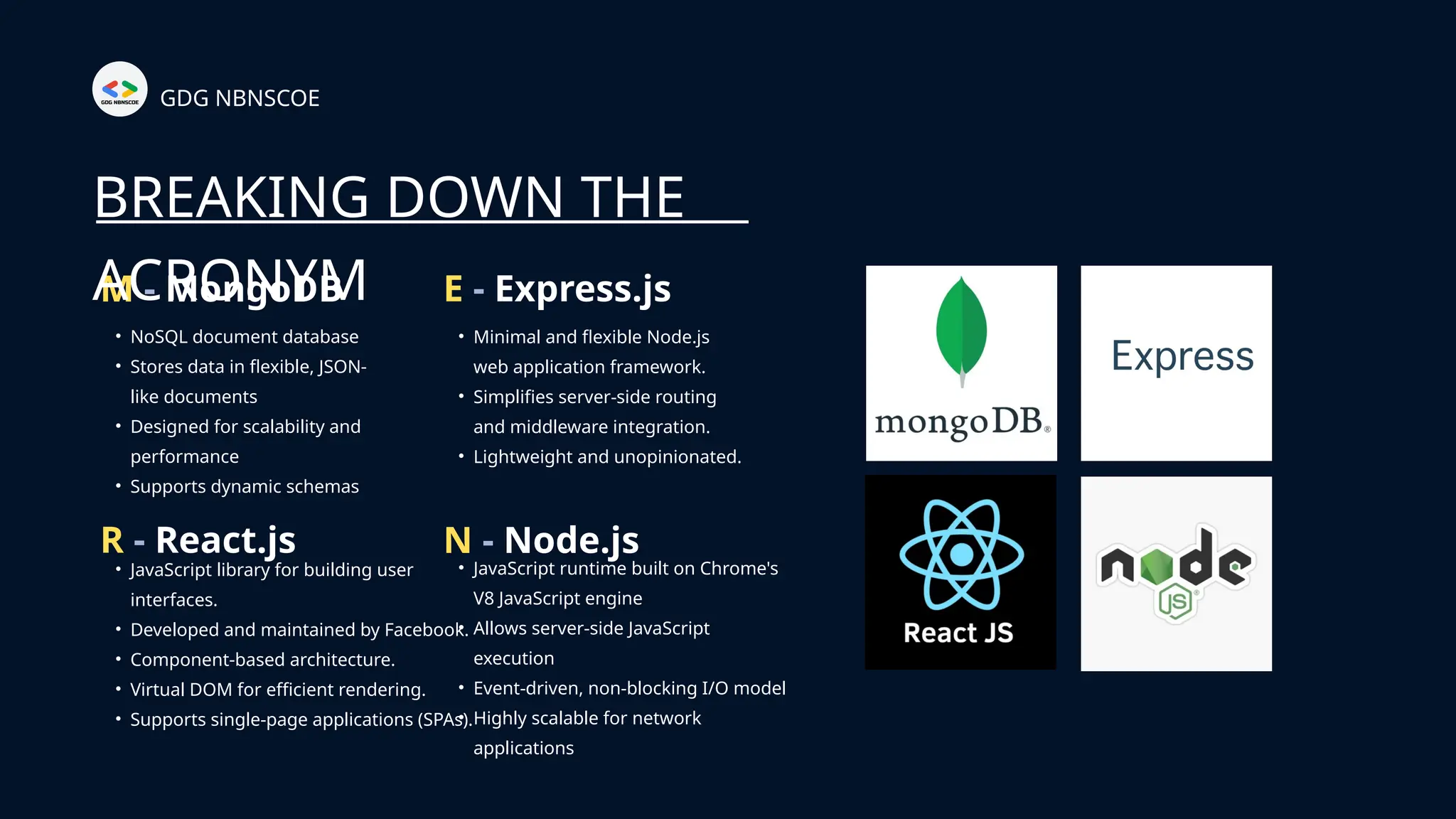
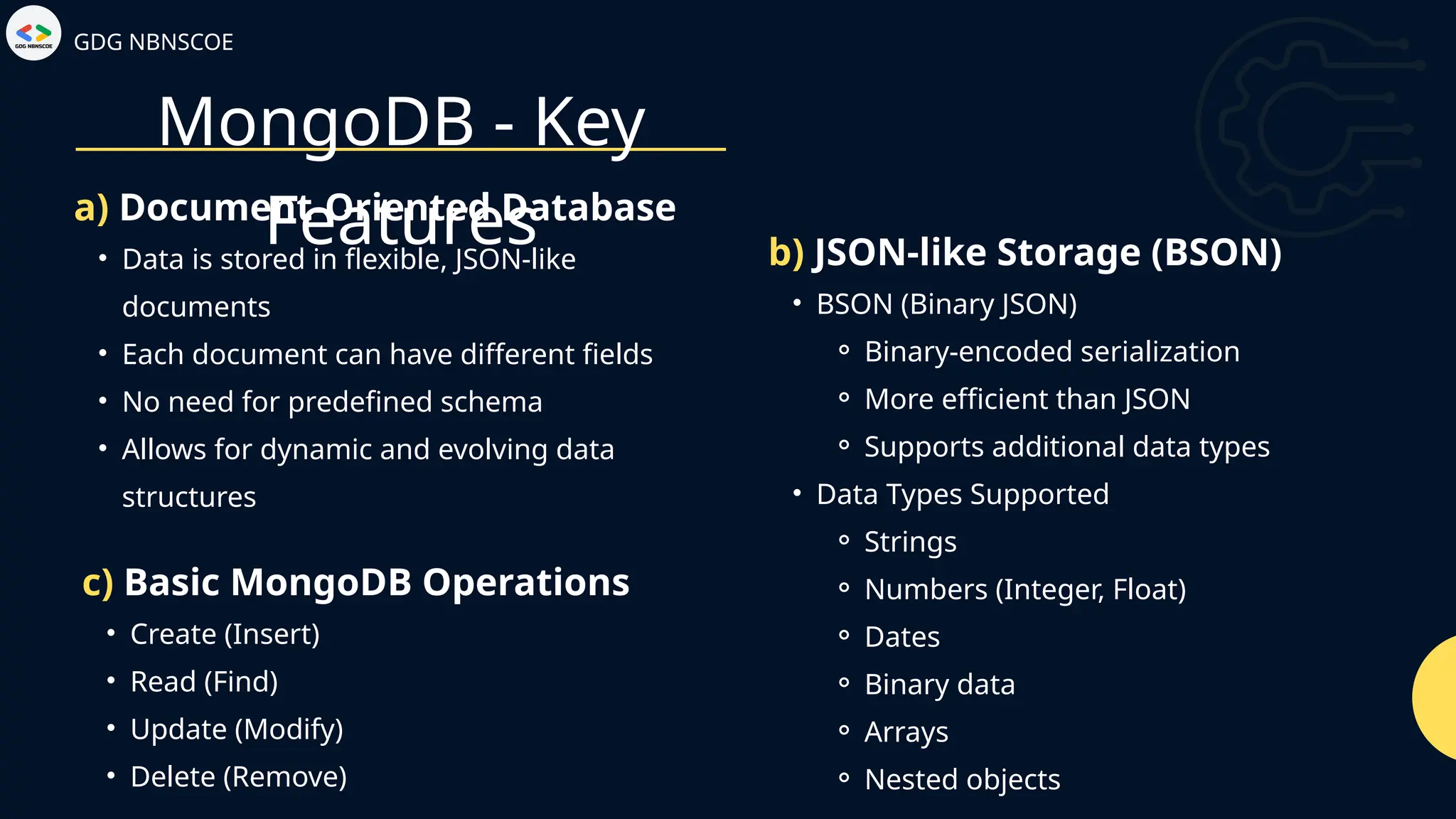
