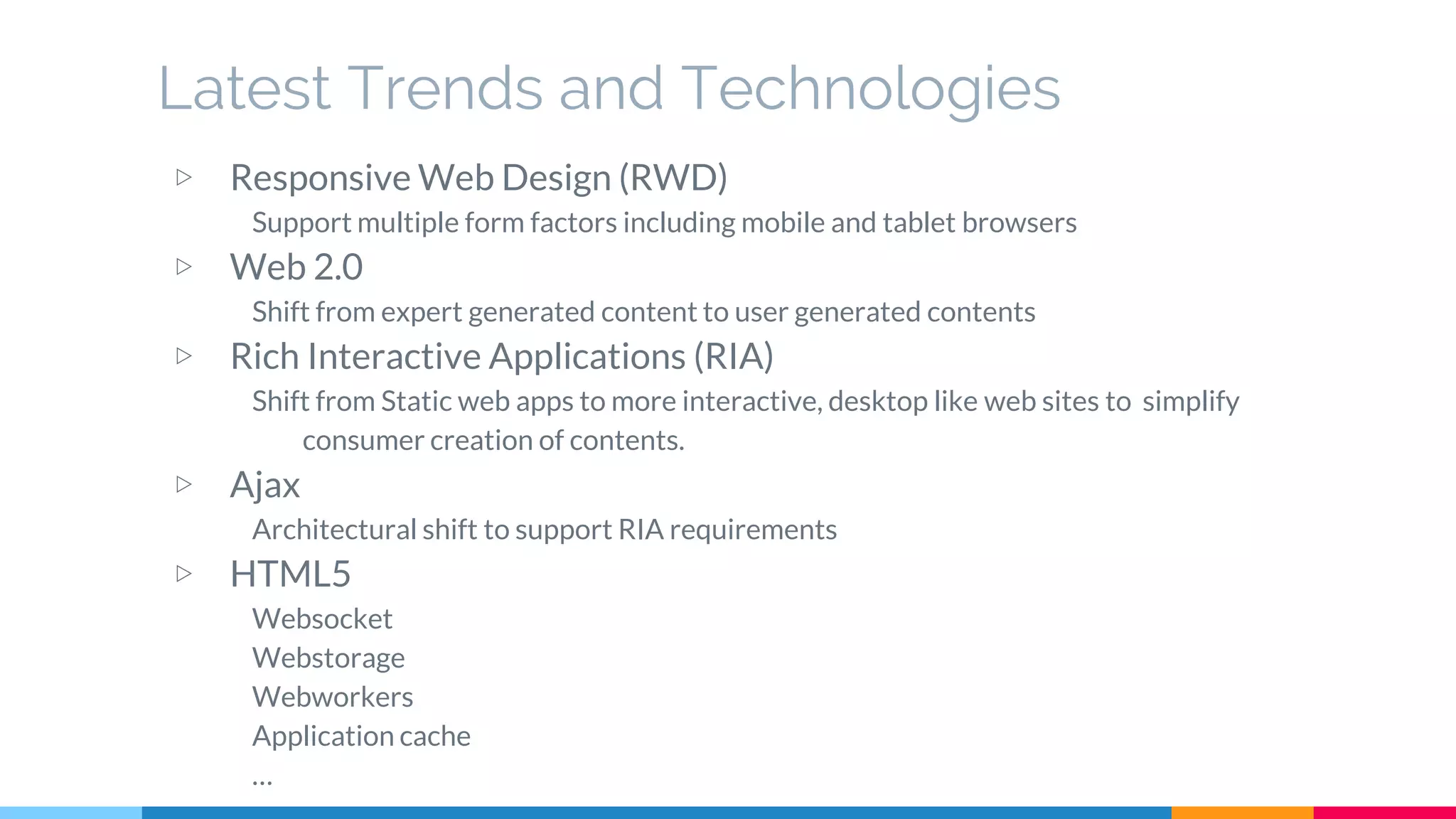
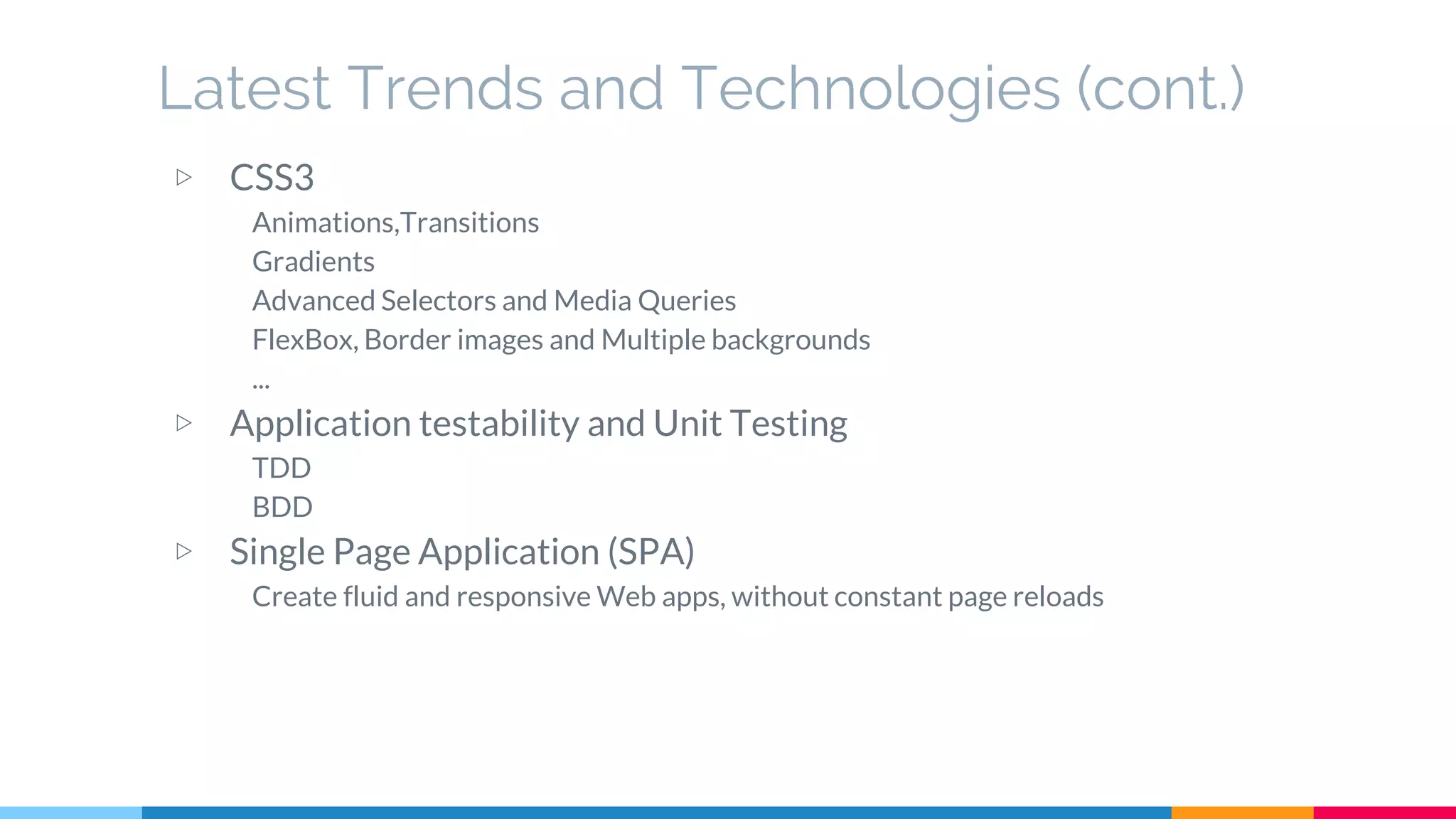
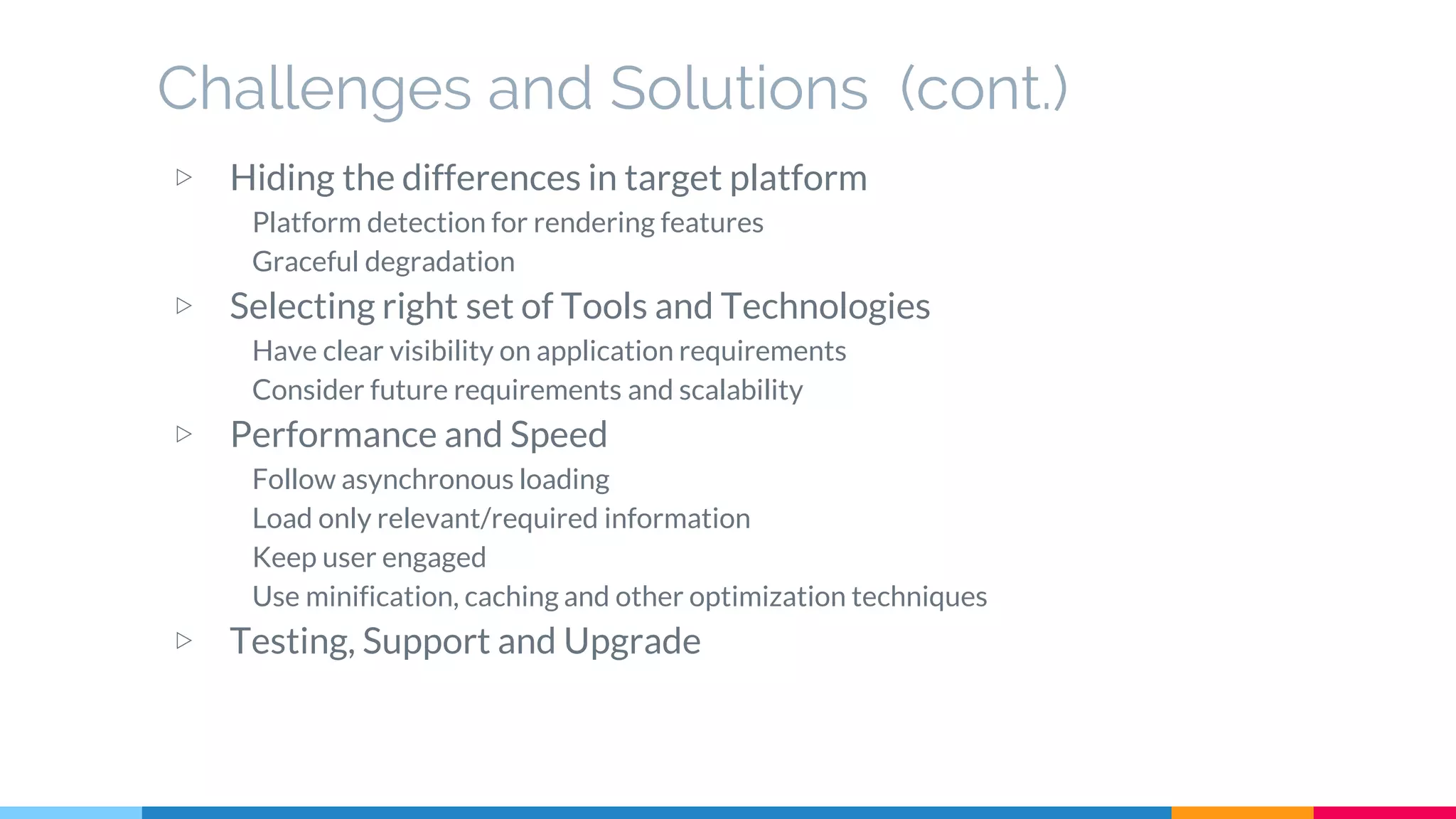
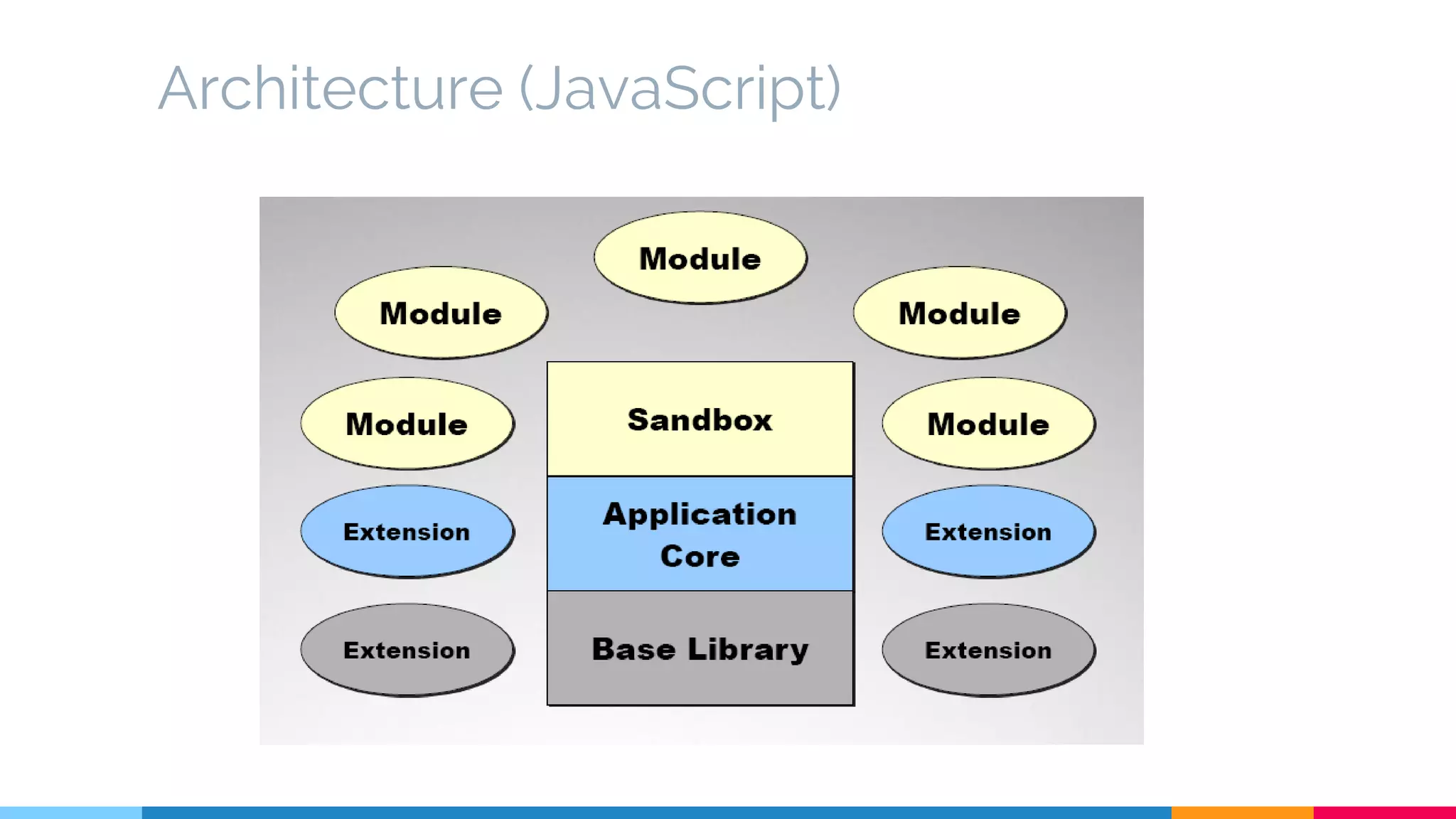
