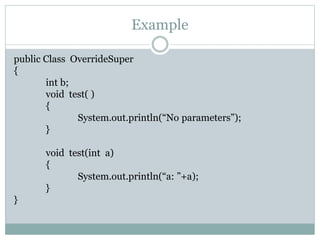
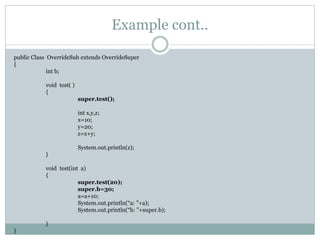
Method overriding allows a subclass to provide a specific implementation of a method that is already provided by its superclass. The subclass method must have the same name, parameters and return type as the superclass method. This allows the subclass to modify the behavior as needed and is how polymorphism is implemented. The super keyword can be used to call the superclass method from the overriding method.


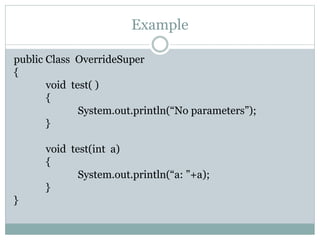
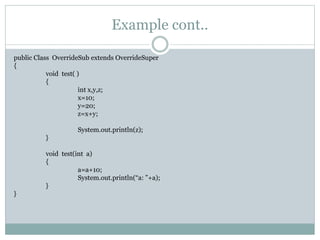
![Example Cont..
public class OverrideDriver
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
OverrideSuper o=new OverrideSuper( );
o.test( );
o.test(10);
OverrideSub s=new OverrideSub( );
s.test( );
s.test(10);
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/methodoverriding-140610124202-phpapp02/85/Method-overriding-5-320.jpg)

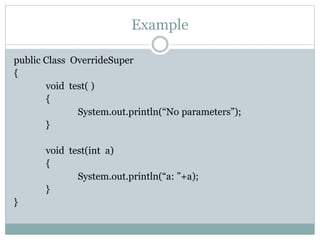
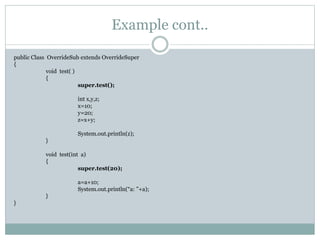
![Example cont..
public class OverrideDriver
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
OverrideSuper o=new OverrideSuper( );
o.test( );
o.test(10);
OverrideSub s=new OverrideSub( );
s.test( );
s.test(10);
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/methodoverriding-140610124202-phpapp02/85/Method-overriding-9-320.jpg)

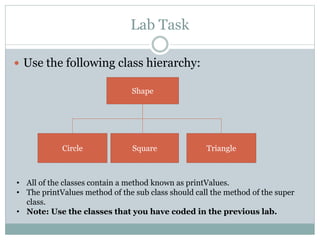
![Example cont..
public class OverrideDriver
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
OverrideSuper o=new OverrideSuper( );
o.test( );
o.test(10);
OverrideSub s=new OverrideSub( );
s.test( );
s.test(10);
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/methodoverriding-140610124202-phpapp02/85/Method-overriding-13-320.jpg)

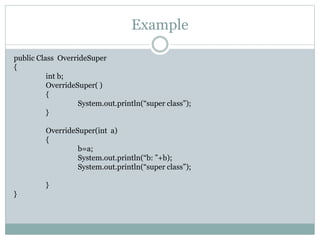
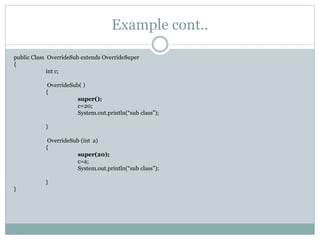
![Example cont..
public class OverrideDriver
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
OverrideSuper o=new OverrideSuper( );
OverrideSuper o=new OverrideSuper(30 );
OverrideSub s=new OverrideSub( );
OverrideSub s=new OverrideSub(40 );
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/methodoverriding-140610124202-phpapp02/85/Method-overriding-18-320.jpg)
