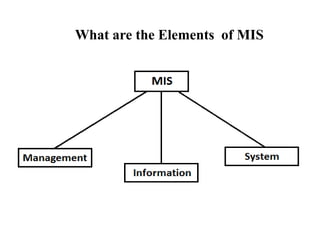
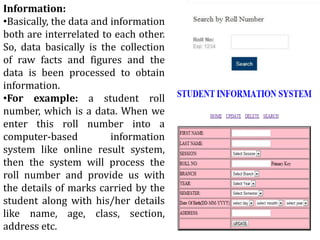
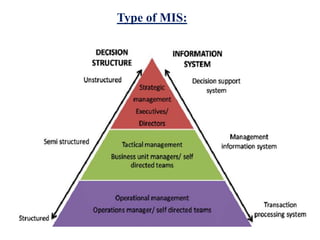
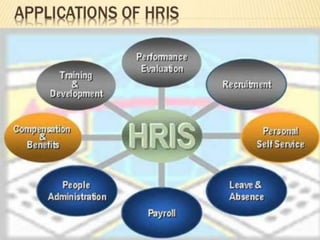
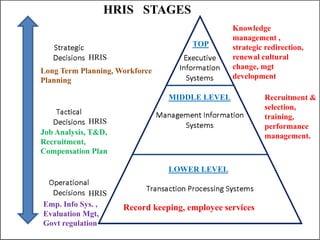
Management information system is a system designed to provide organizational levels with information to assist in analyzing, planning, controlling and decision-making. It involves people, equipment, procedures, documents and communications that collect, validate, operate, store, retrieve and present data to aid in planning, budgeting, accounting, controlling, organizing and decision making. An MIS gathers data from transaction processing systems and uses it to provide reports and additional insights to tactical managers. Decision support systems then use input from internal systems like MIS and external sources to help senior management with non-routine decisions.