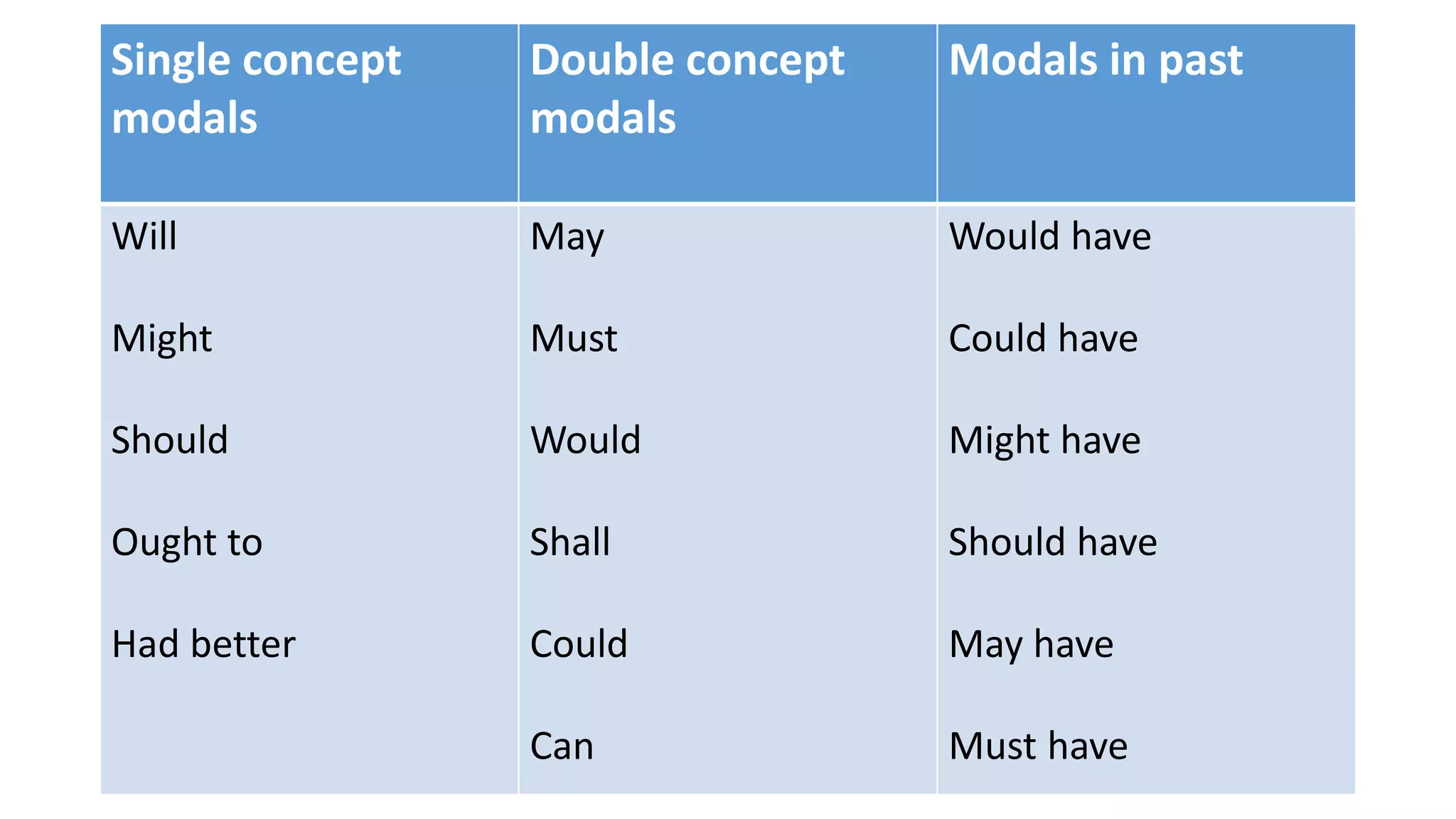
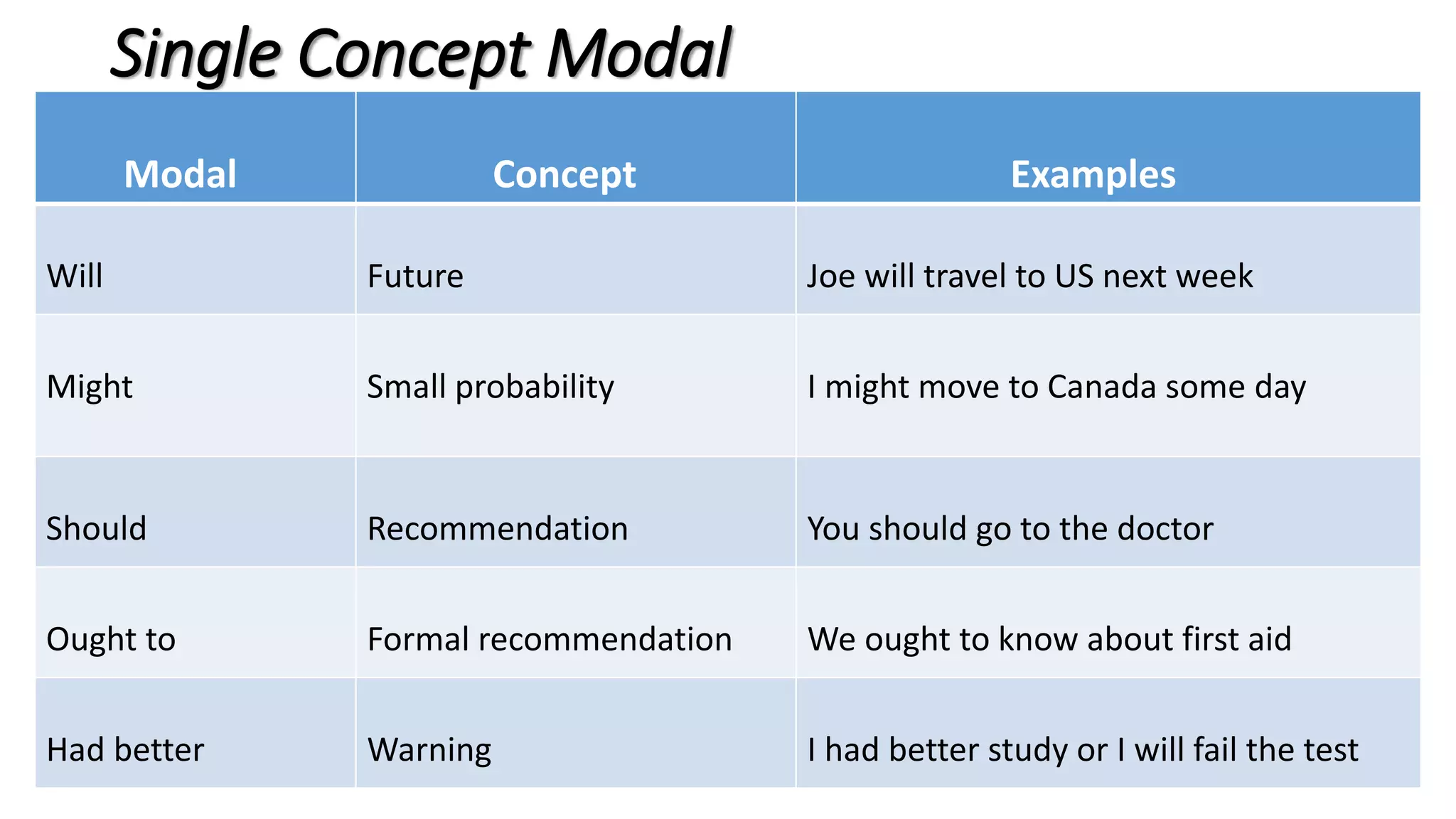
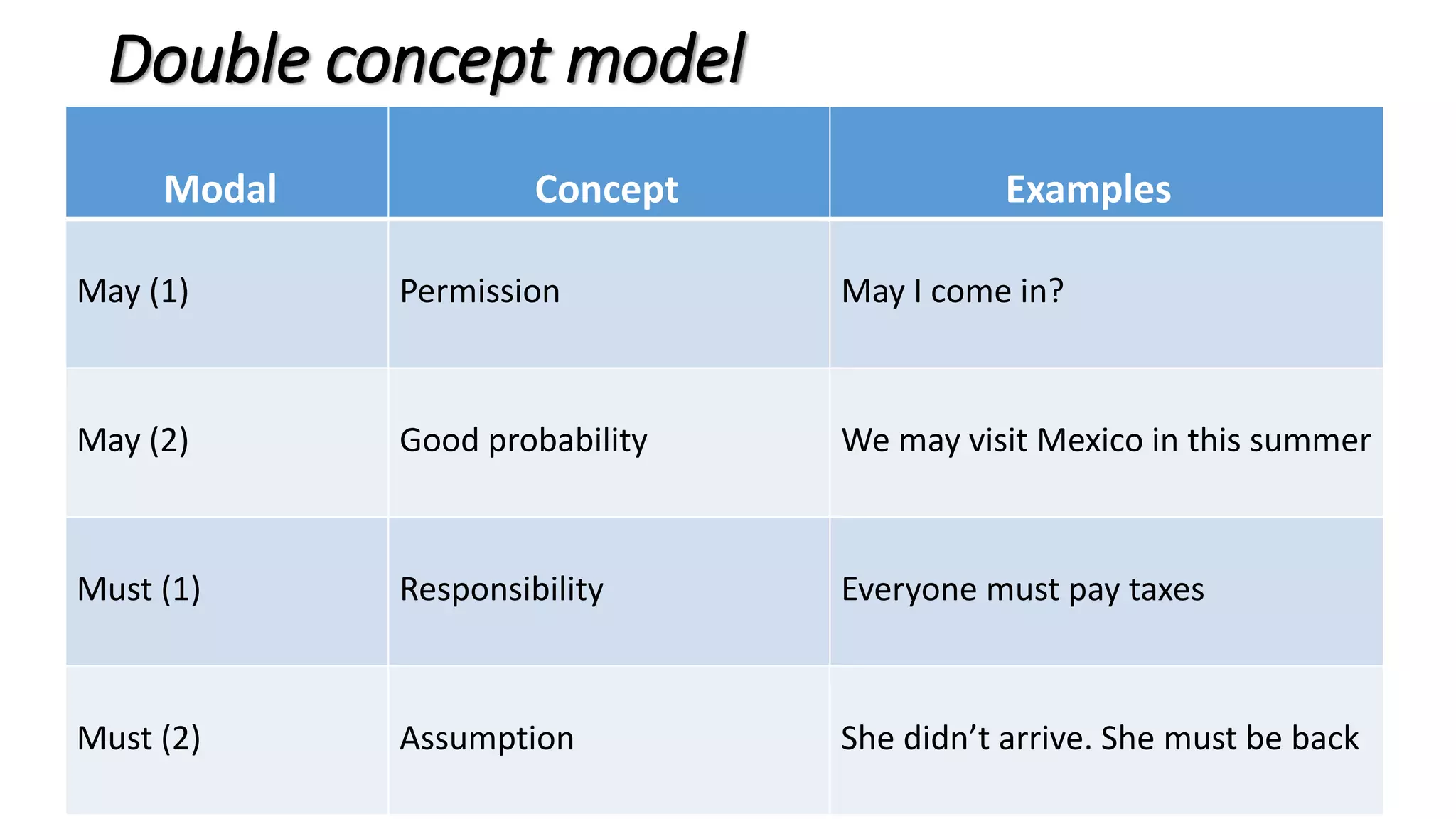