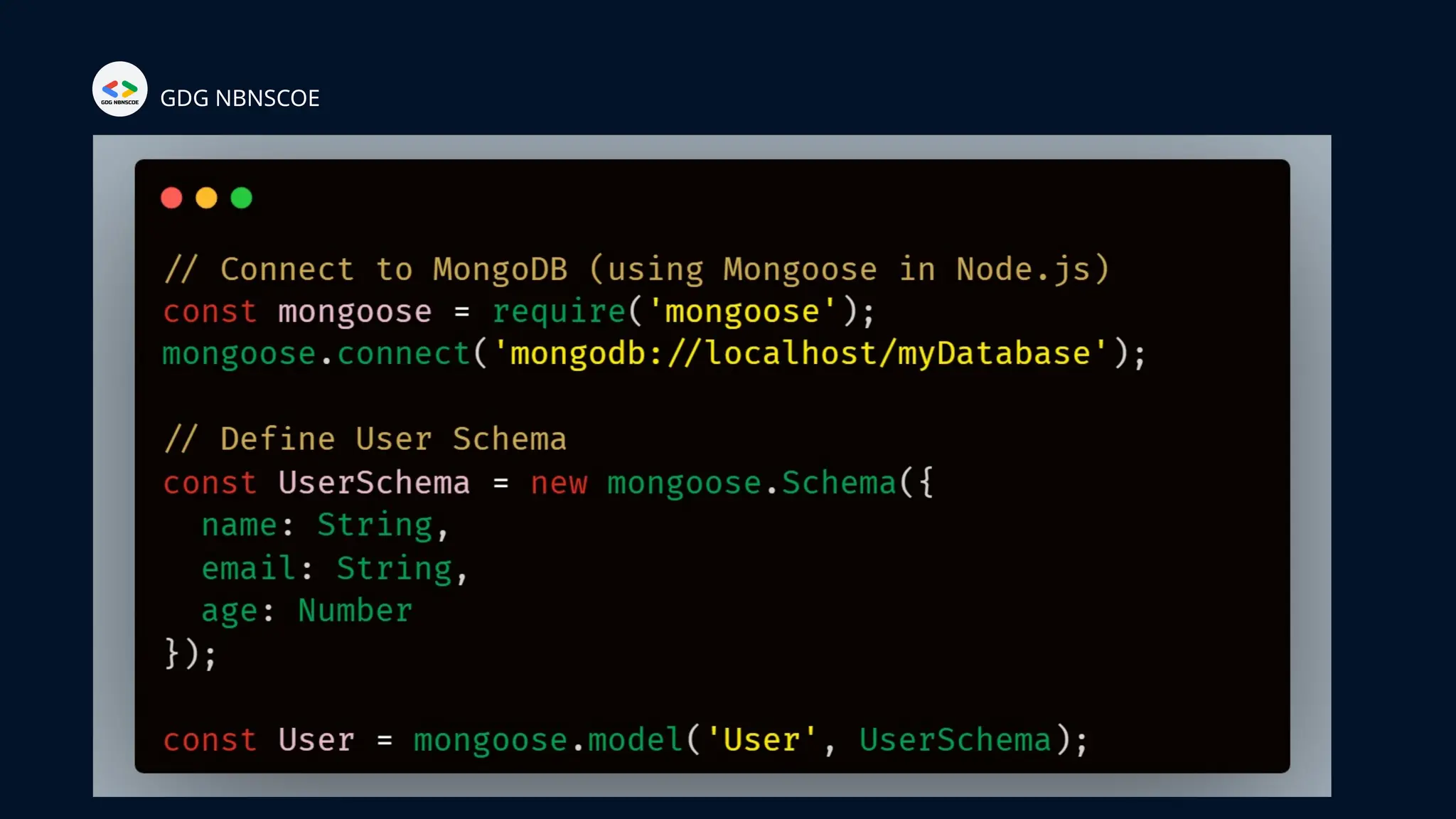
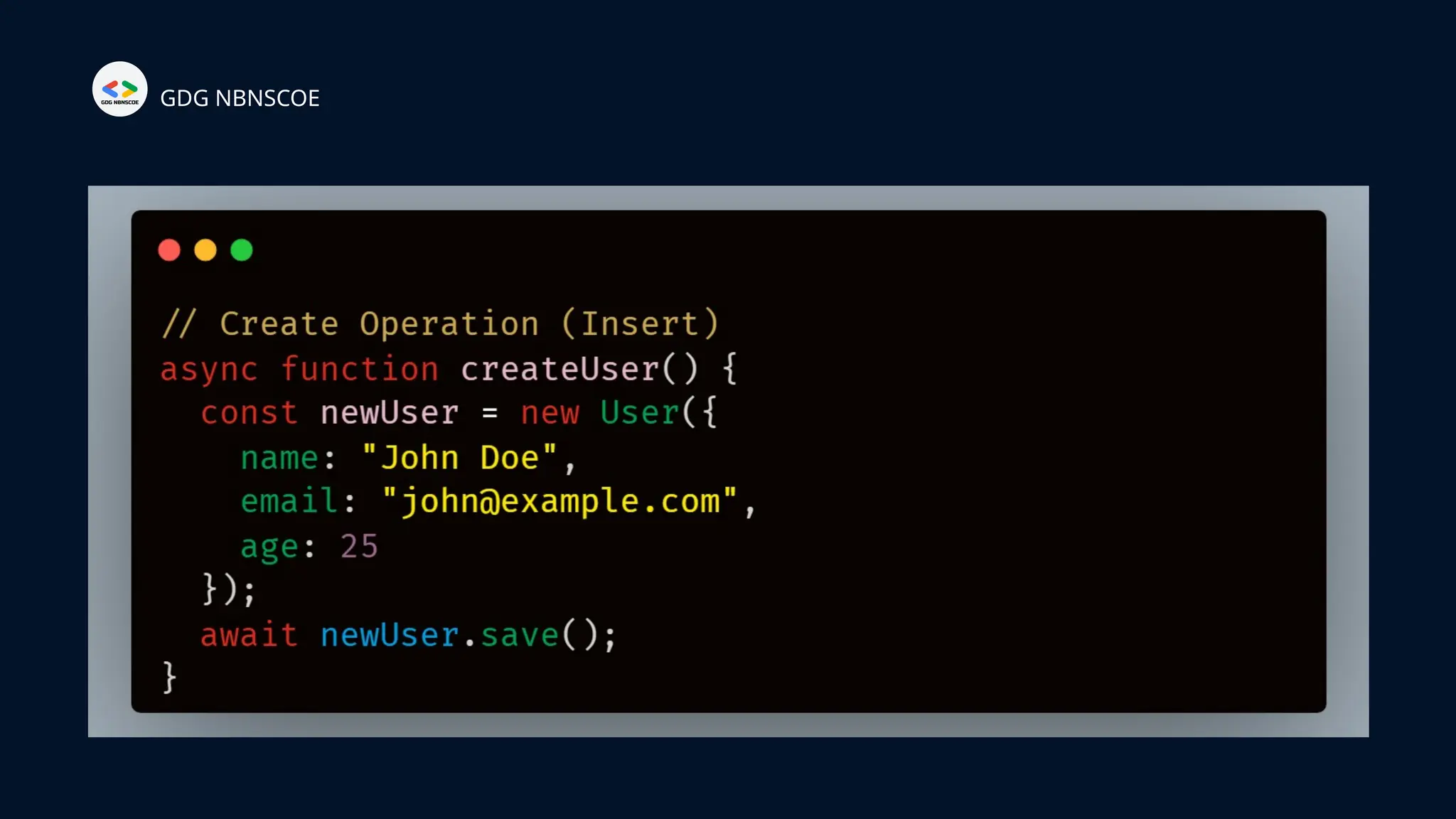
