This document analyzes Microsoft's shareholder equity between 1994-2000 when the company grew rapidly. It discusses several key points:
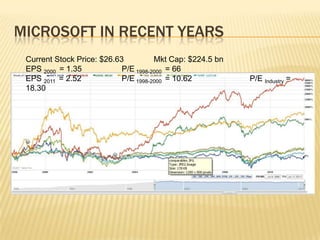
1. Microsoft's revenue grew 700% and earnings grew 1200% during this period, with its stock price peaking between $36-120 per share.
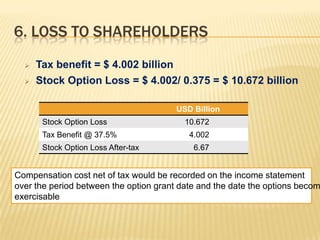
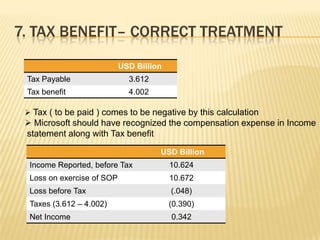
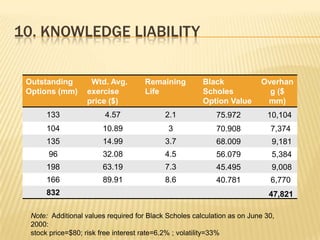
2. Microsoft used stock options extensively to attract talent, but GAAP accounting did not report this significant cost as an expense or liability.
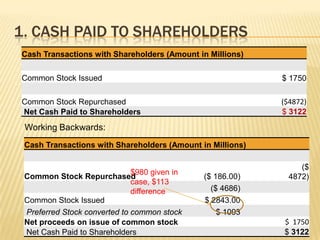
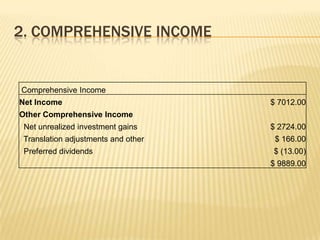
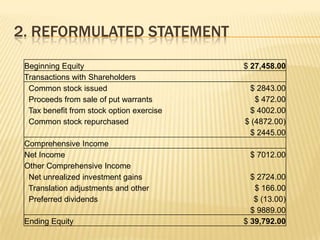
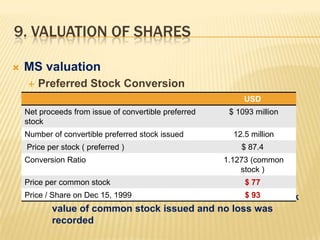
3. Various issues are analyzed including cash paid to shareholders, comprehensive income calculation, dilution from stock options, and proper valuation of shares given stock option treatment.
4. The quality of Microsoft's reported income and share valuations during this period are questionable given the underreporting of significant