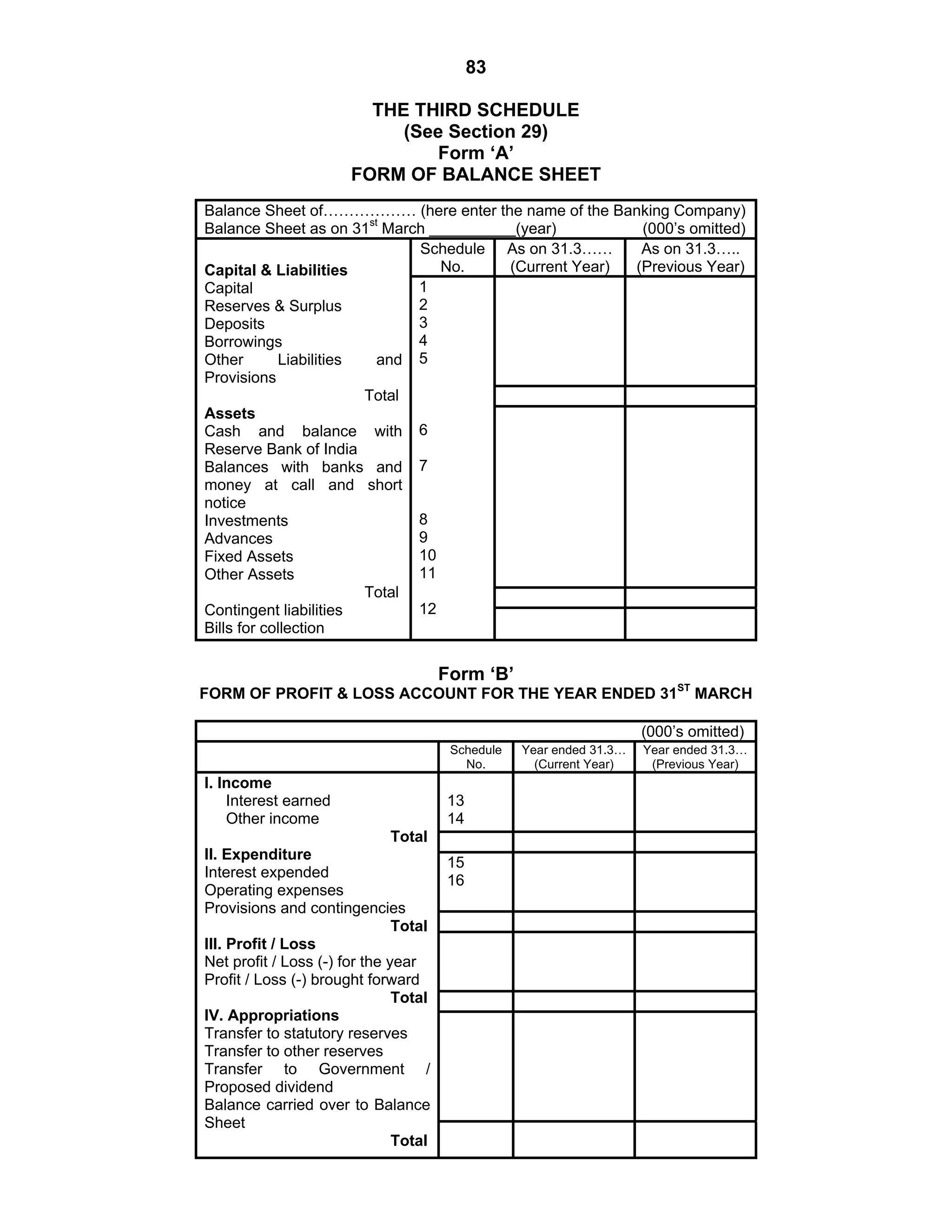
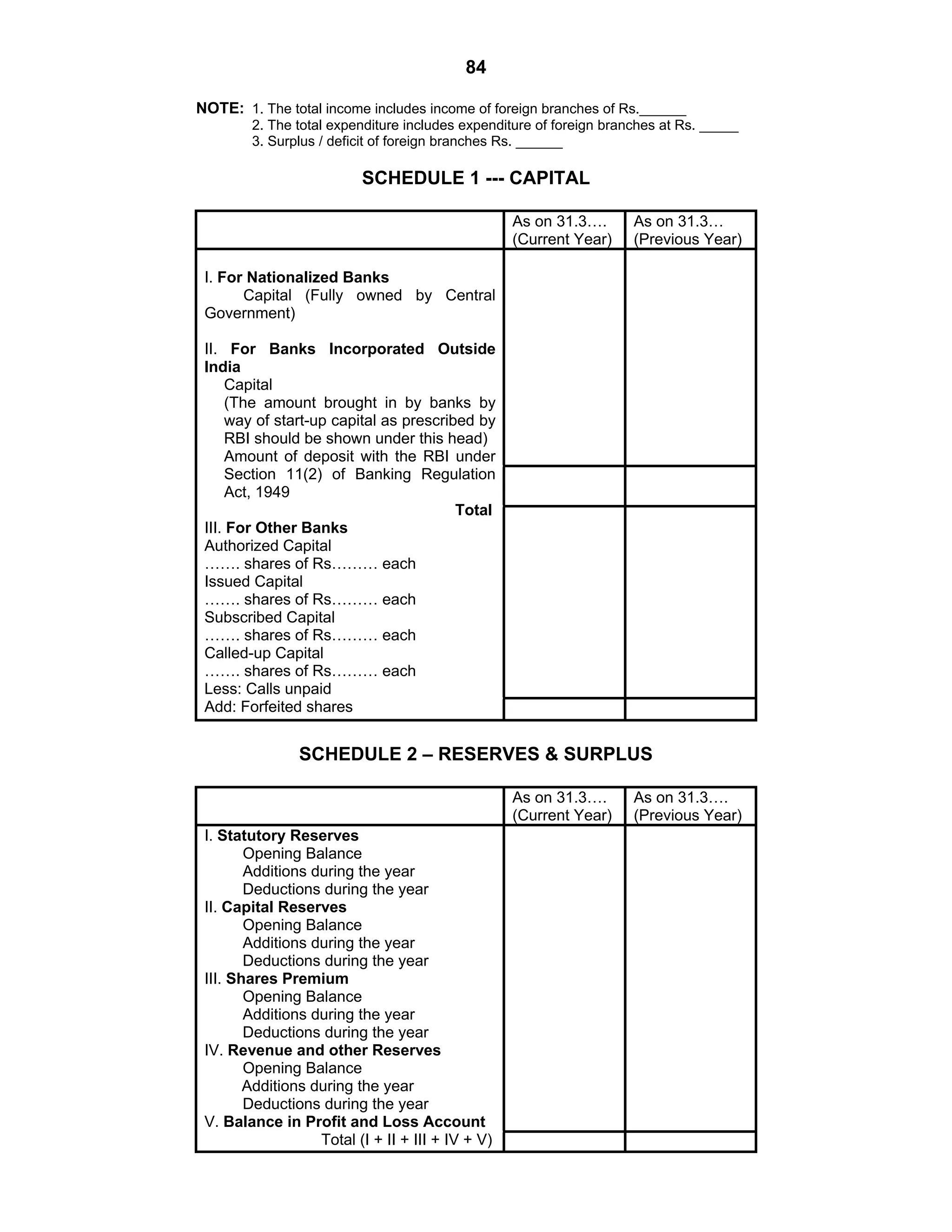
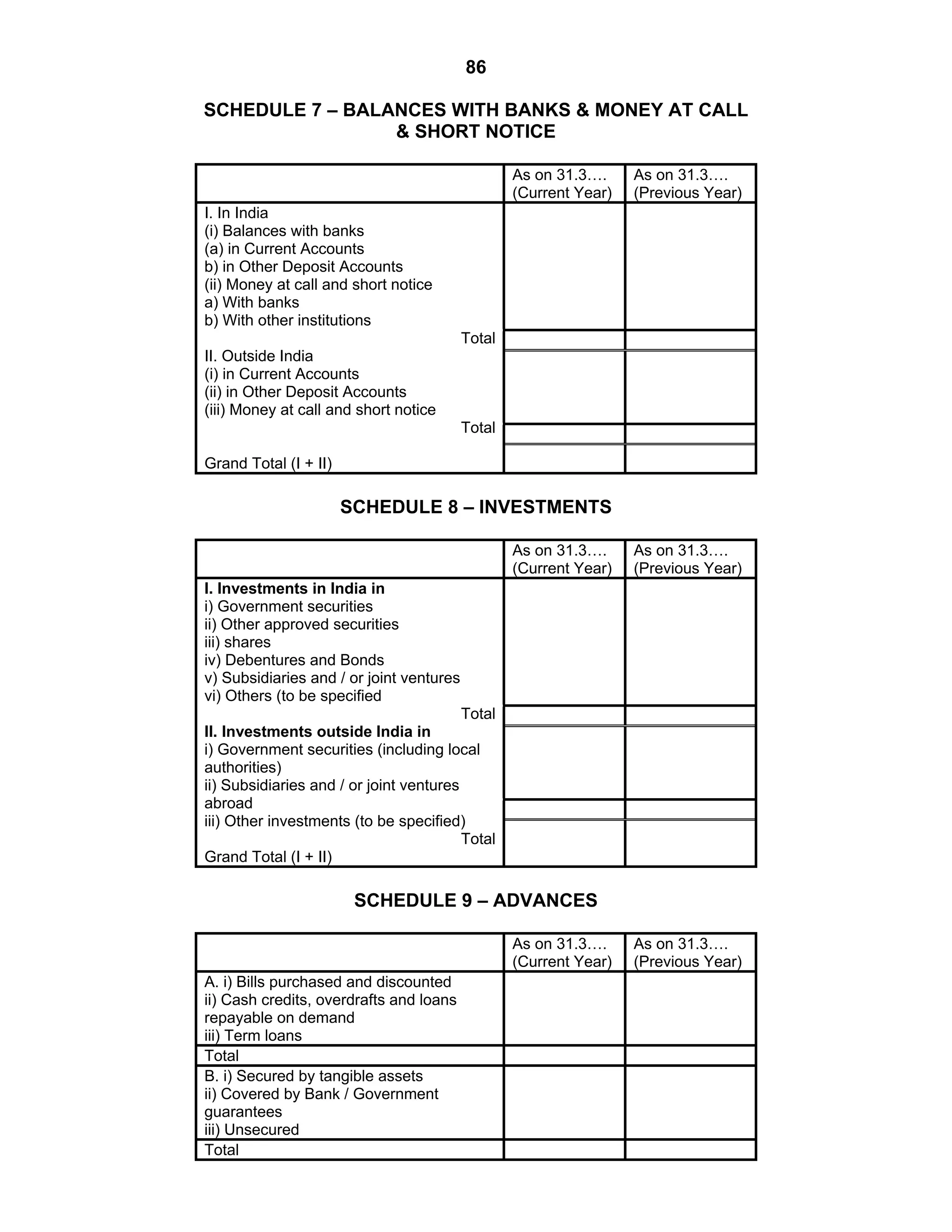
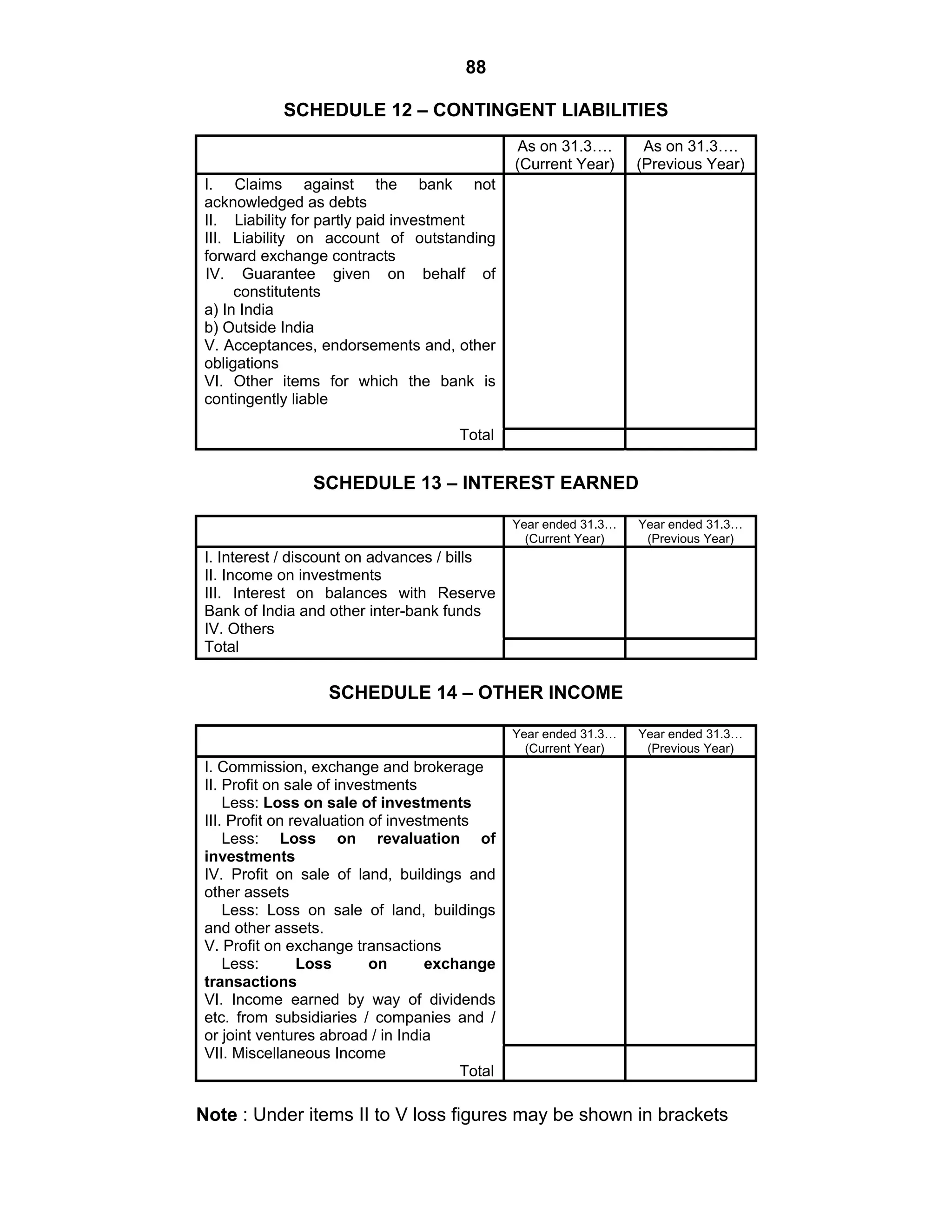