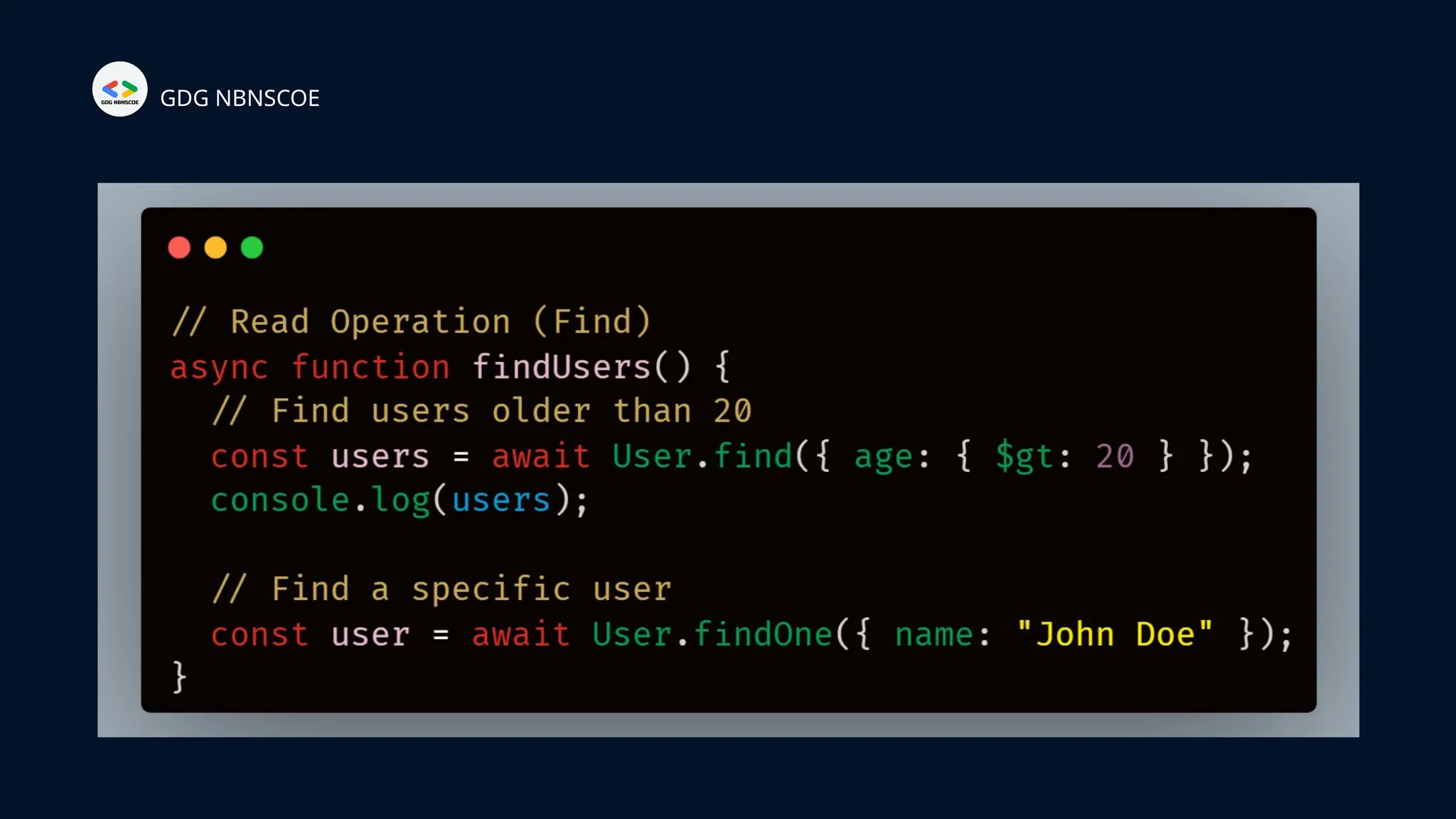
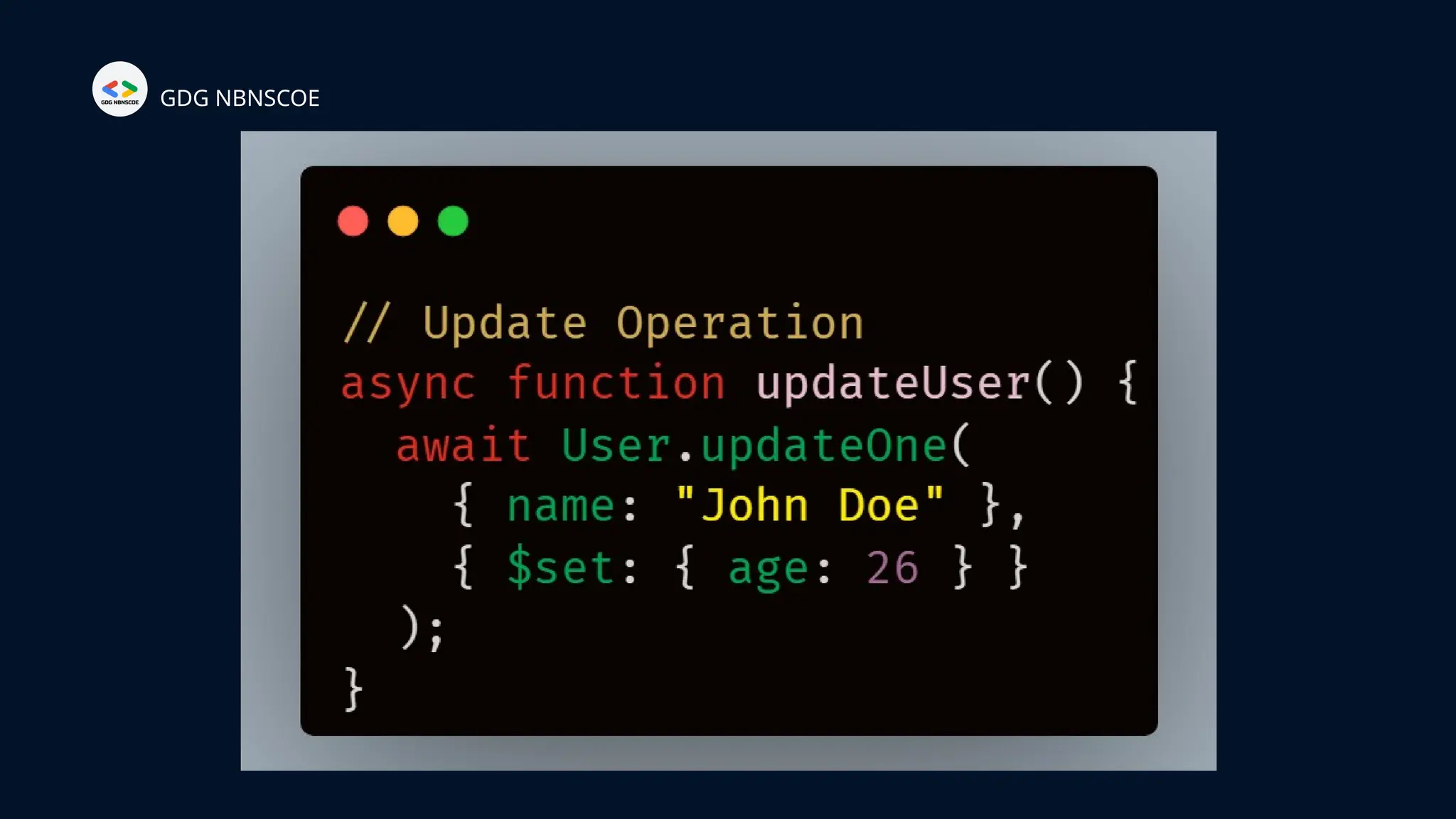