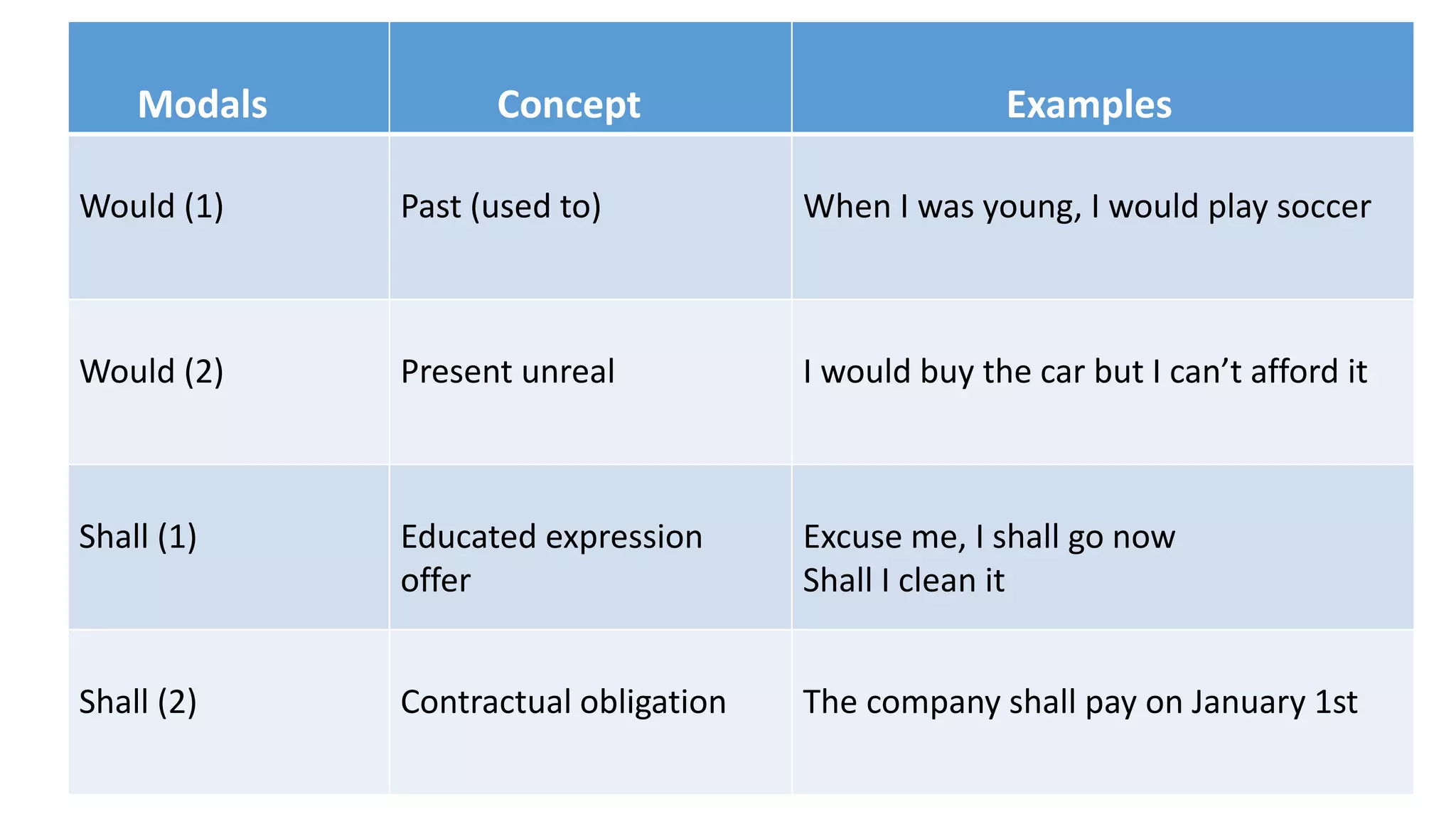
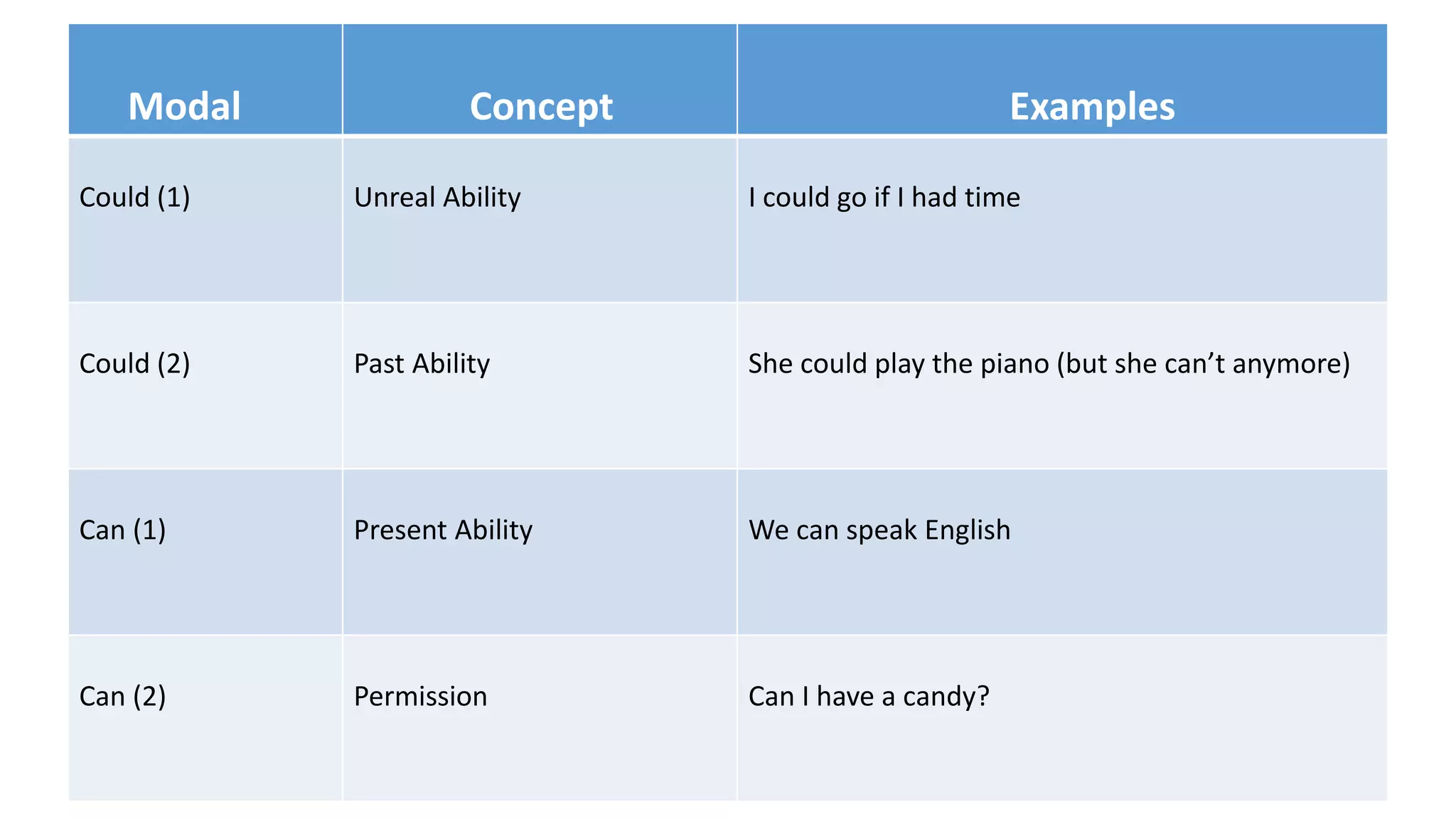
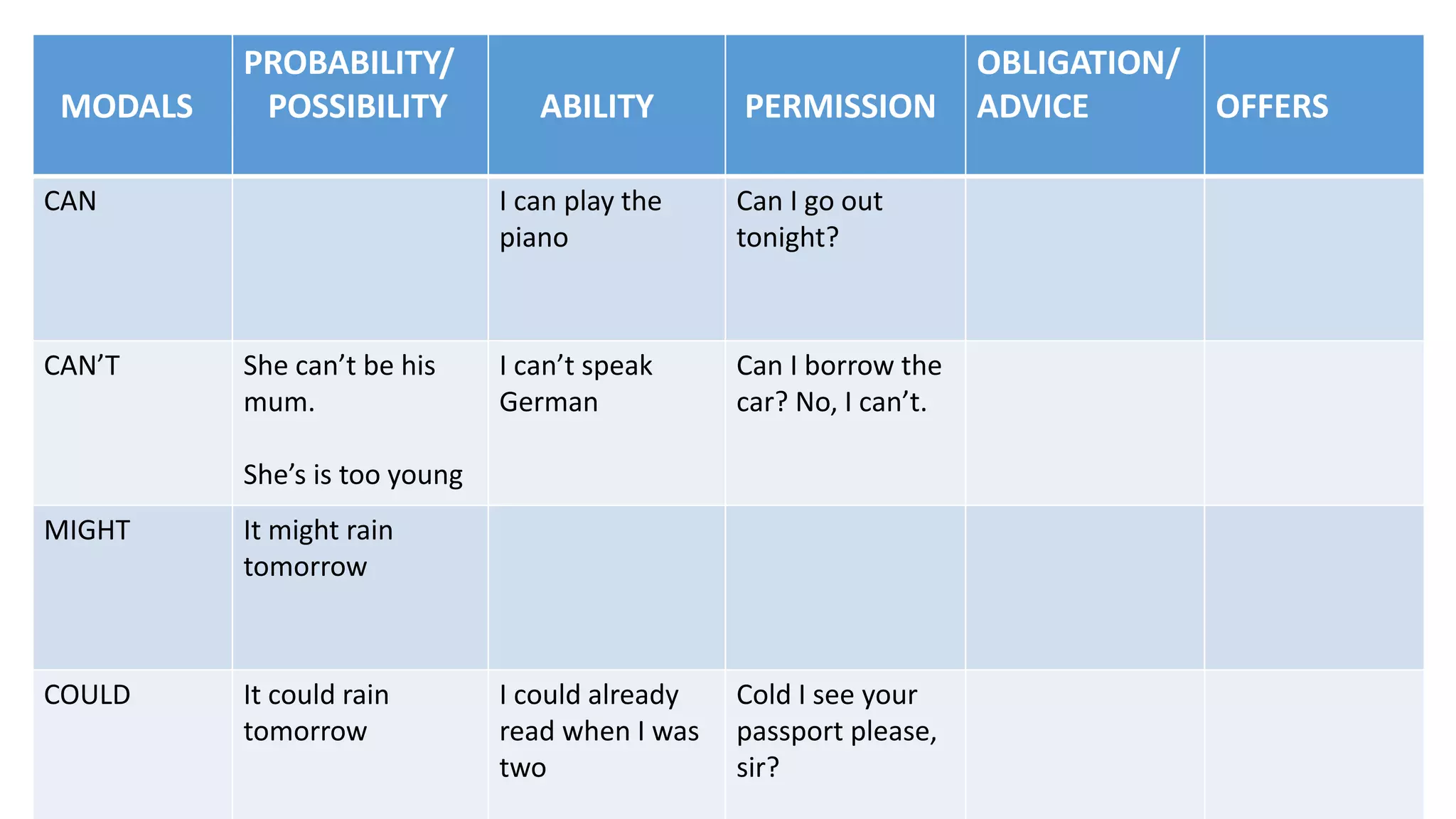