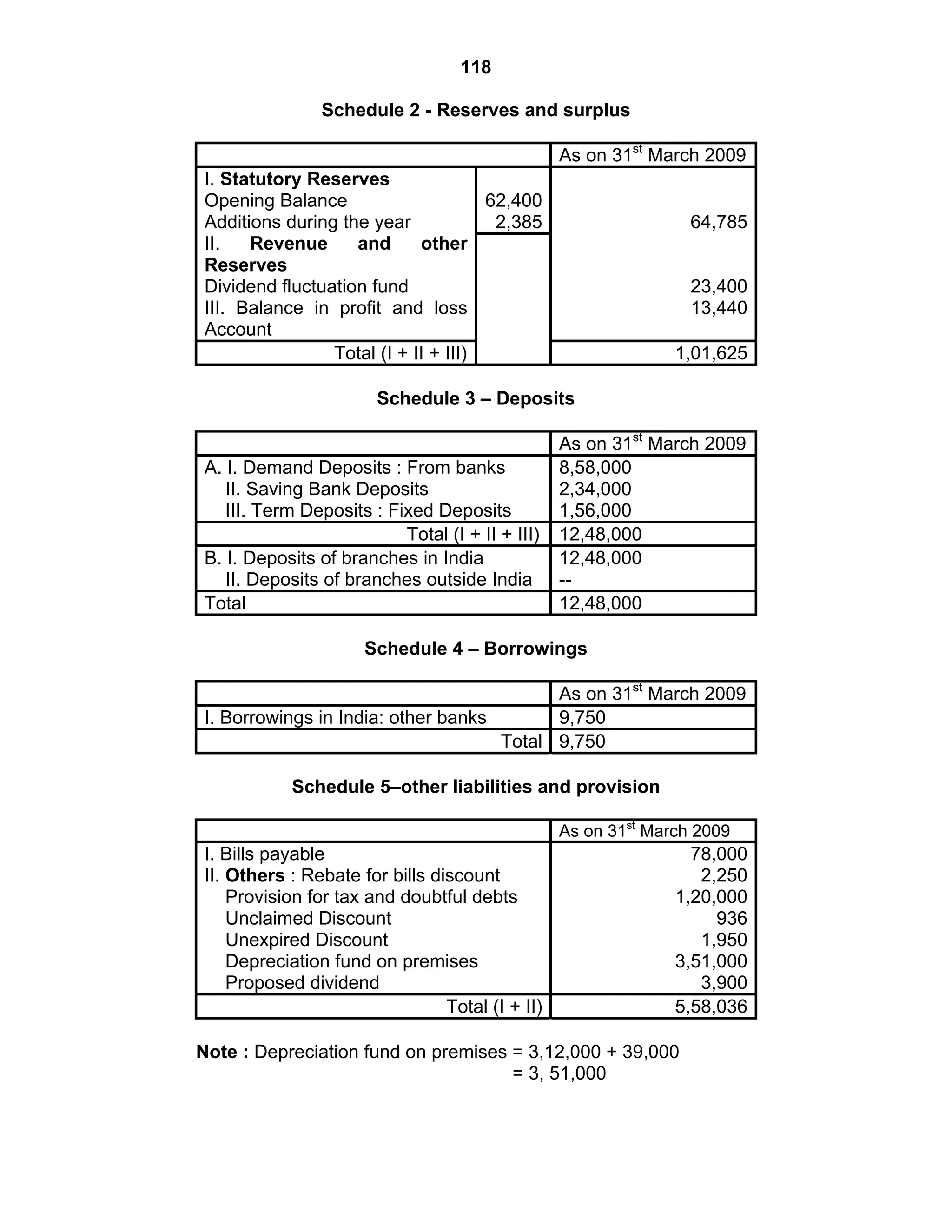
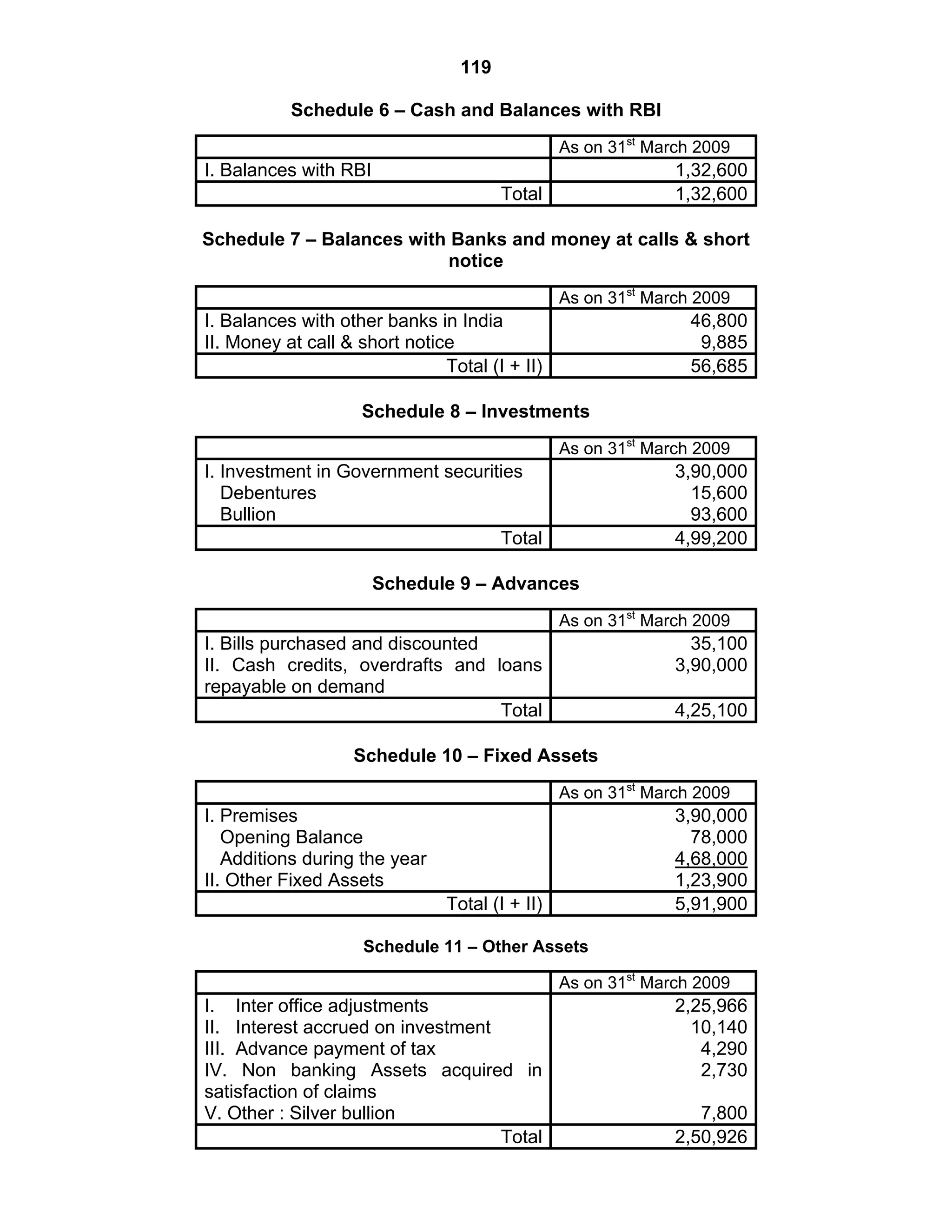
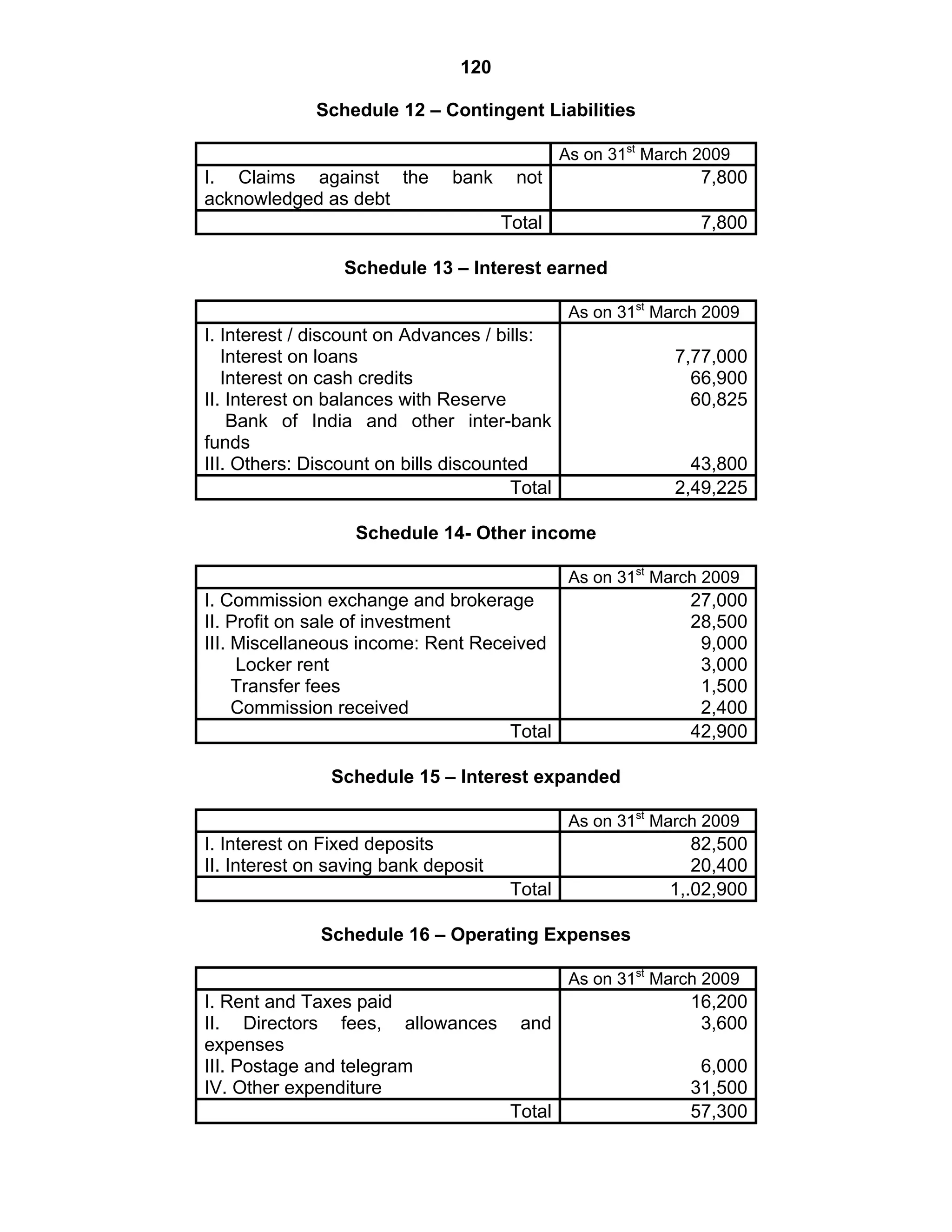
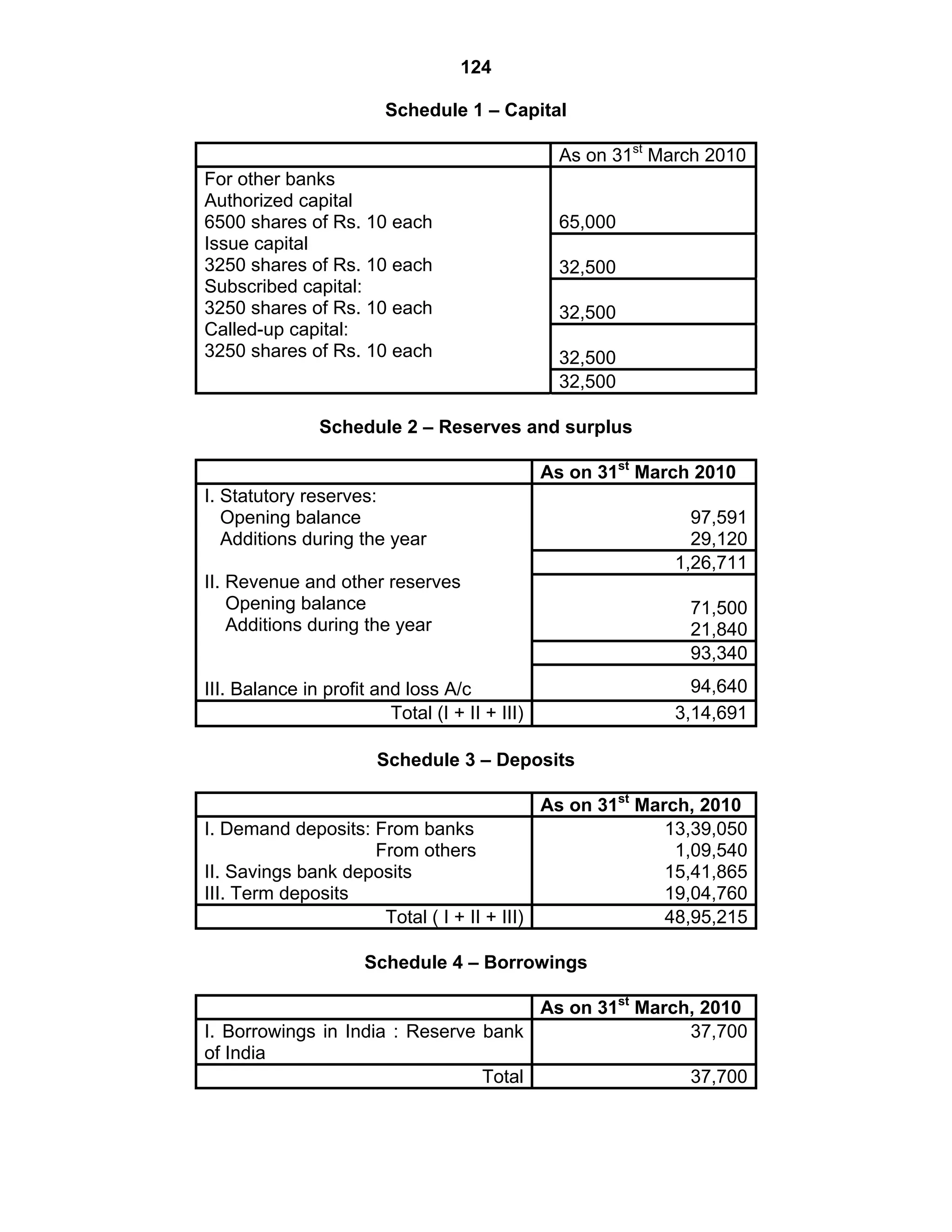
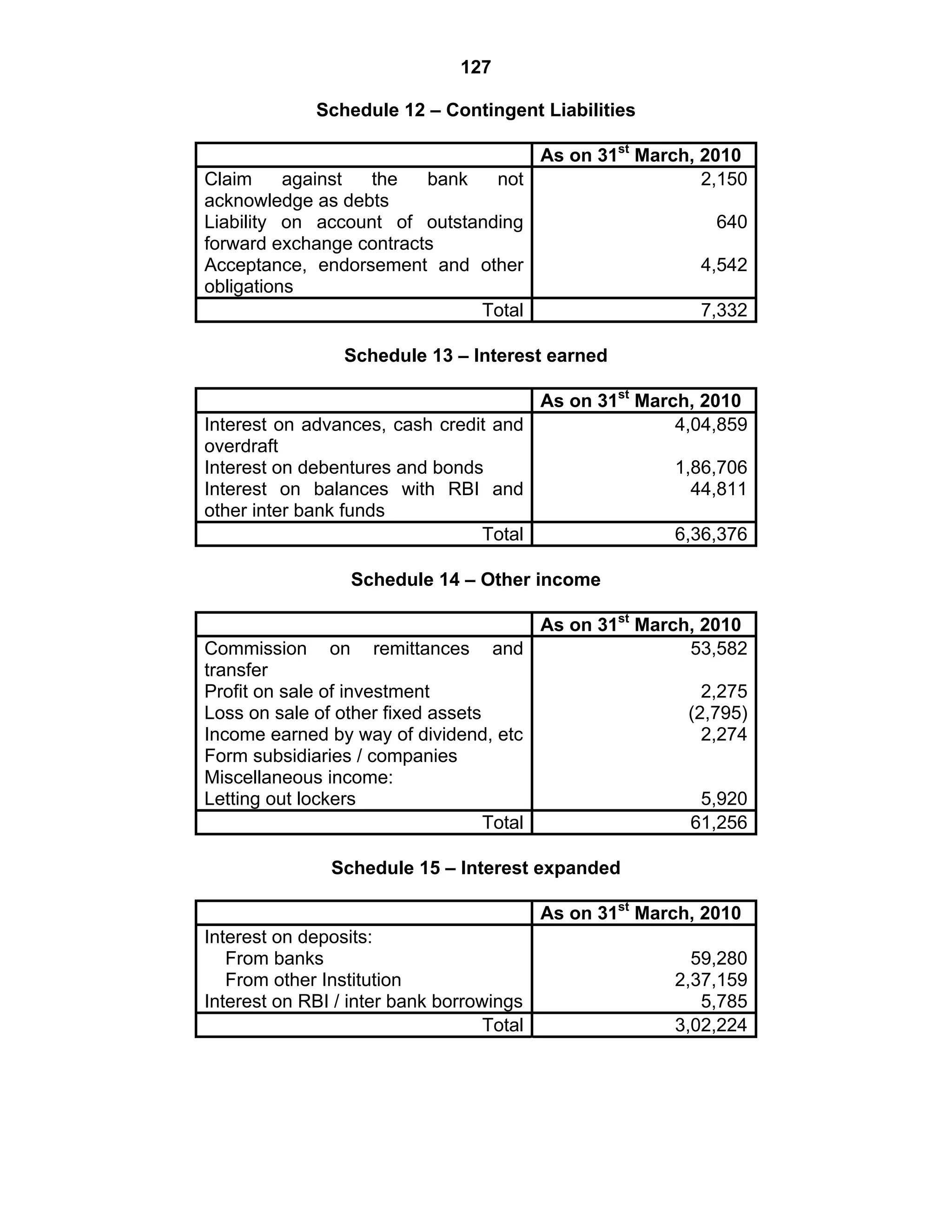