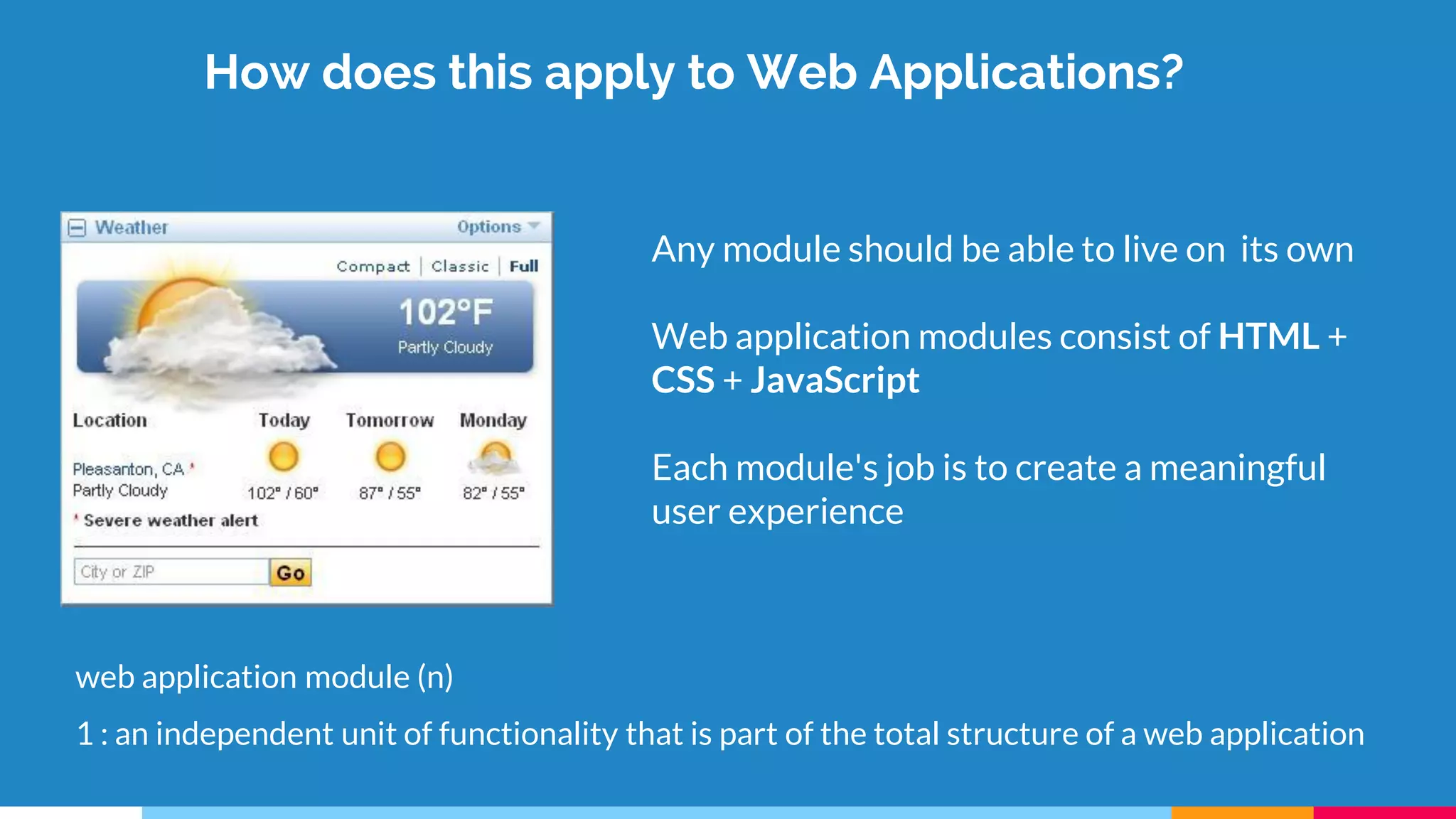
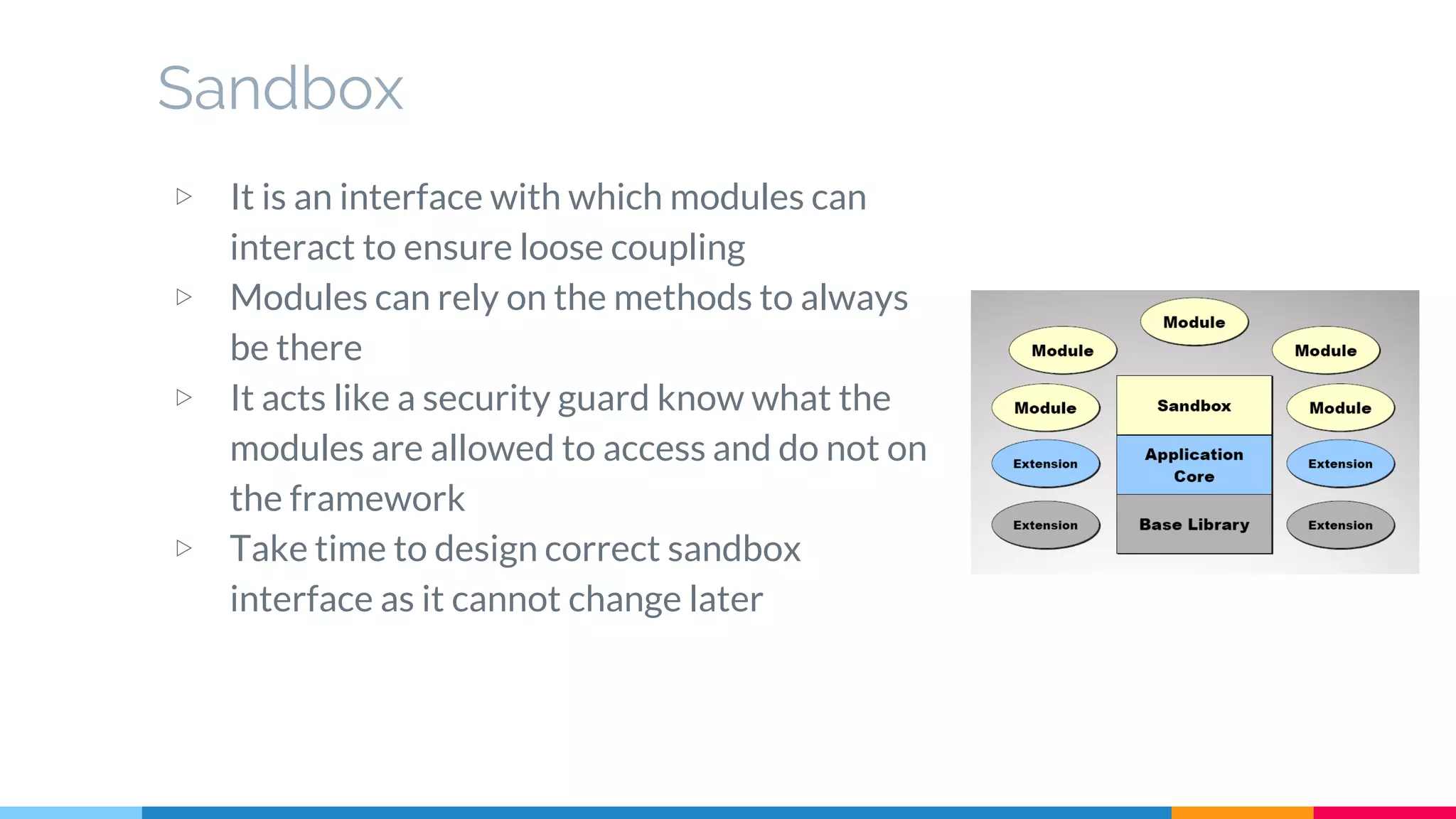
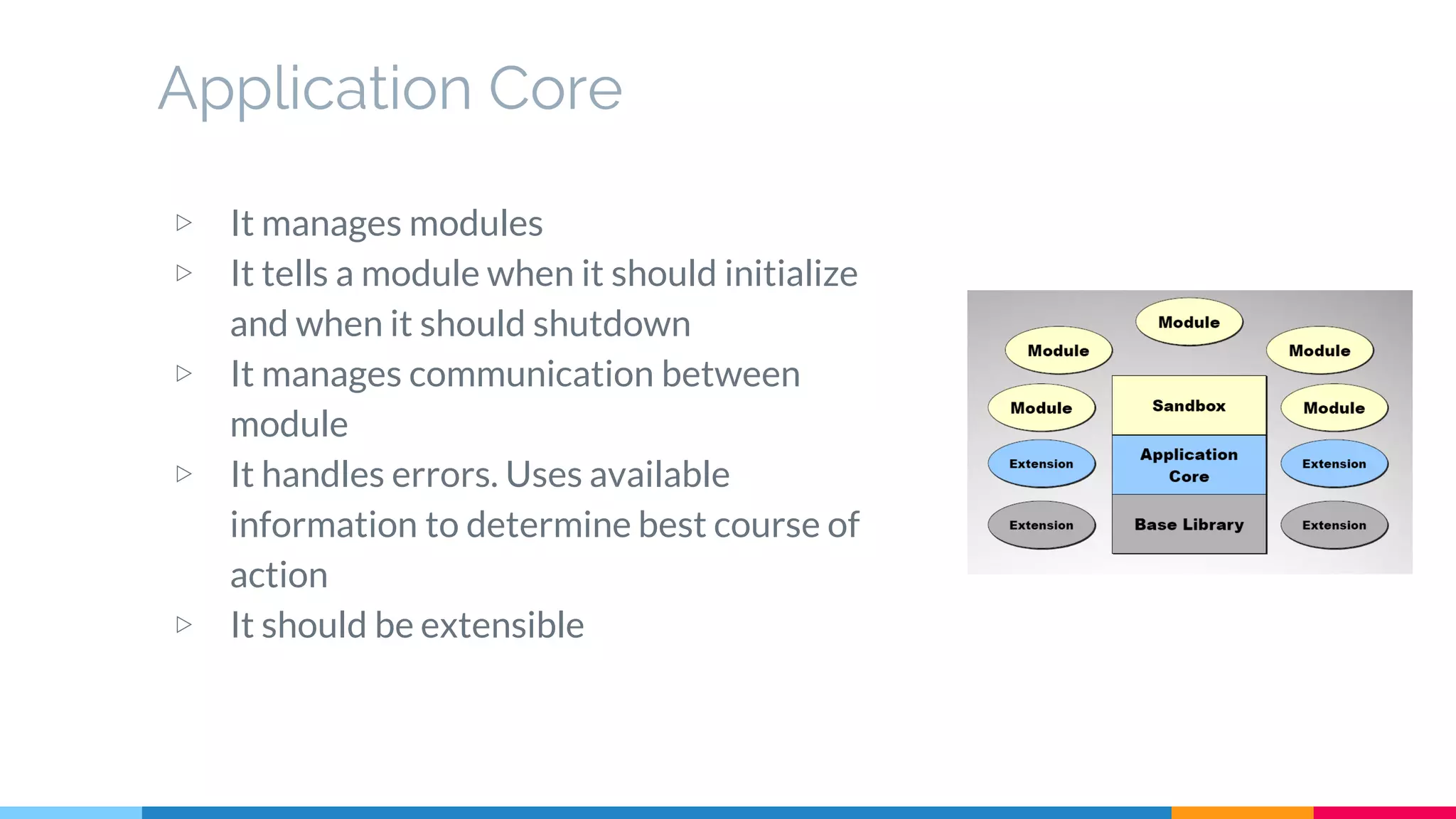
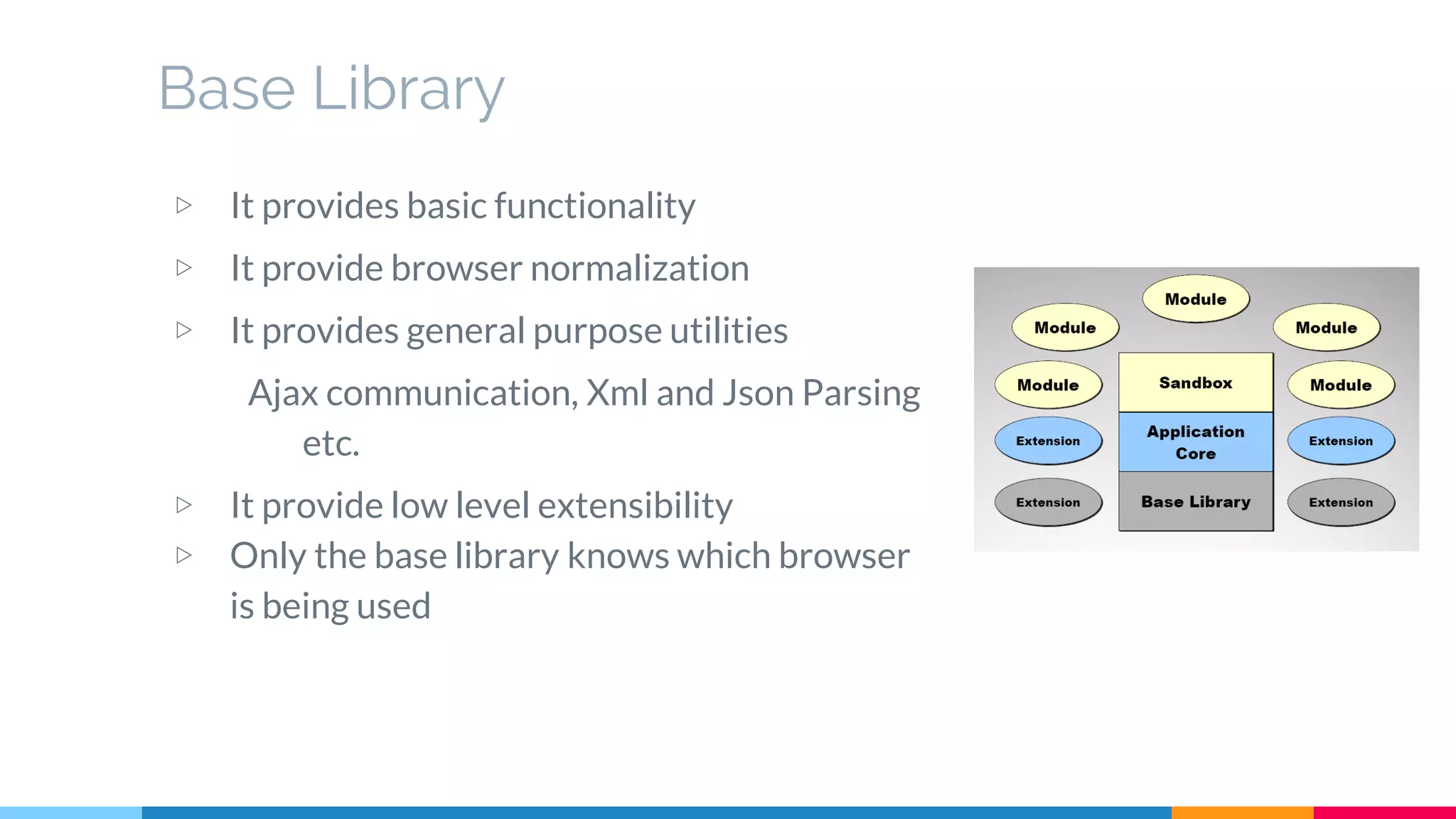