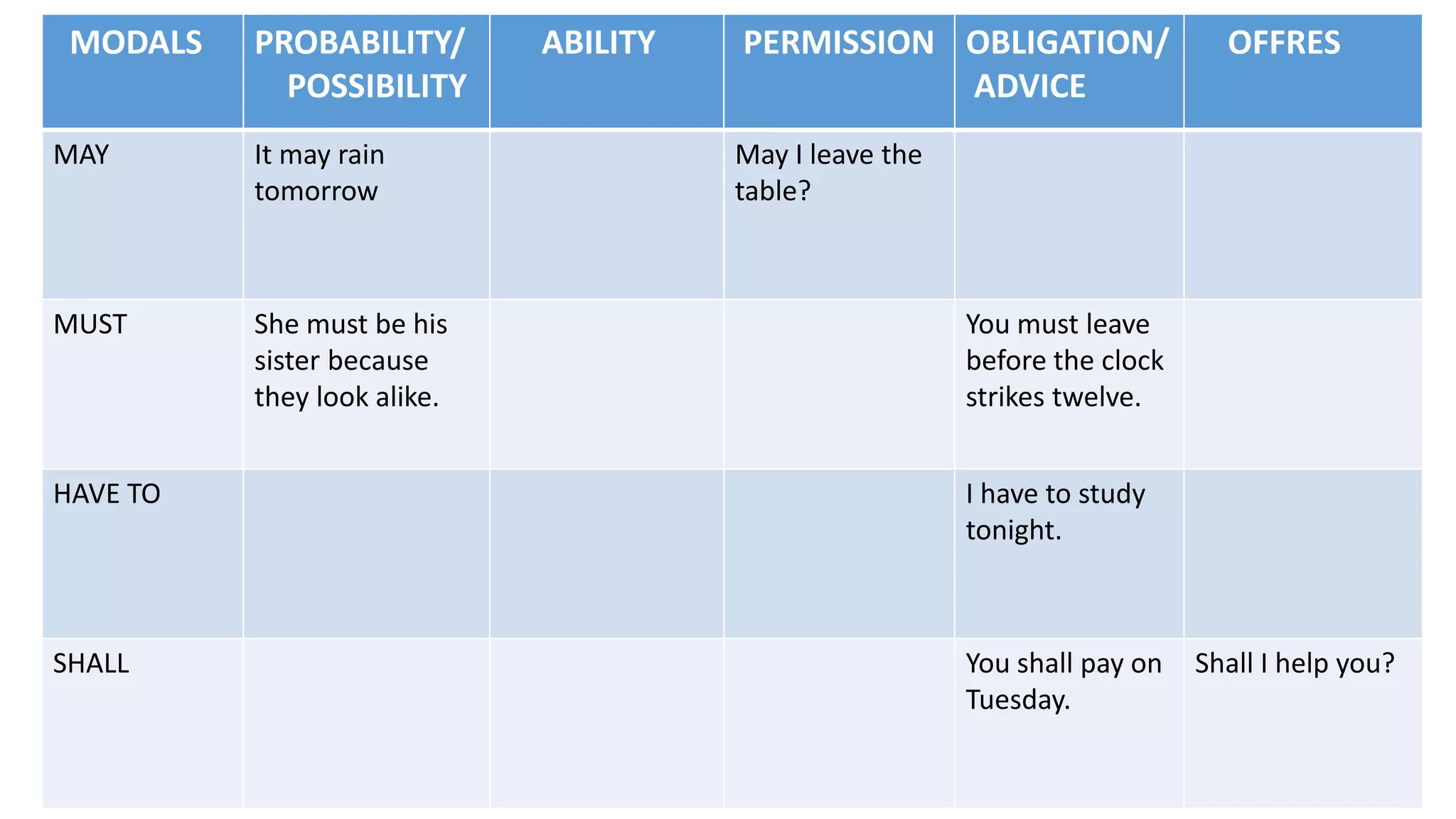
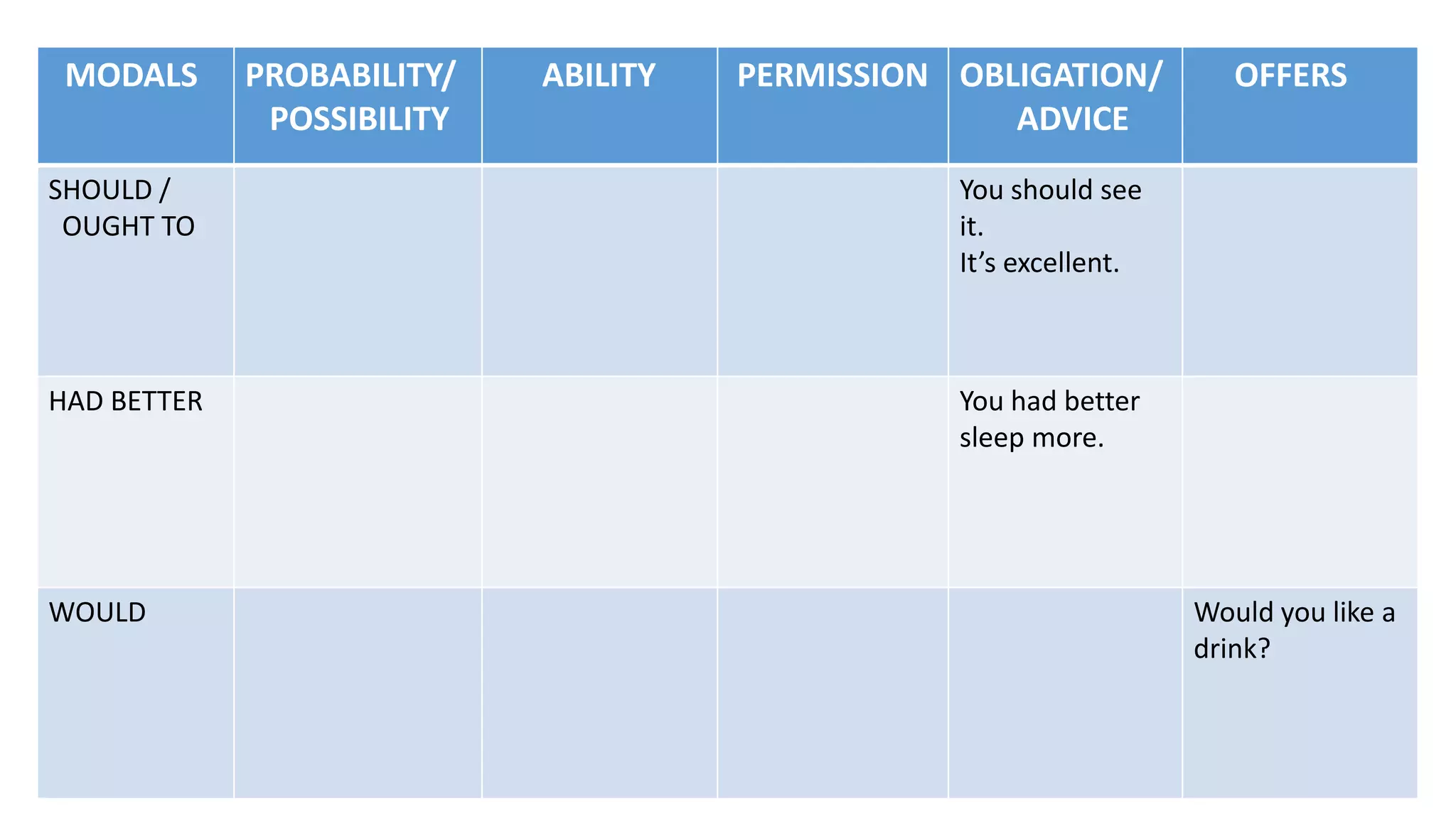
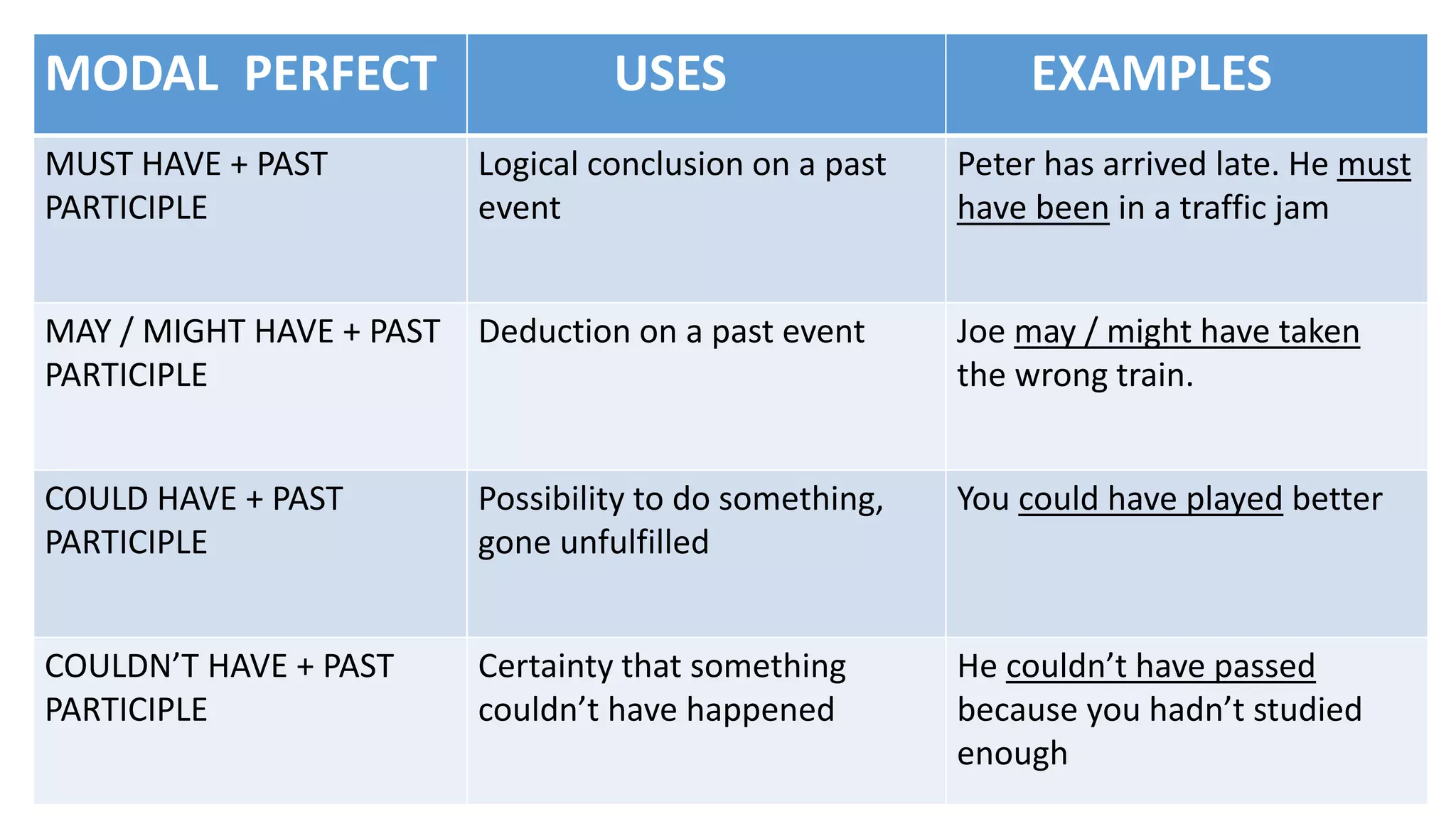