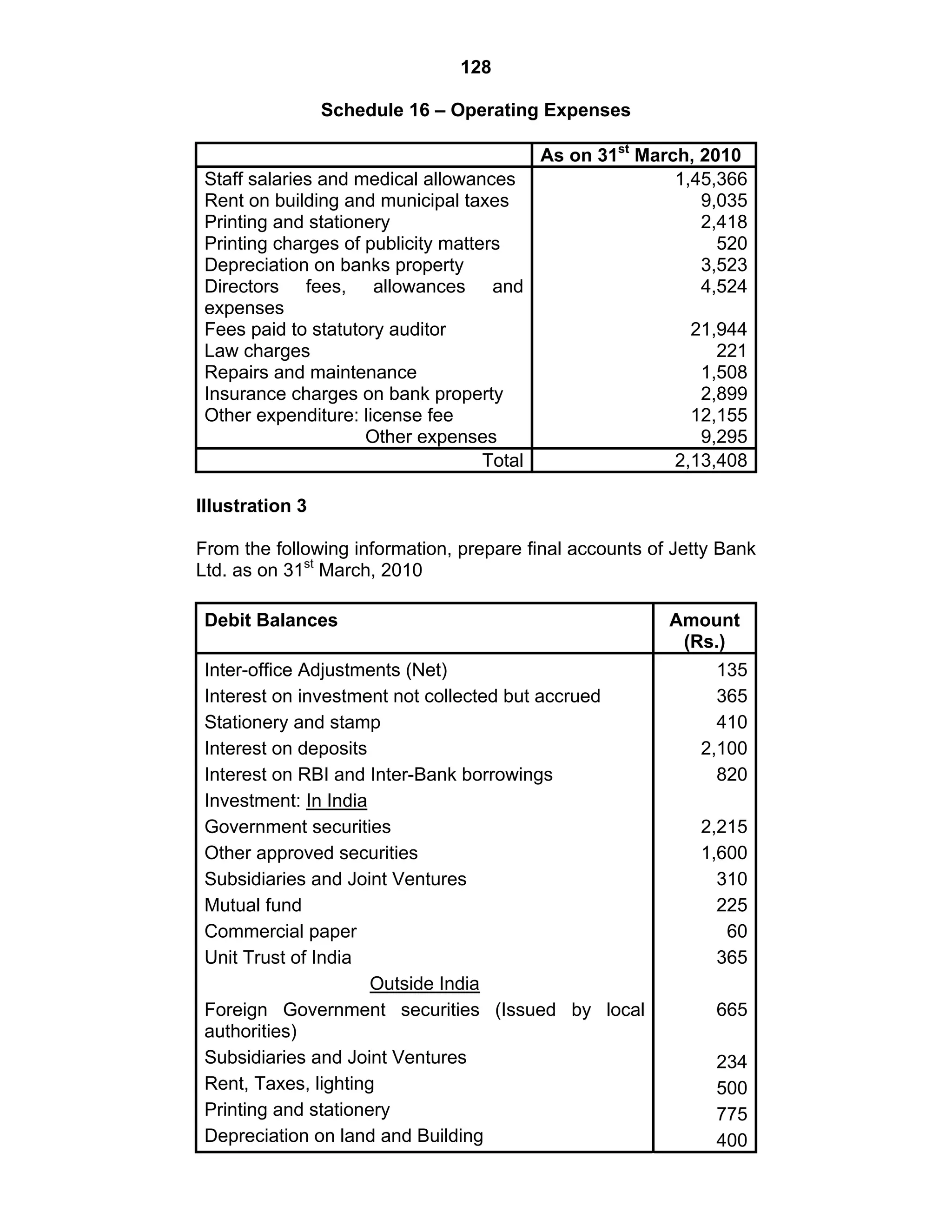
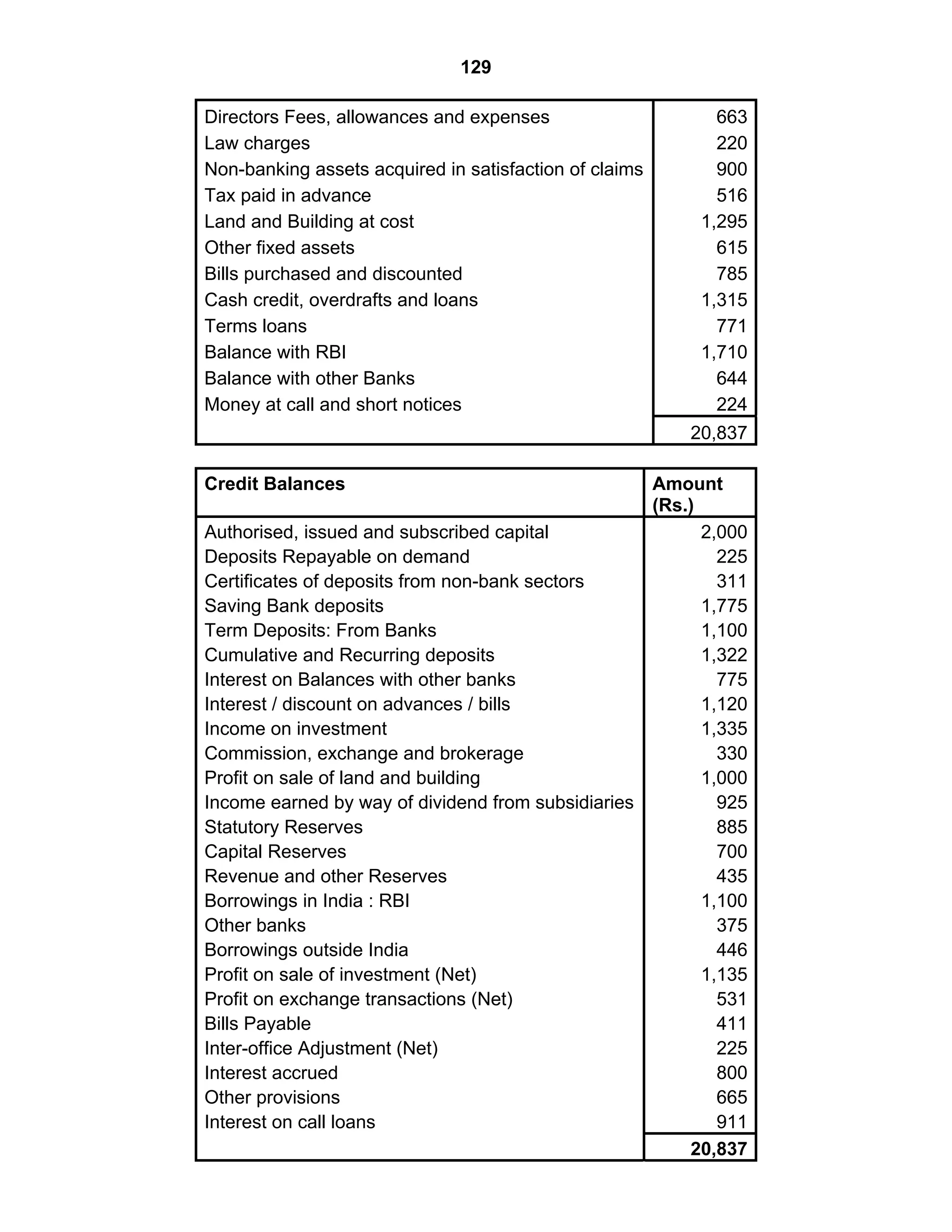
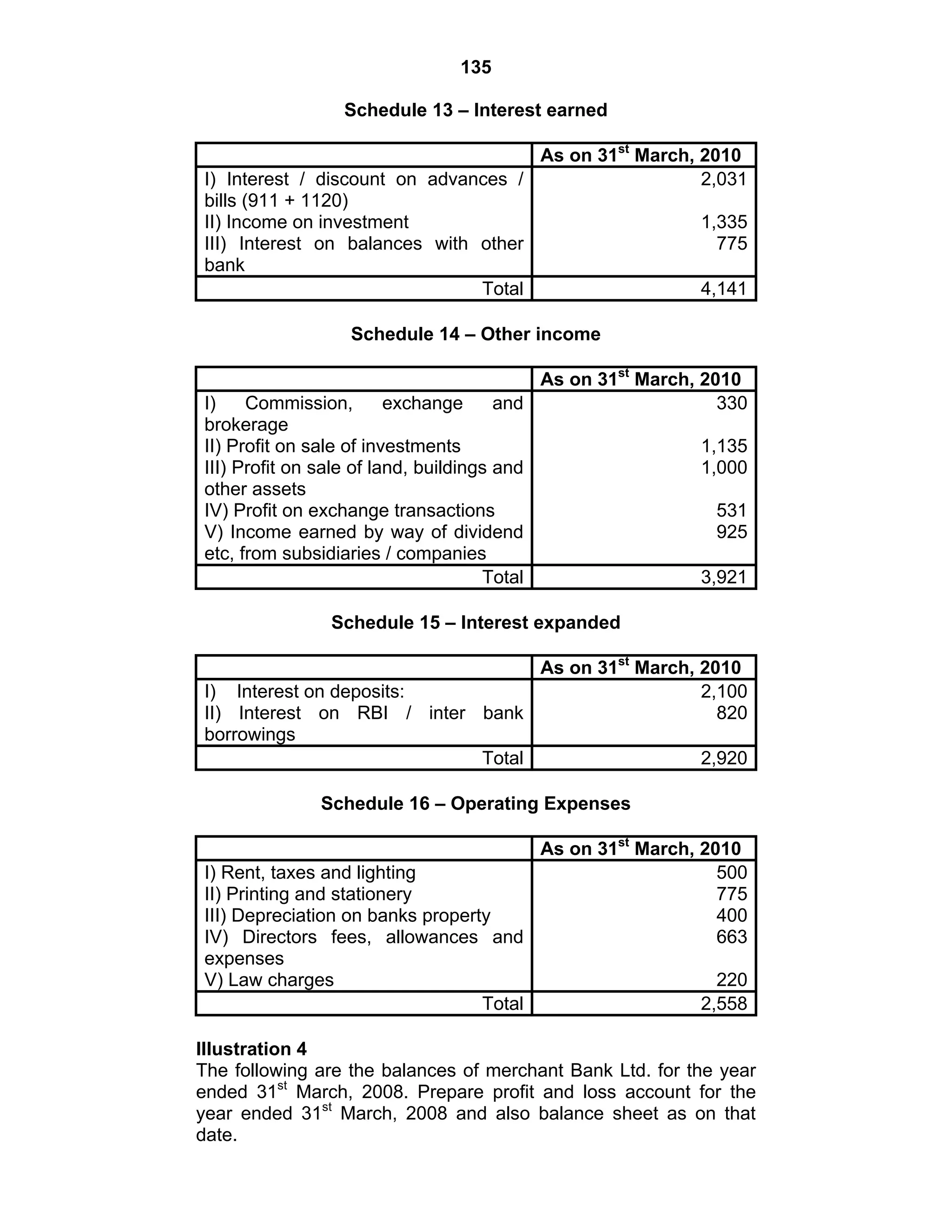
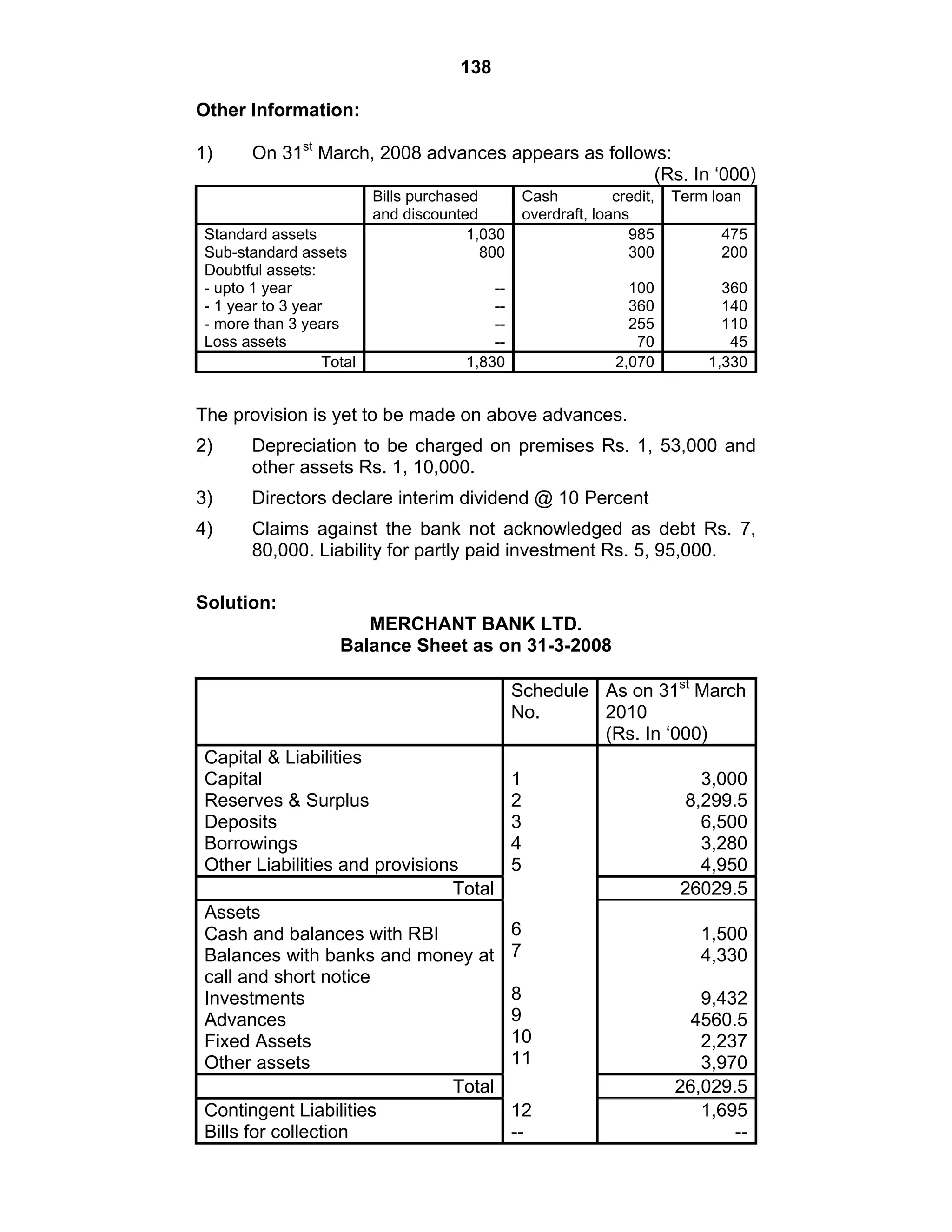