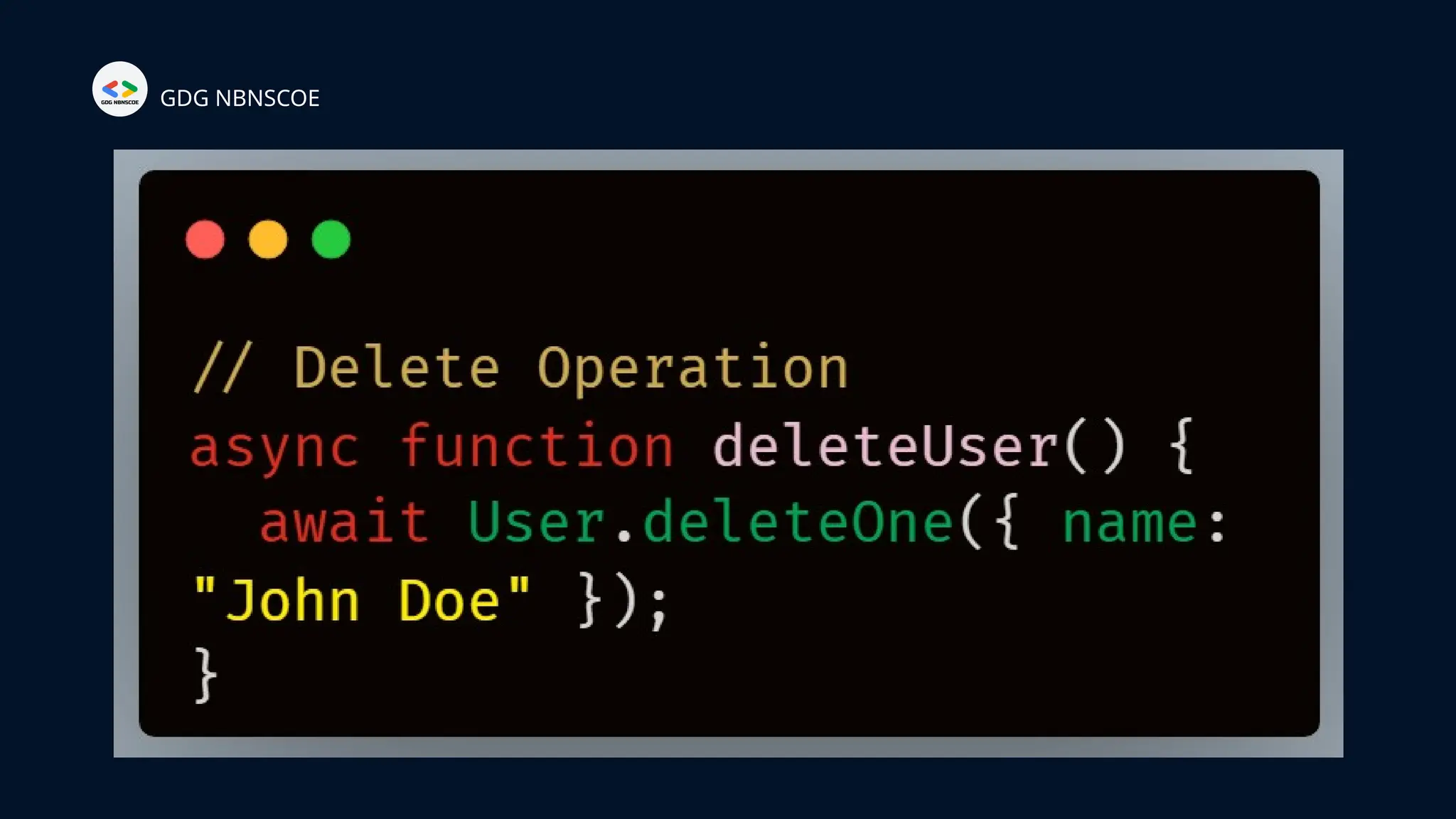
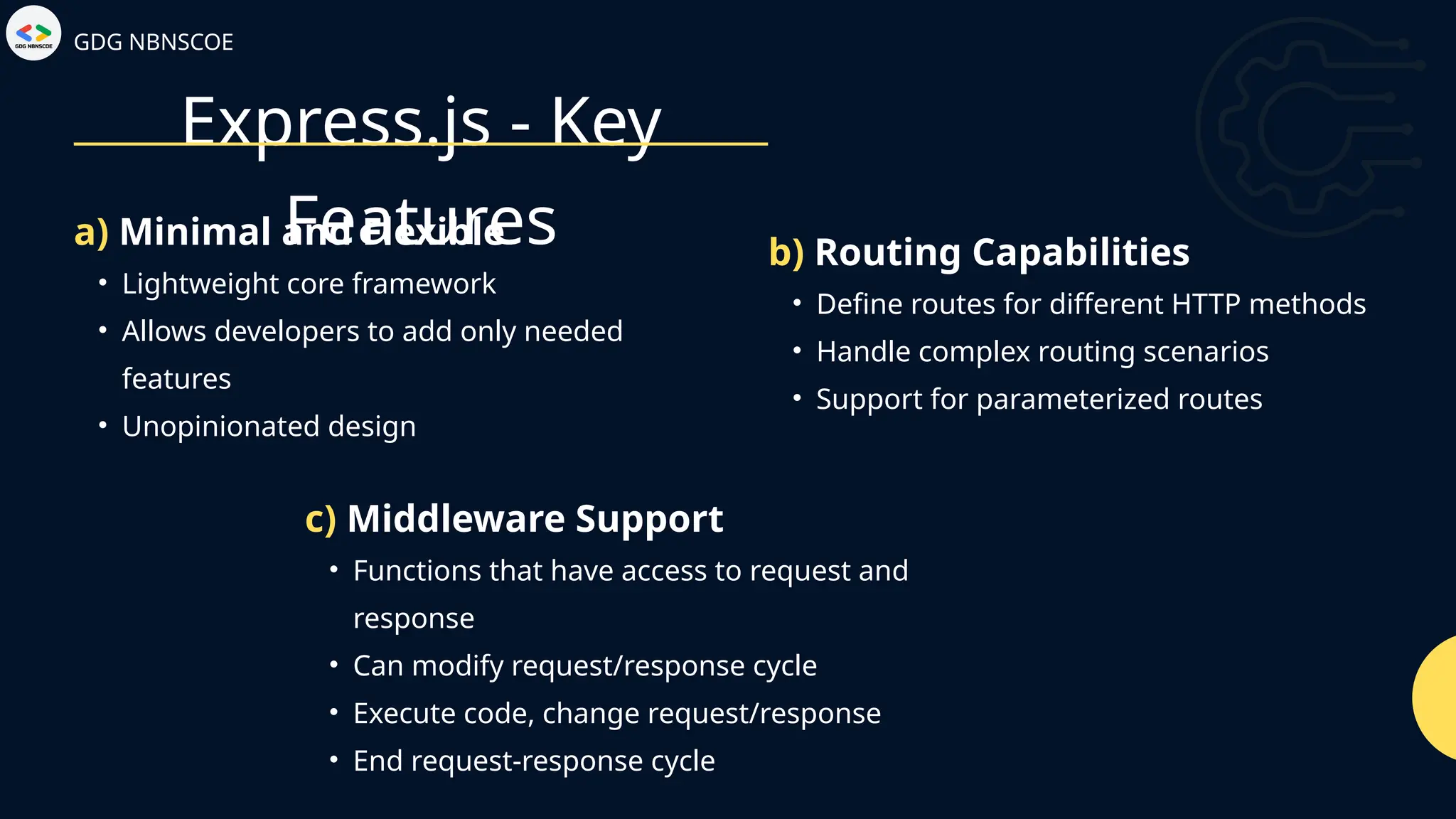