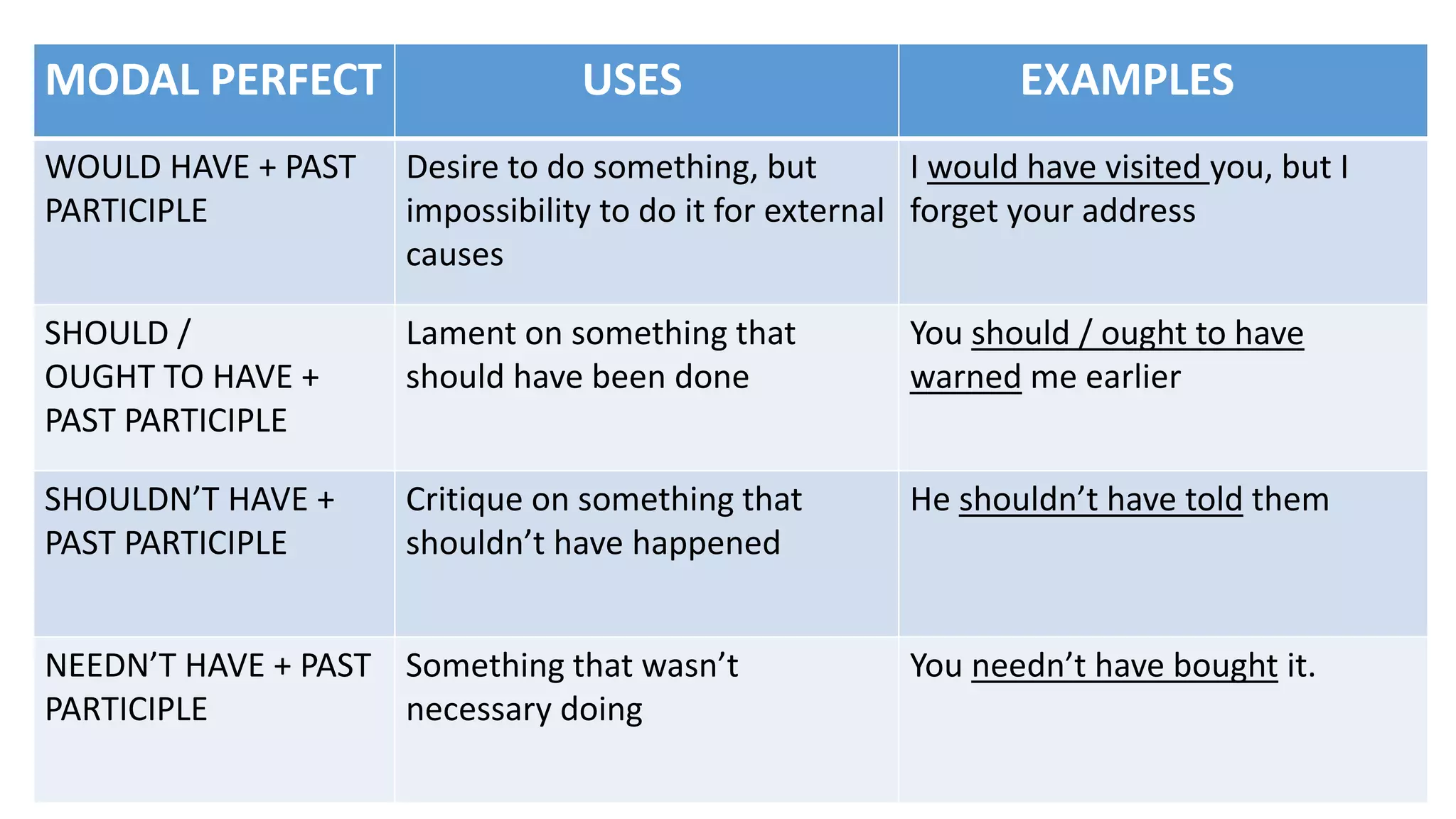
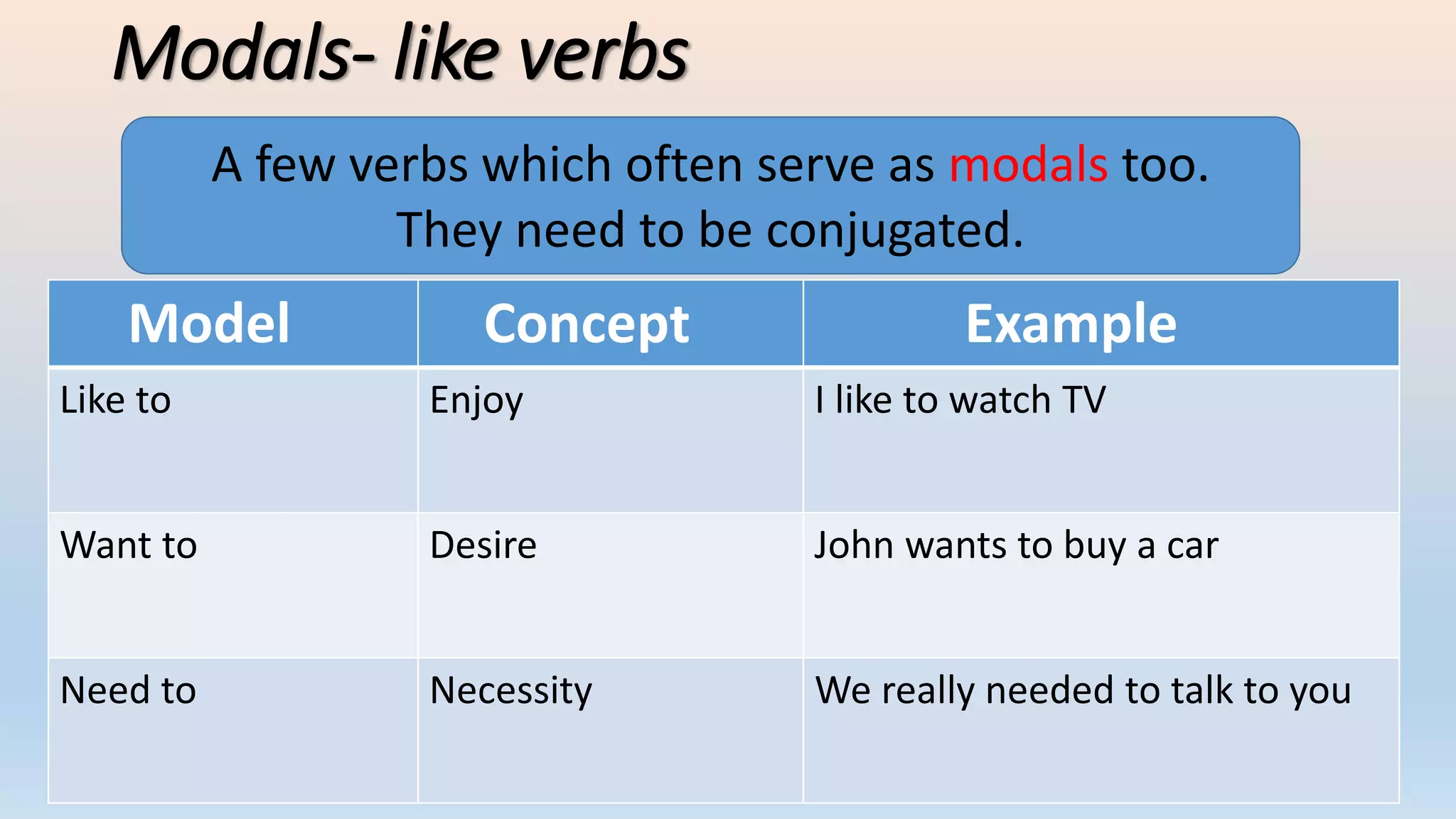
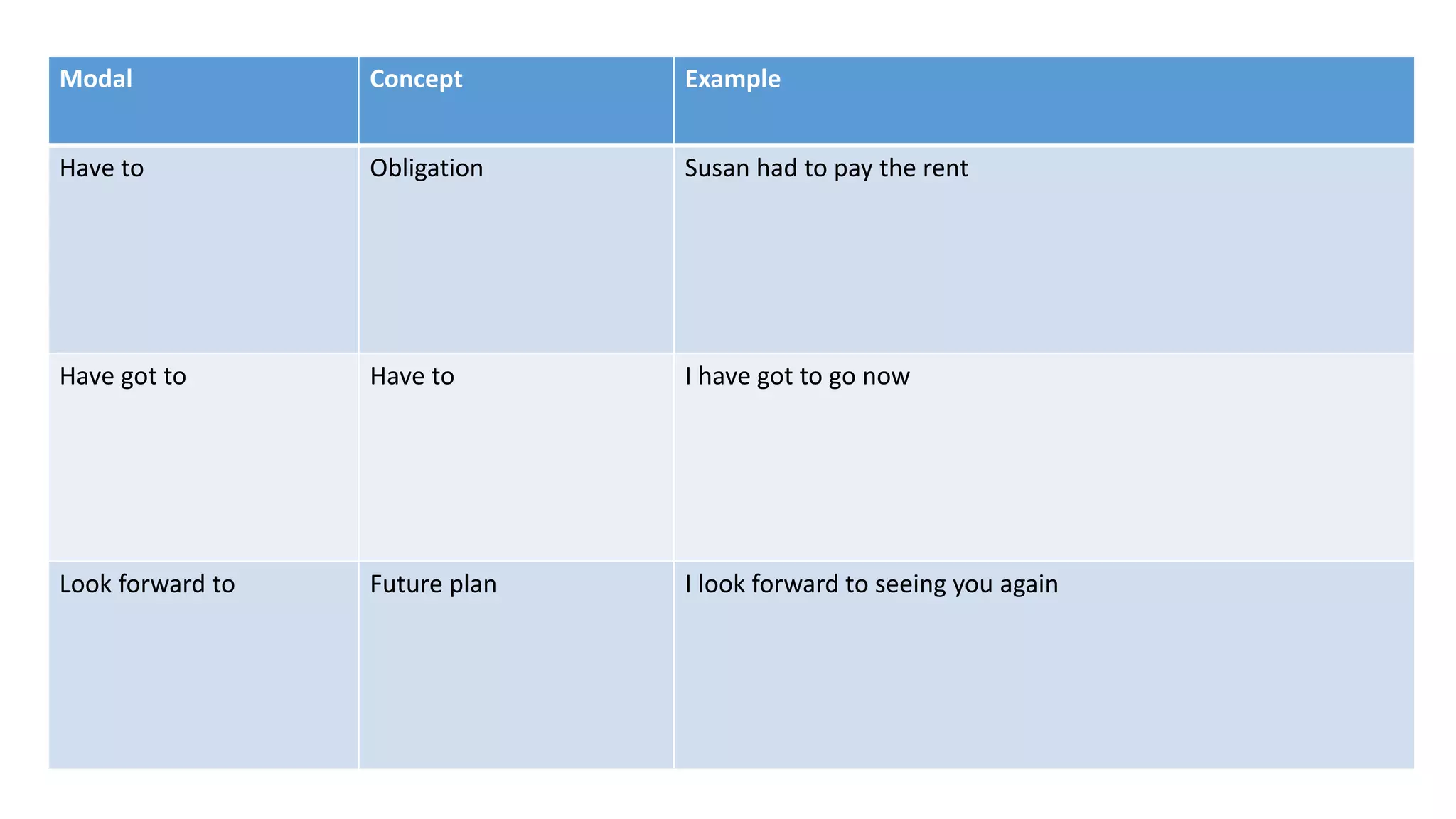
Modal verbs provide additional meaning to the main verb of a sentence by expressing ideas like ability, permission, obligation, or possibility. The common modal verbs in English are can, could, shall, should, will, would, may, might, must. Modal verbs do not change form or require auxiliary verbs. They are followed by the base form of the main verb. Modal verbs can express single or double meanings depending on context and can also be used in the past tense with "have" to talk about past possibilities, obligations, or abilities.