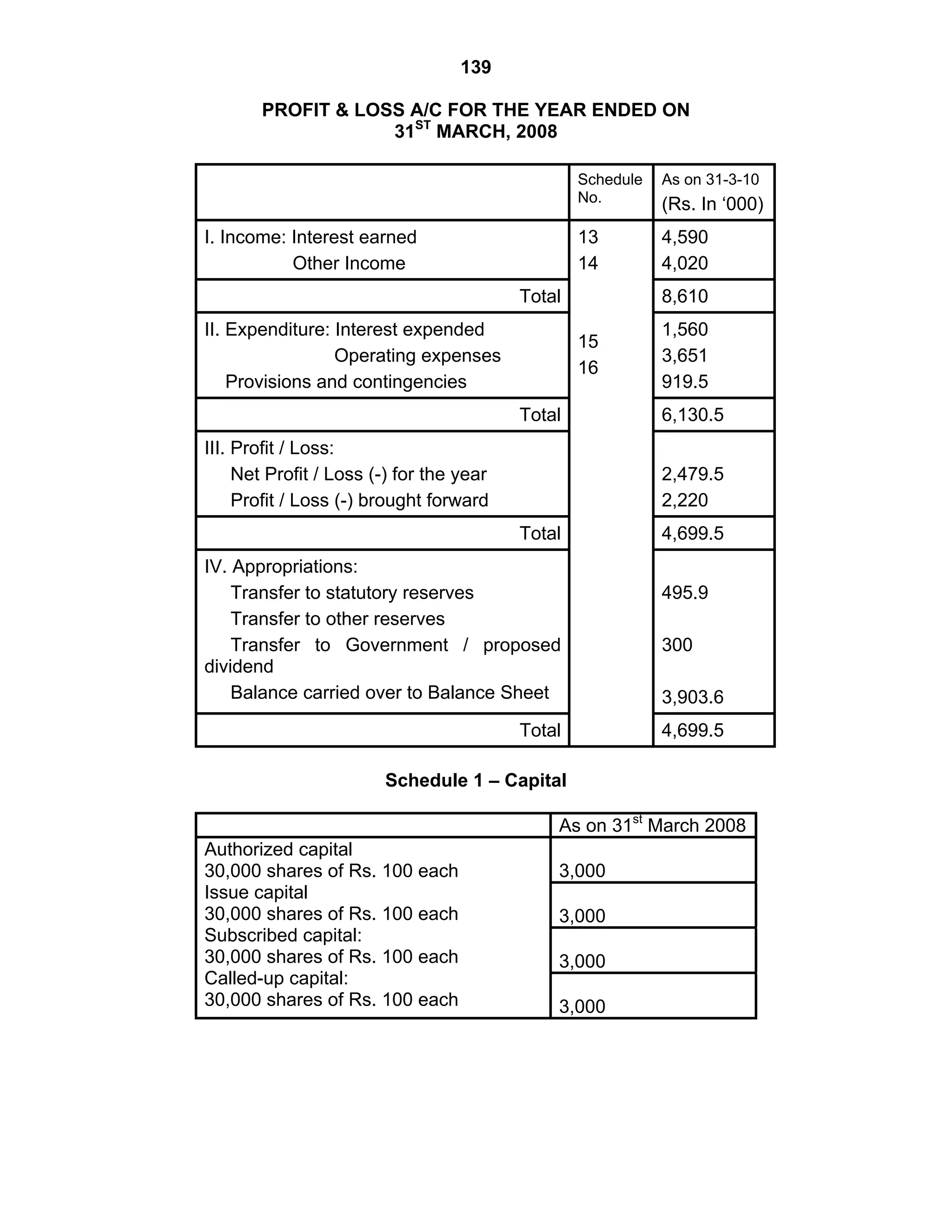
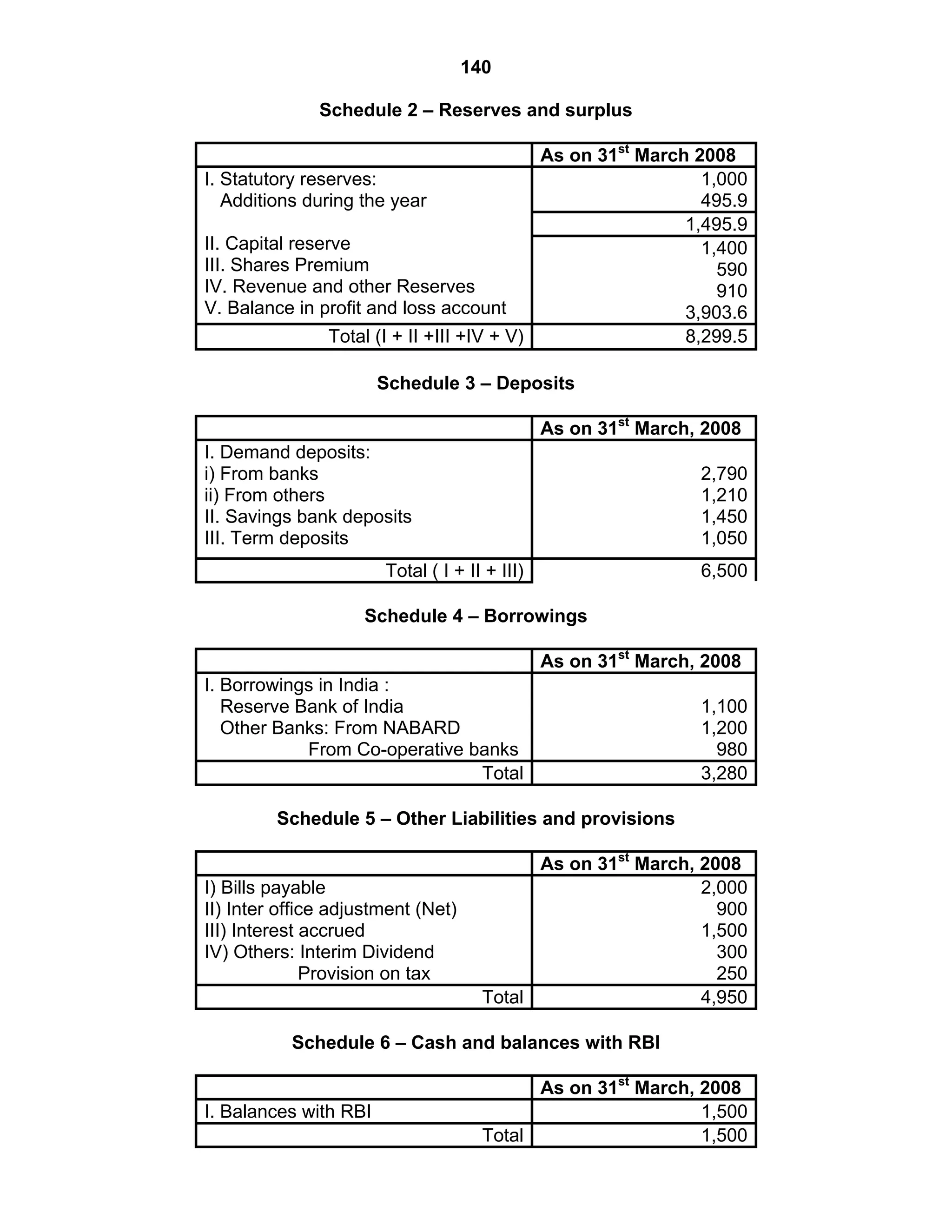
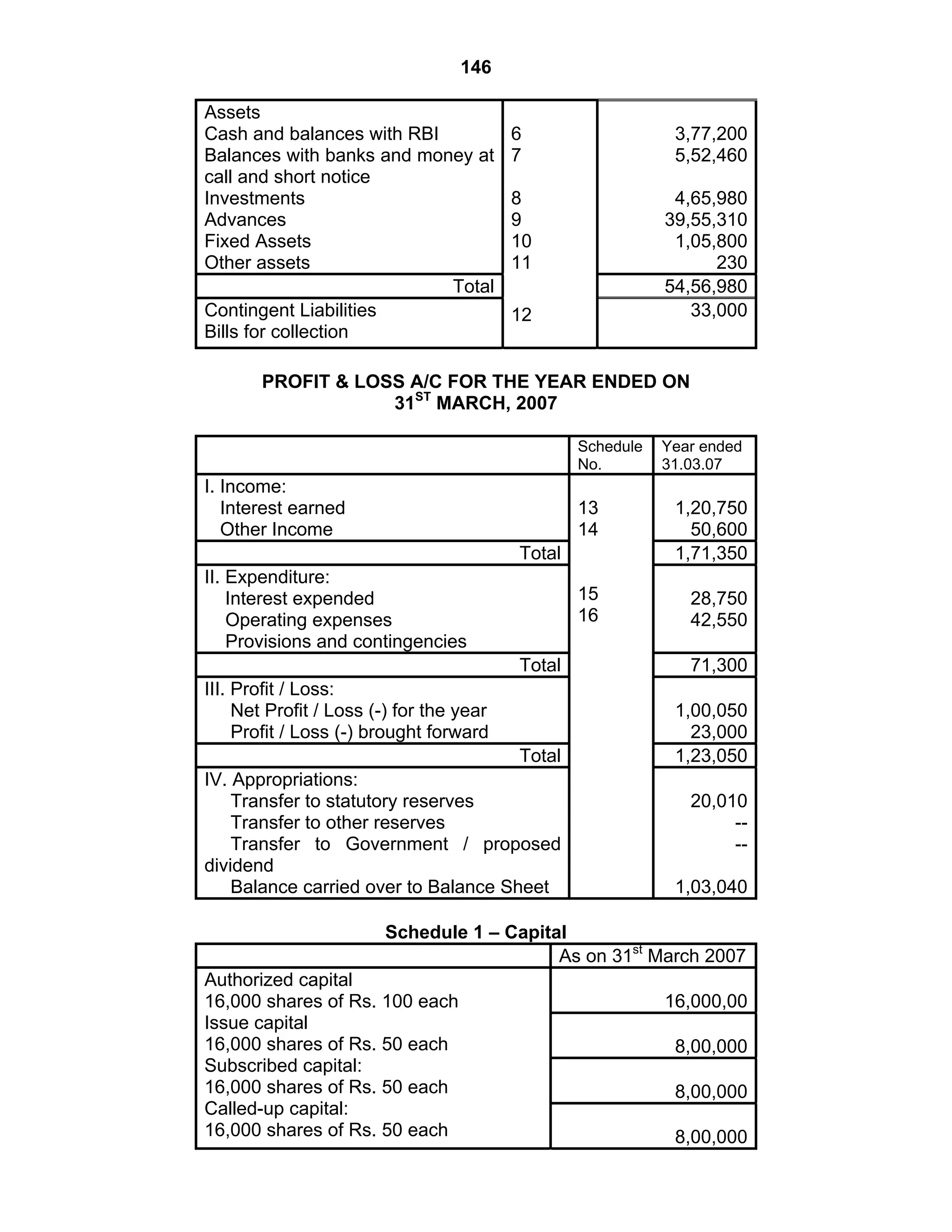
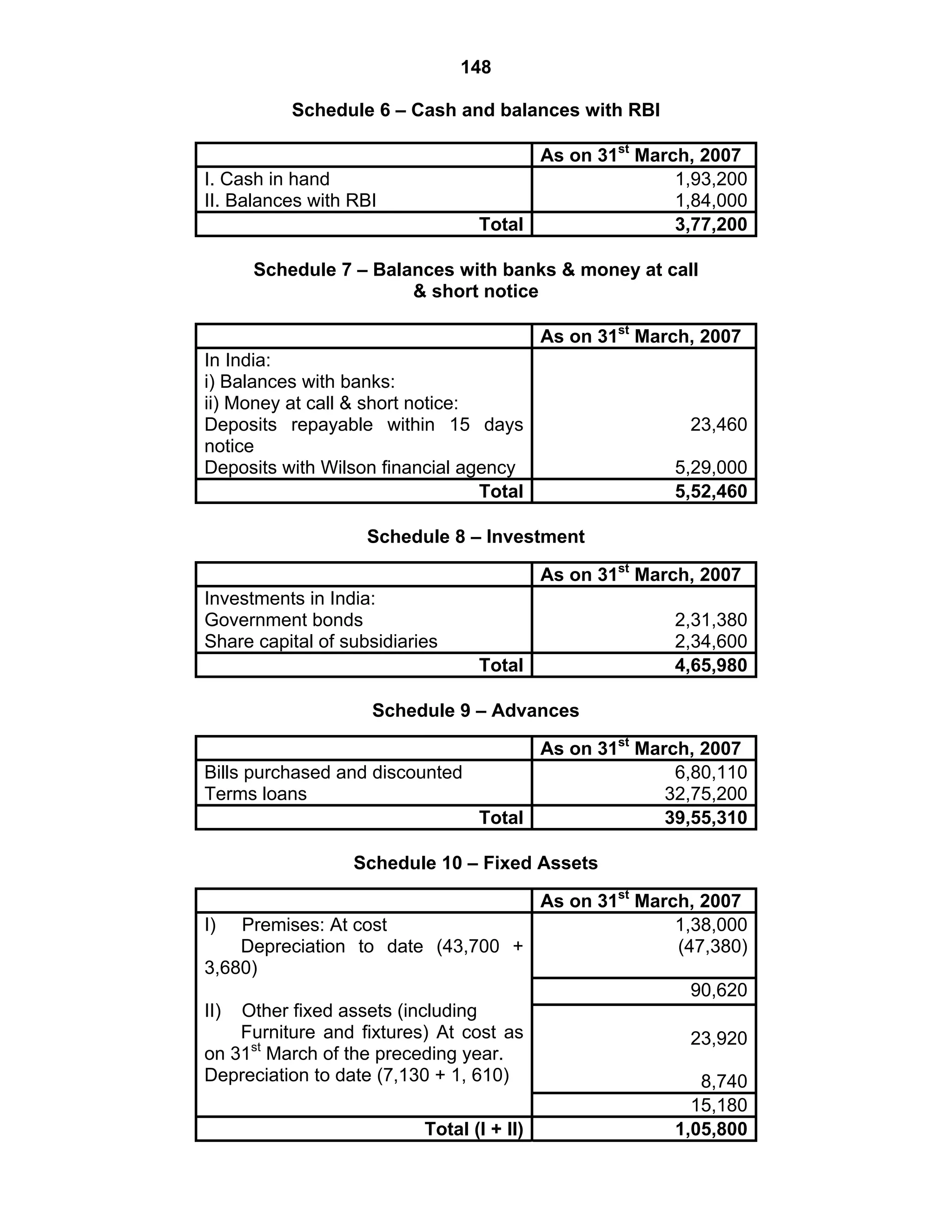