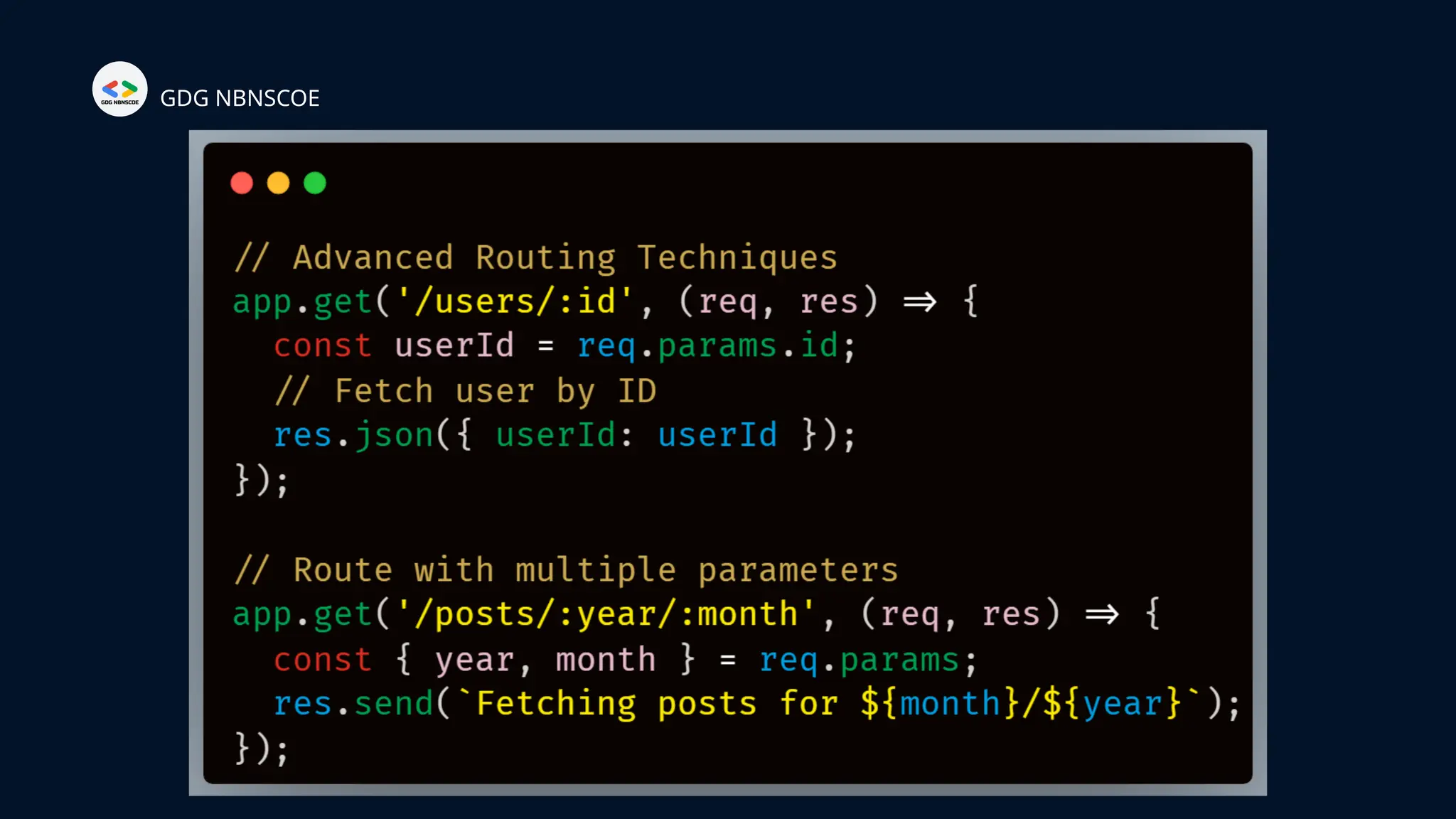
