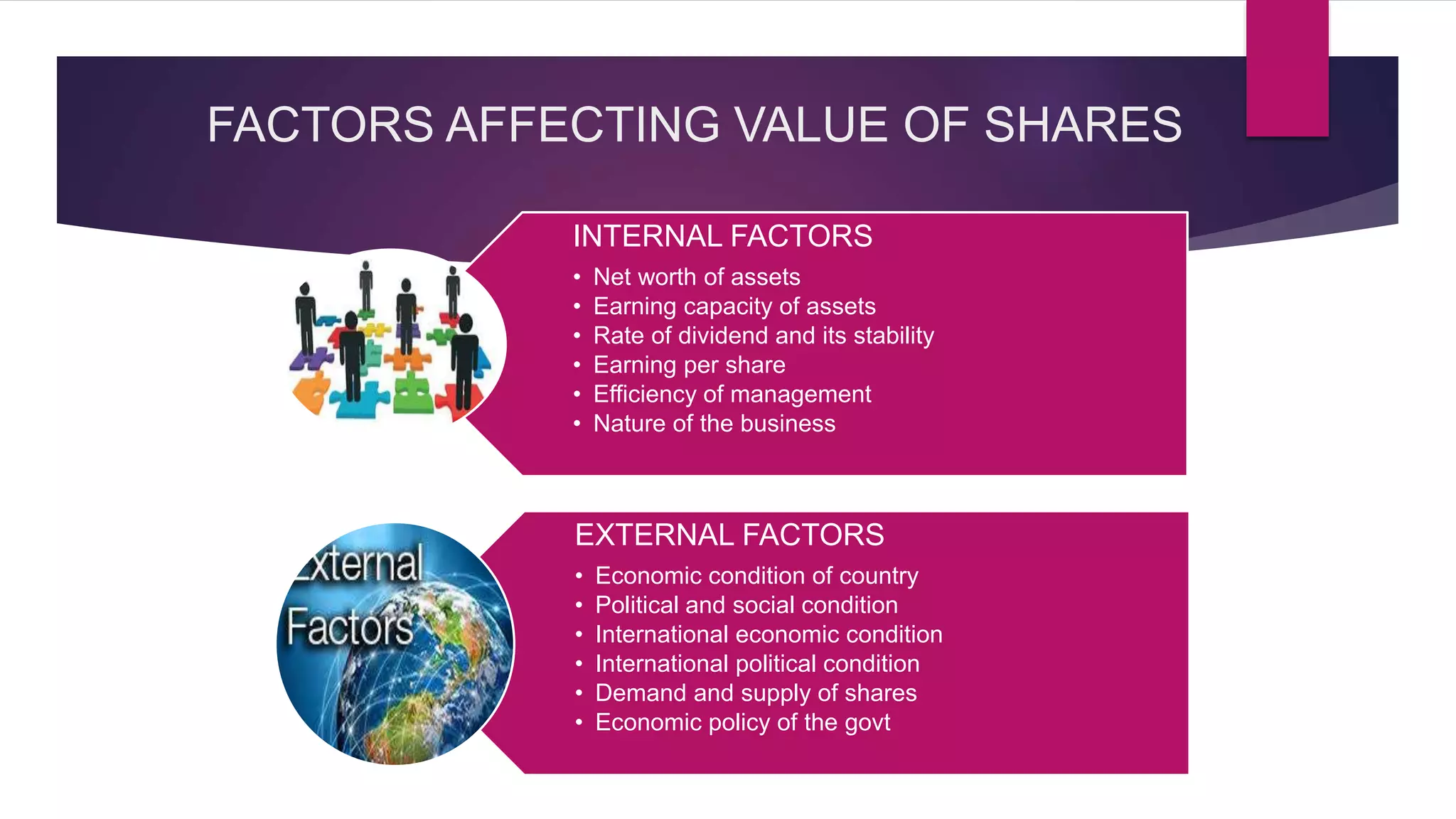
Factors like a company's net worth, earnings, dividends, management, and economic conditions can impact share values. Methods like net assets, earnings yield, and dividend yield are outlined to calculate share values. The document also discusses ex-dividend and cum-dividend share values