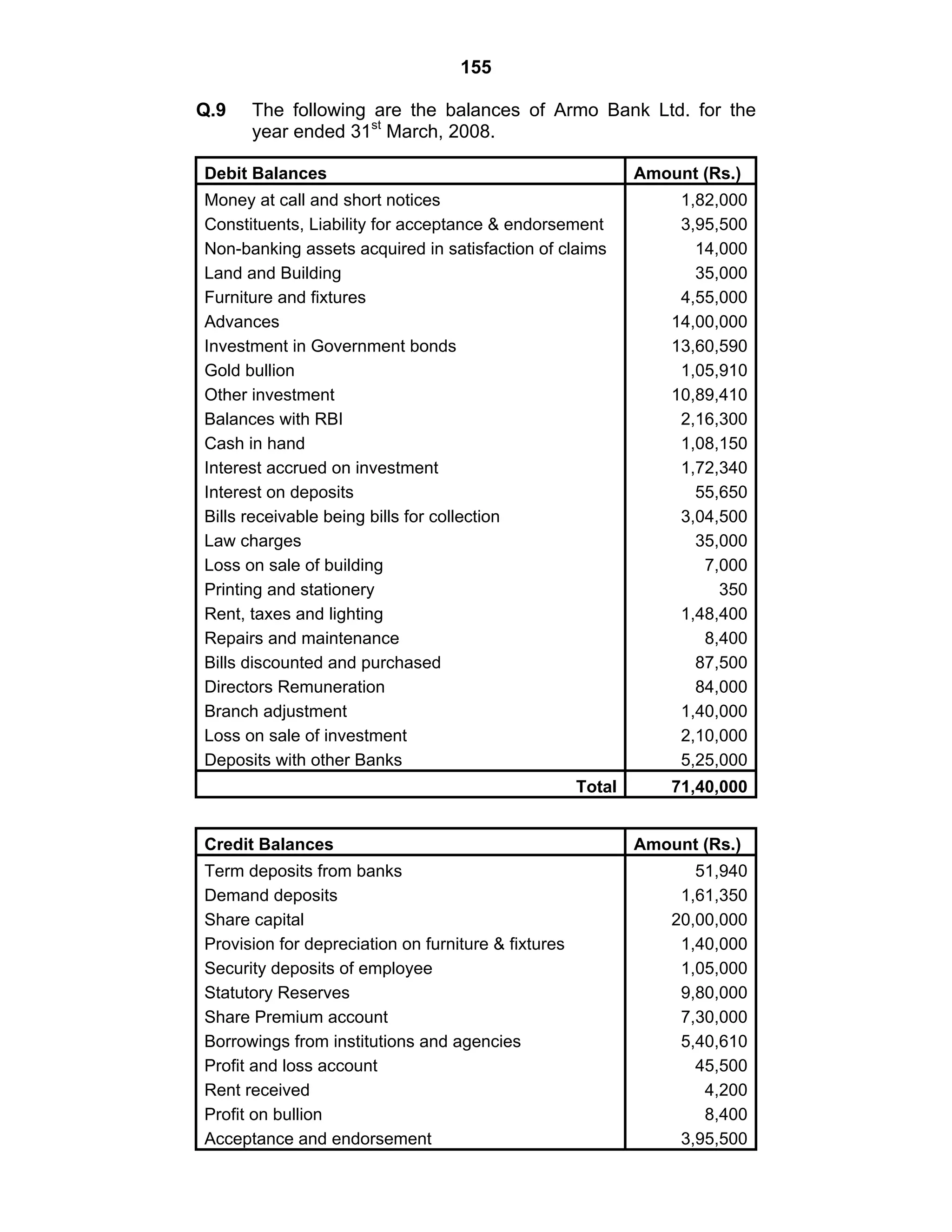
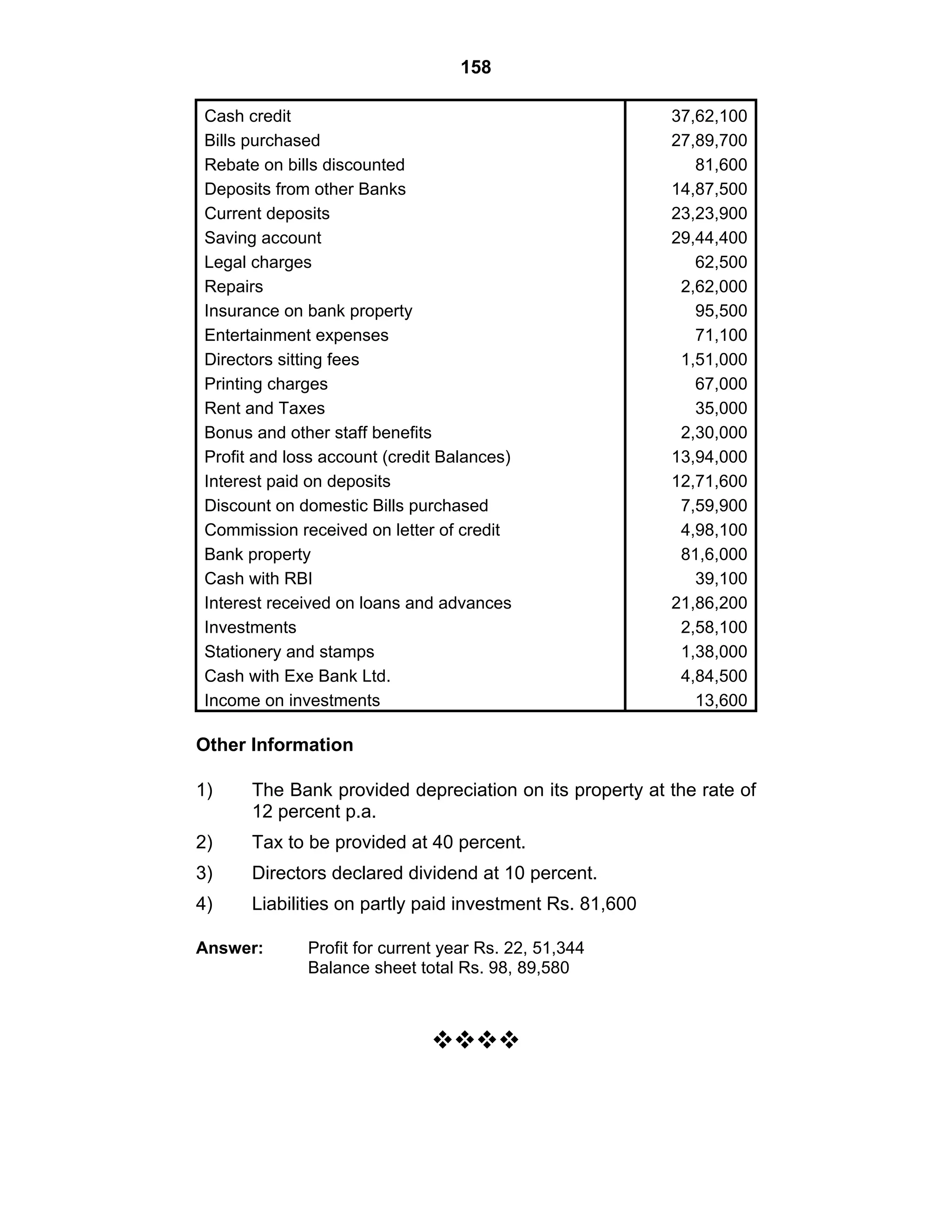
This document provides an overview of the accounting and statutory requirements for banking companies in India. It discusses key provisions of the Banking Regulation Act of 1949 regarding minimum capital and reserves, restrictions on commissions and dividends, statutory reserves, cash reserves, restrictions on loans and advances, books of accounts, provisioning of non-performing assets, and preparation of final accounts using the prescribed formats in the Third Schedule of the Act. The document also outlines the various types of business activities permitted for banks and restrictions placed on certain activities.