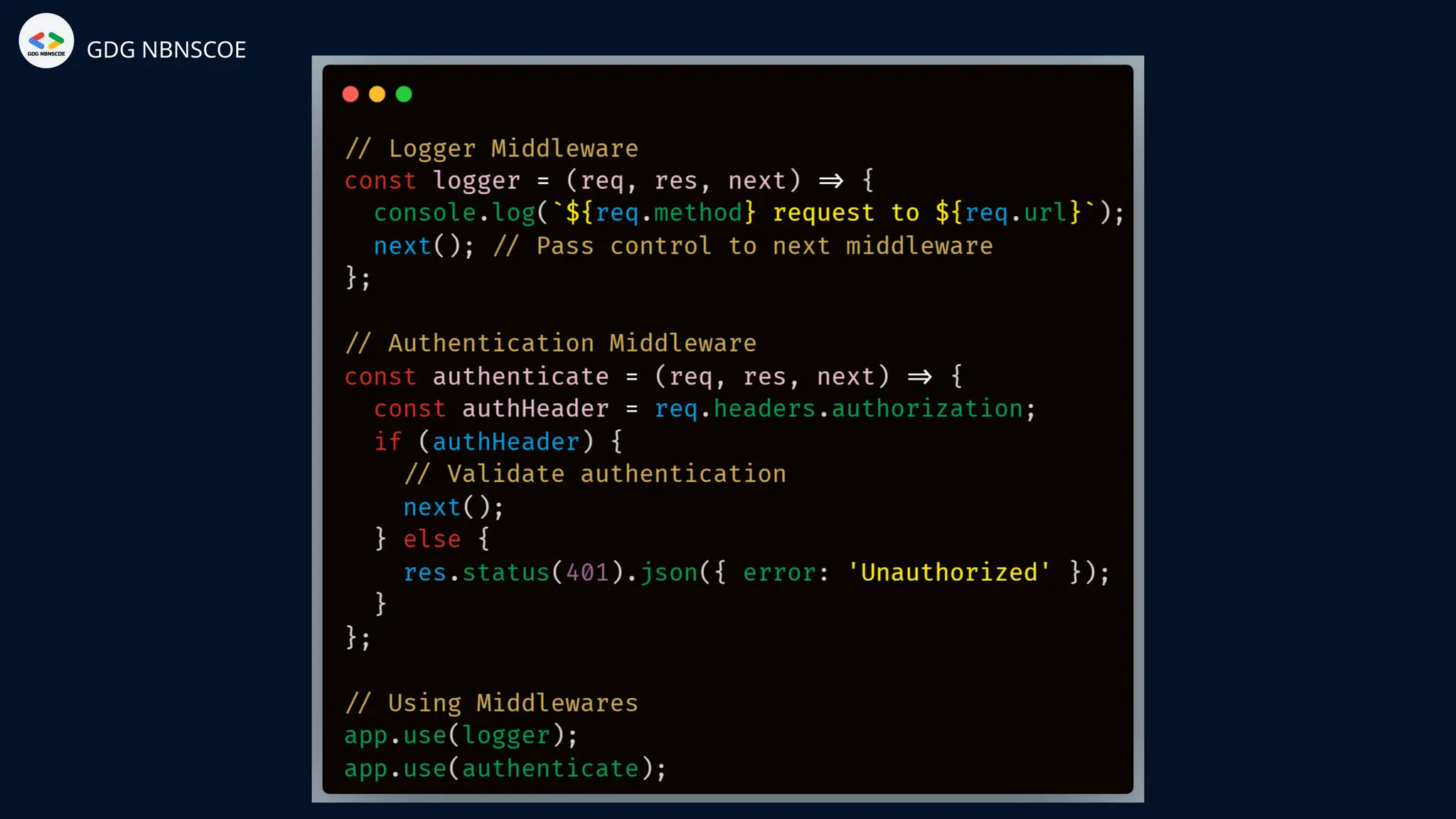
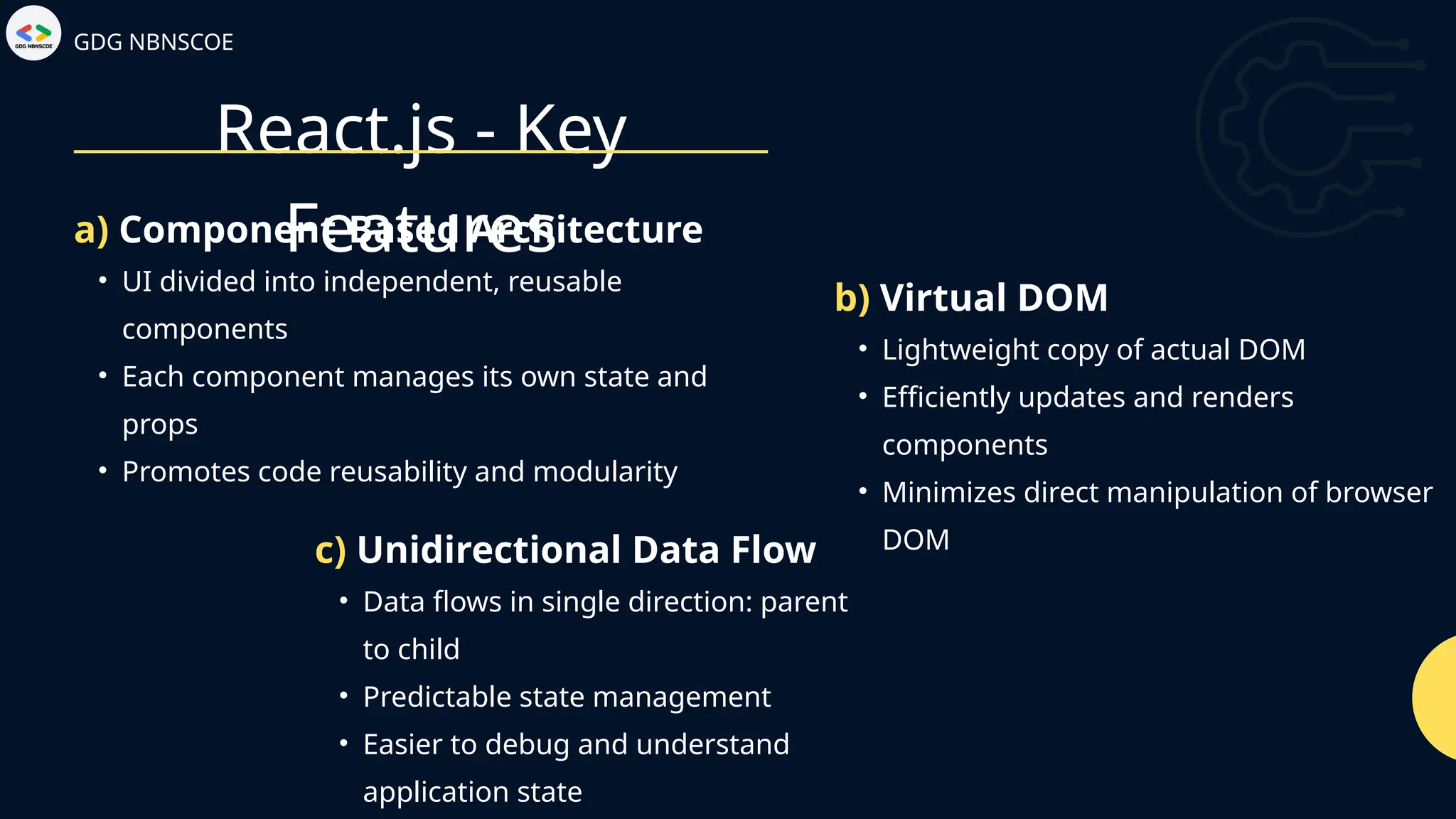