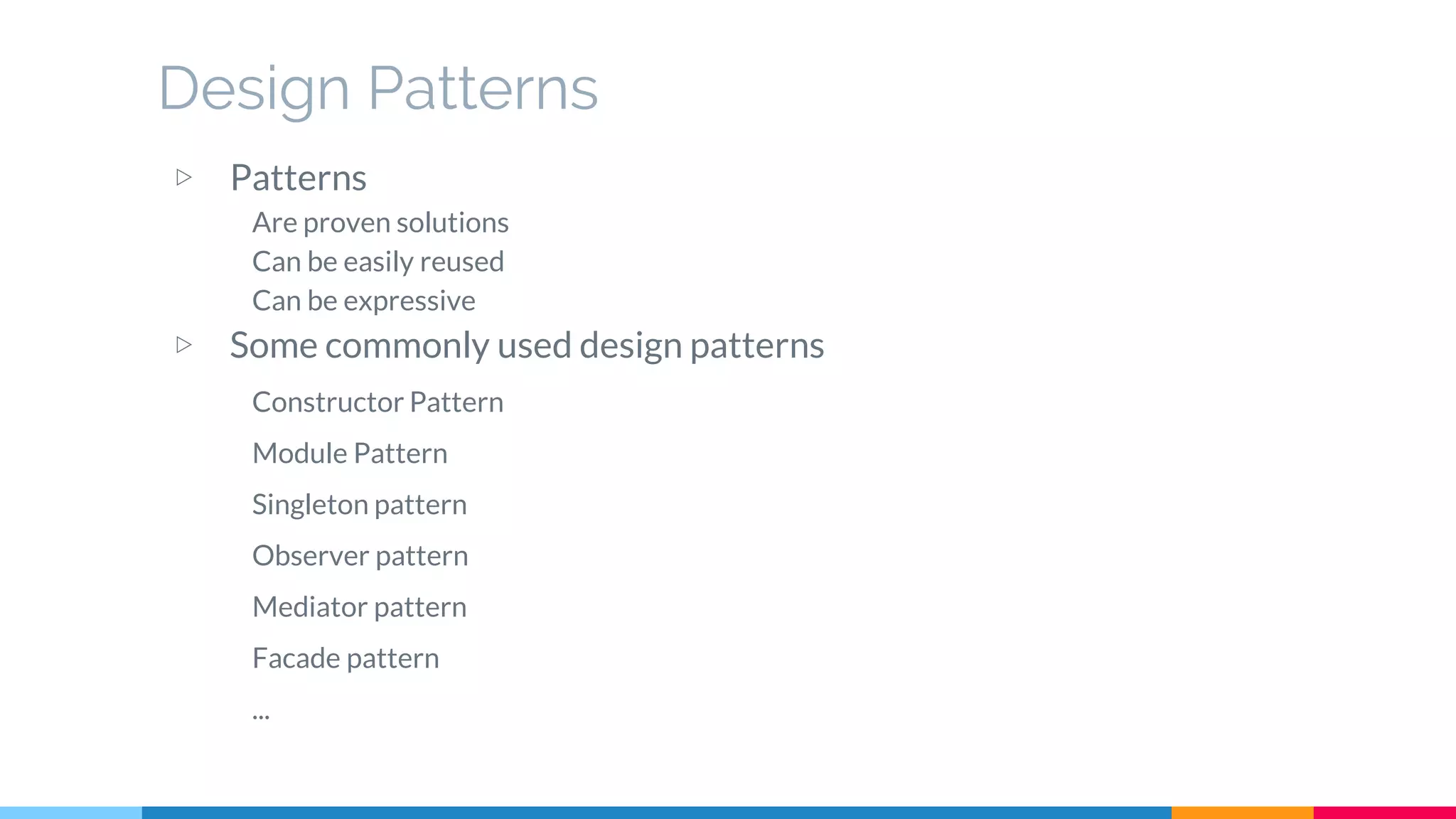
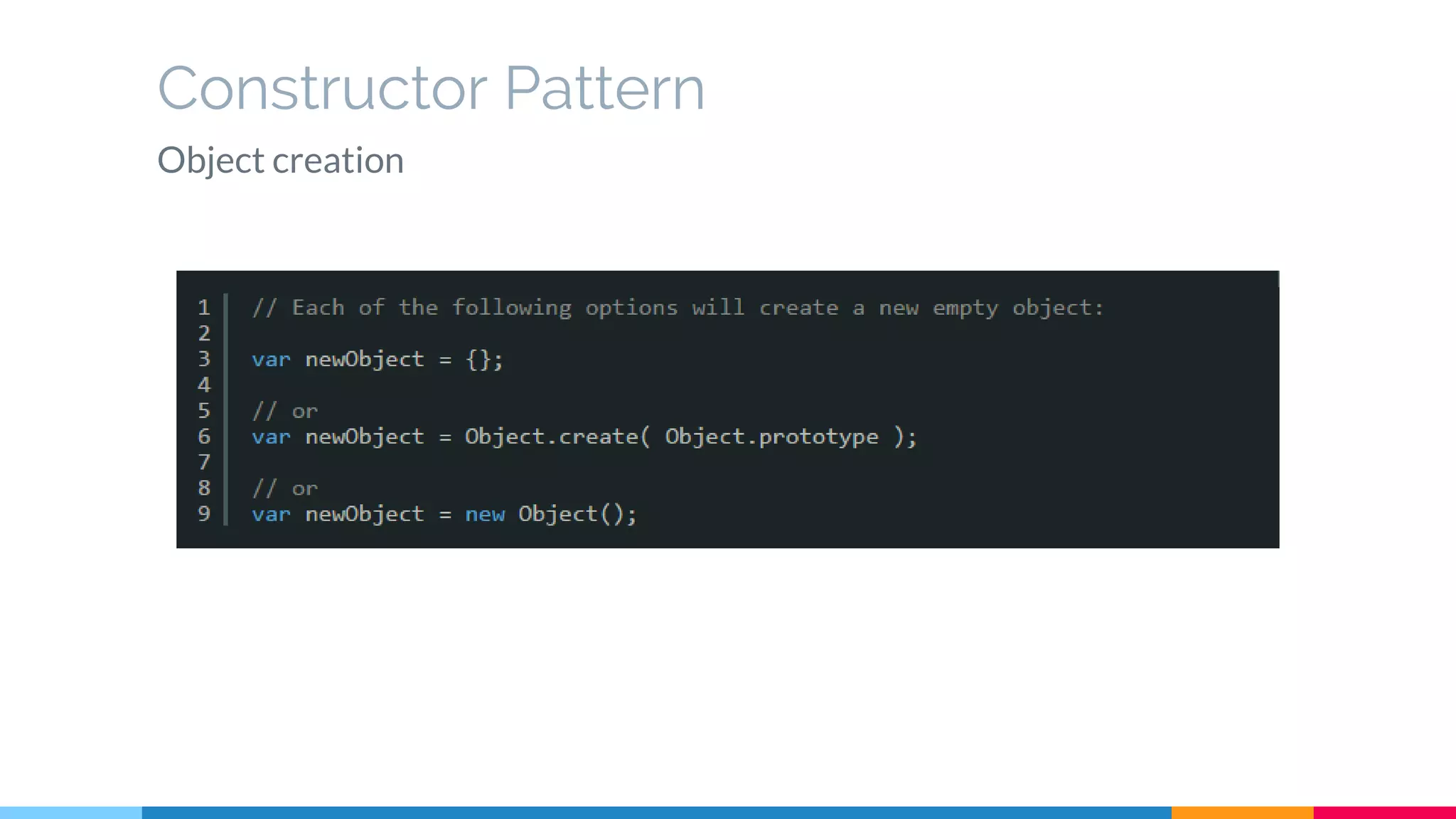
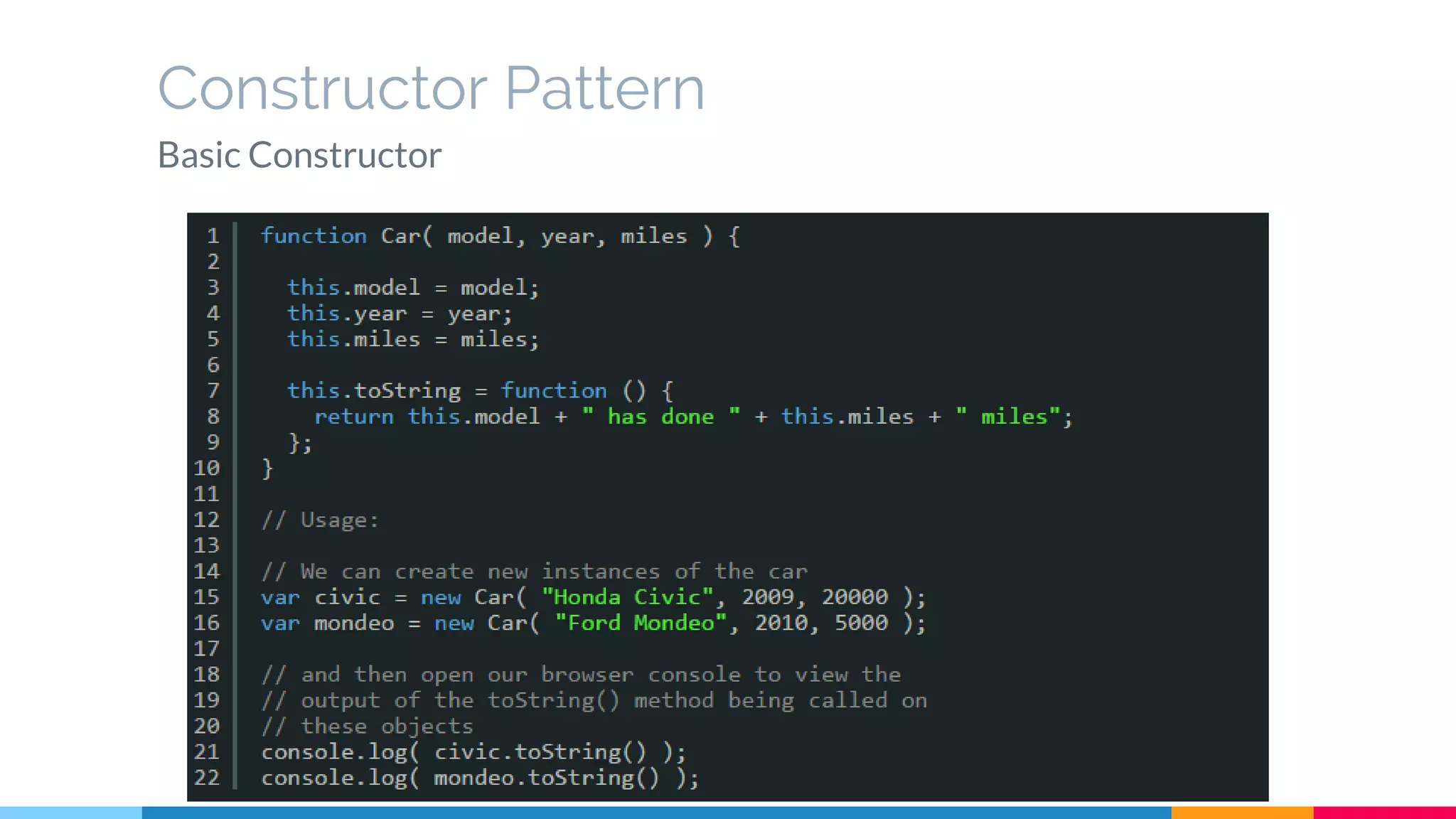
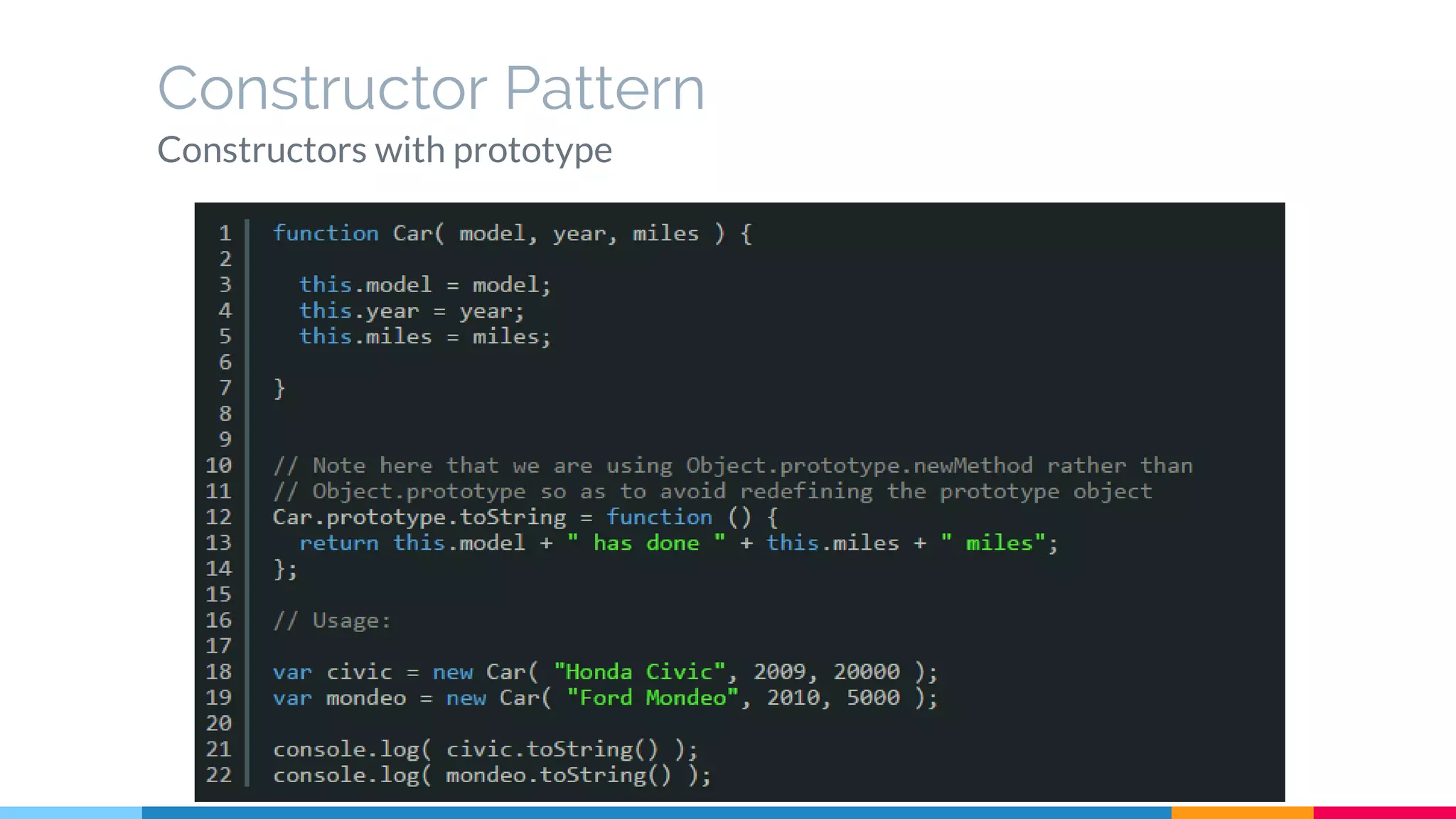