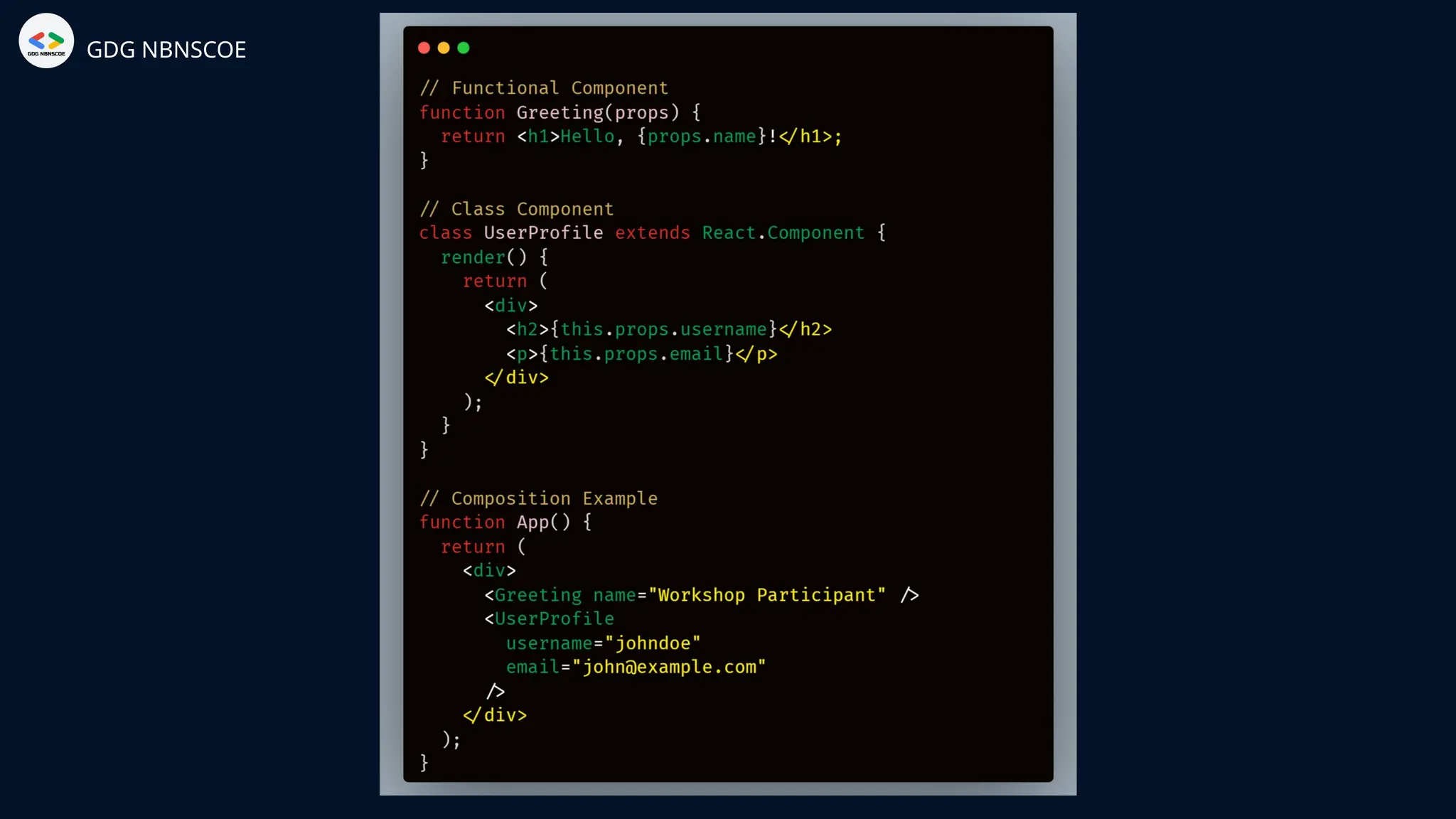
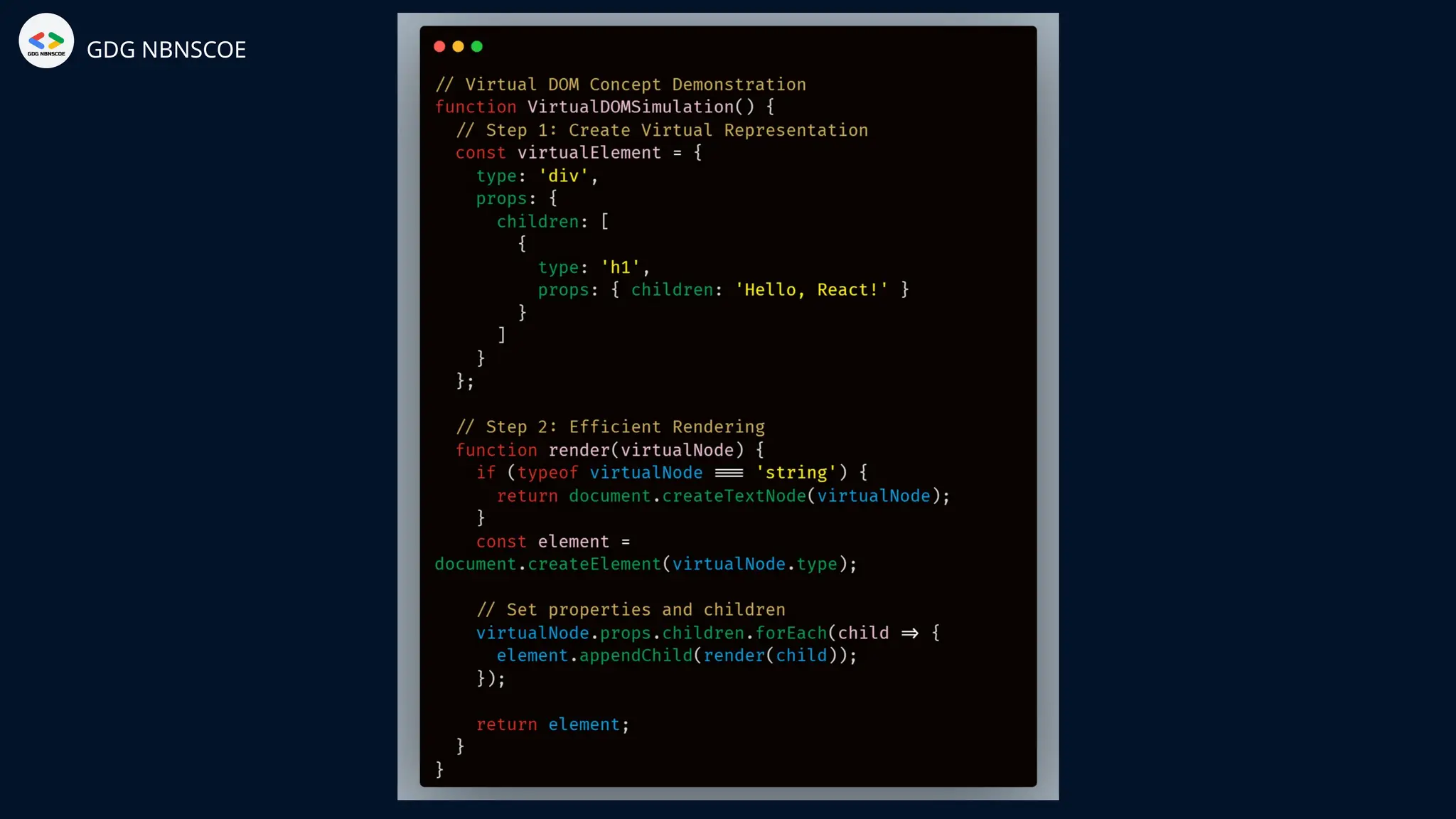