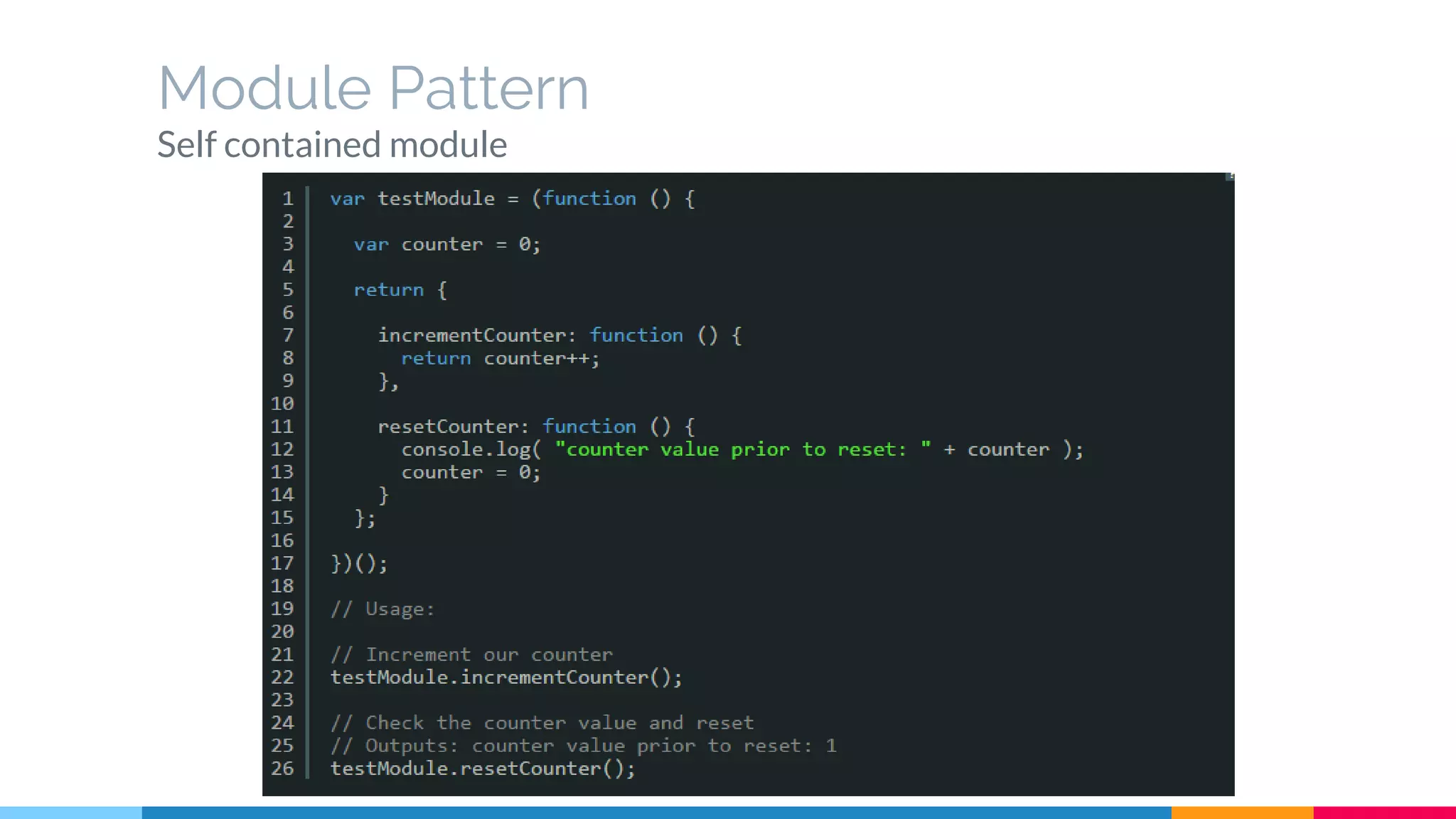
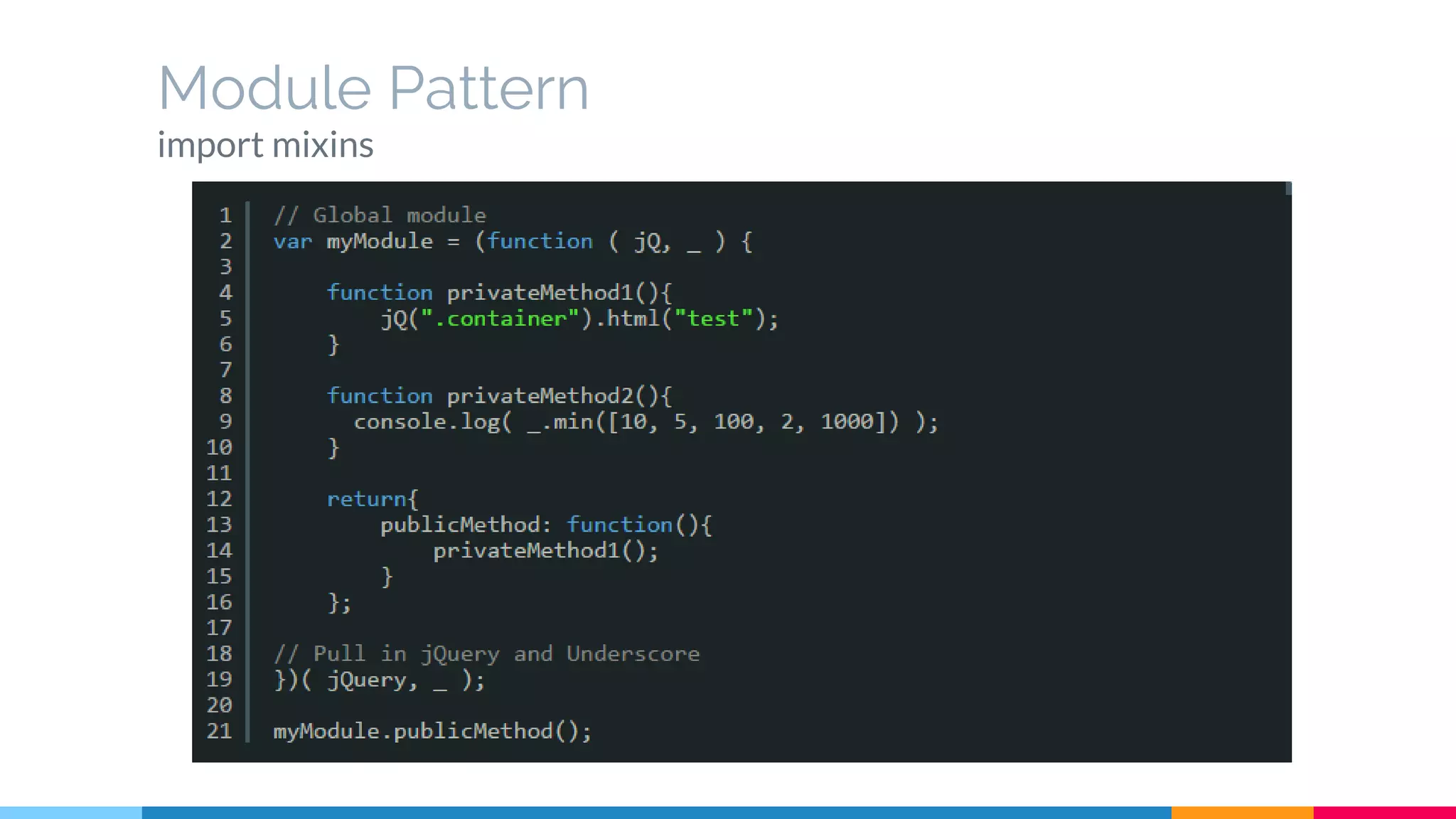
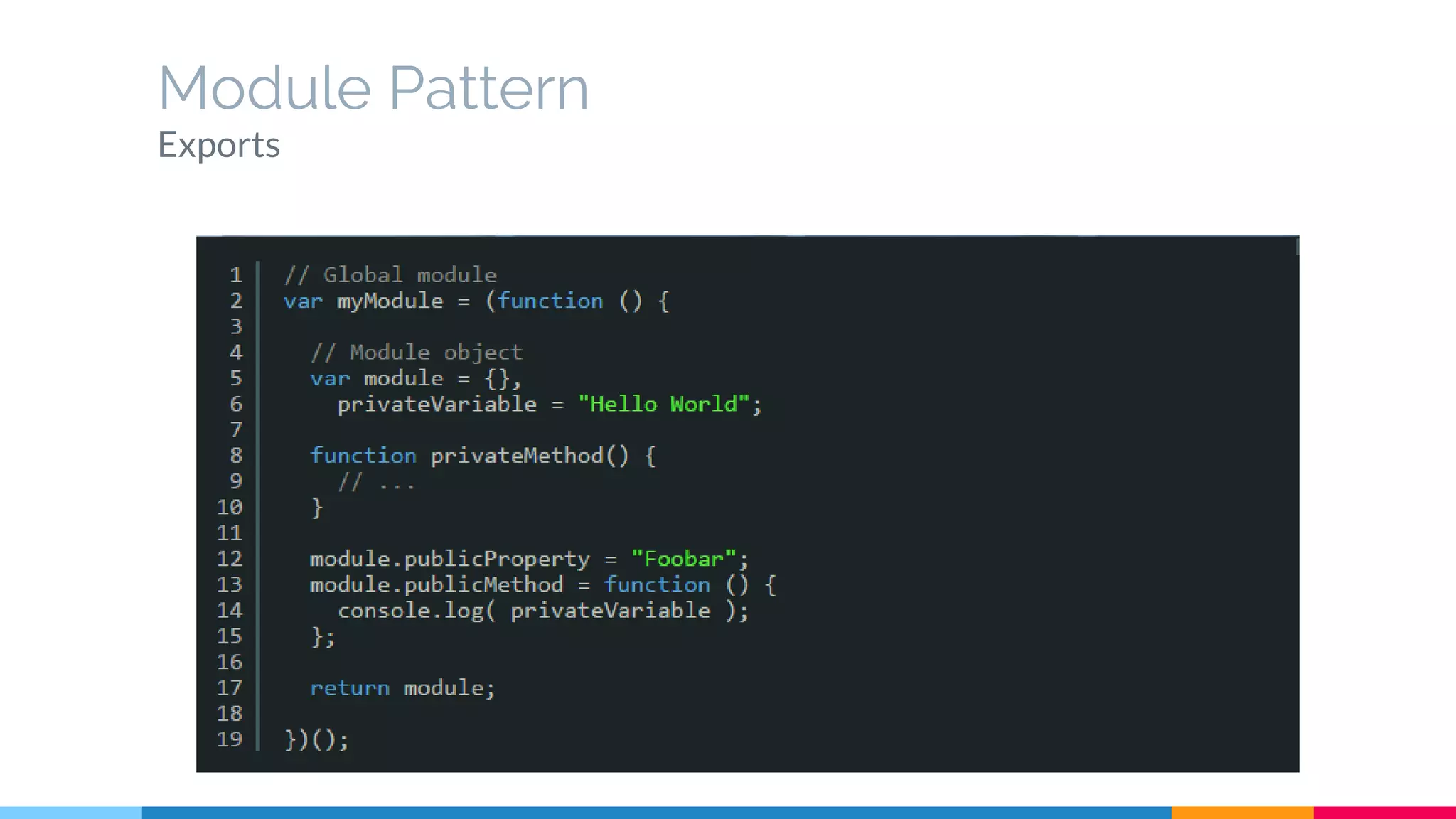
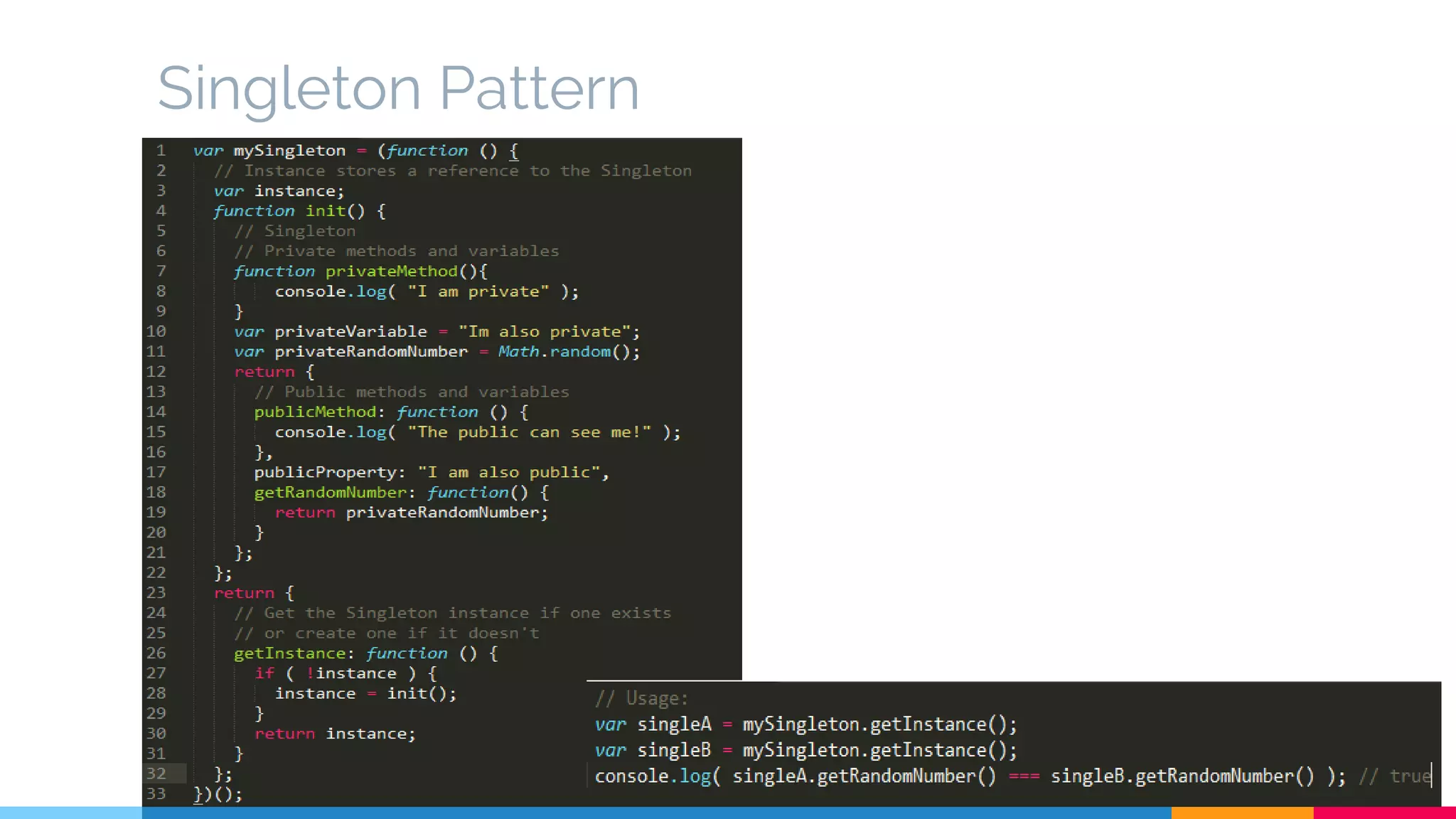
The document discusses modern web development trends and technologies. It begins with an introduction of the author and an overview of the topics to be covered, including the shift from classical to modern web development, latest frontend technologies and frameworks, challenges and solutions, and best practices for JavaScript and CSS. Specific technologies covered include responsive design, Ajax, HTML5, CSS3, single page applications, and popular frameworks. Architecture approaches like modular design and common patterns like MVC, MVP and MVVM are explained. The document concludes with reminders about defensive coding practices.