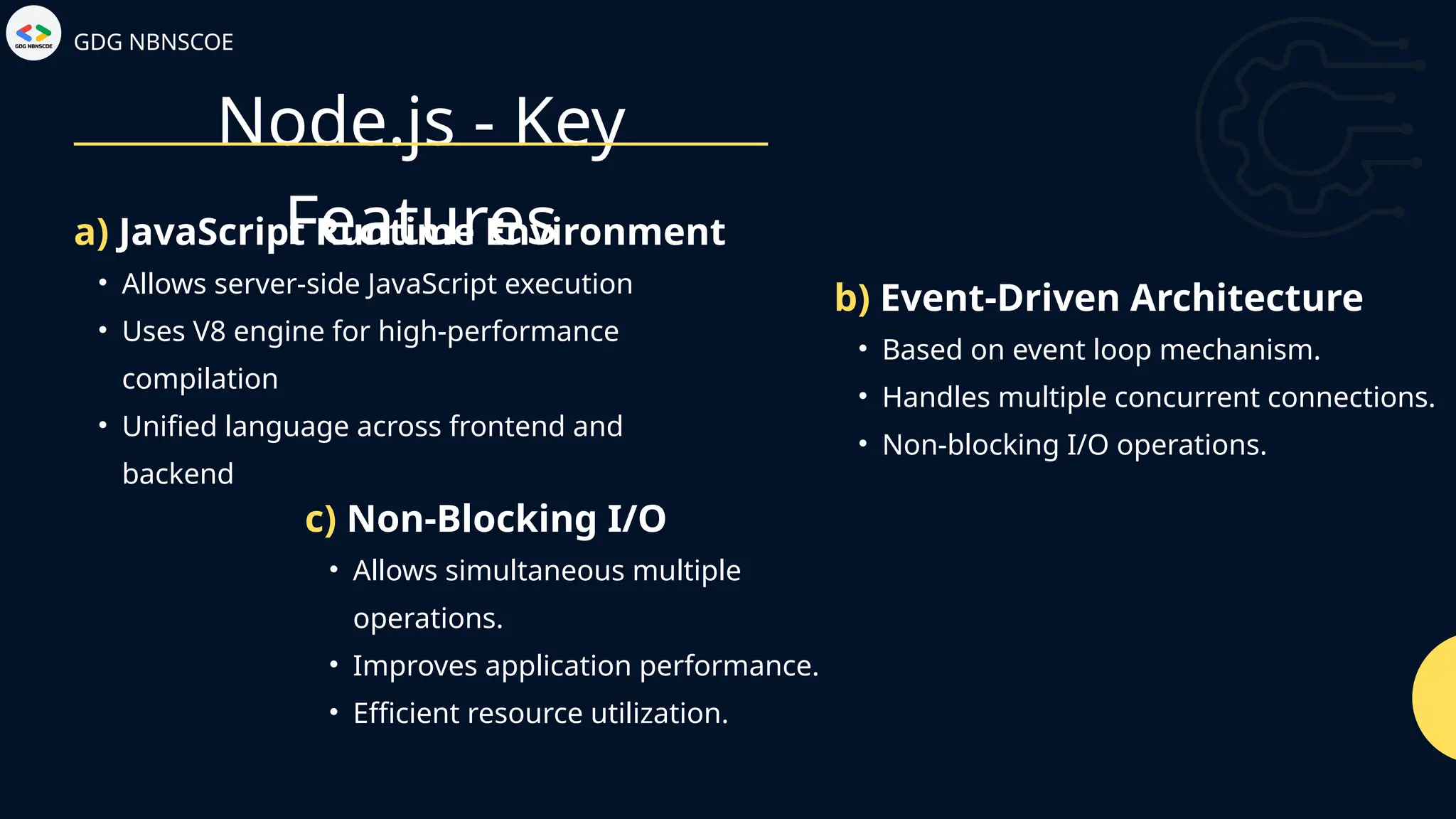
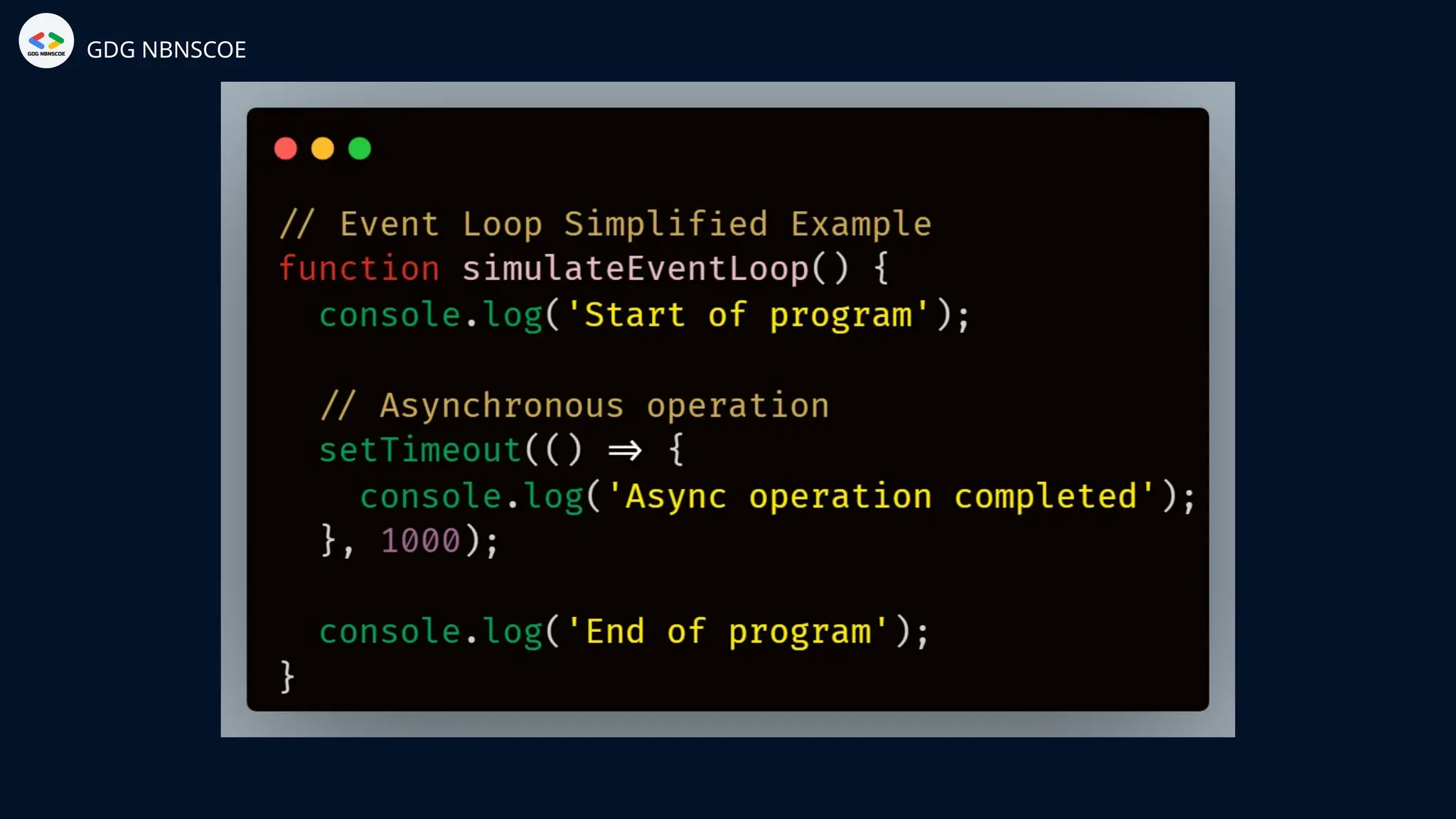
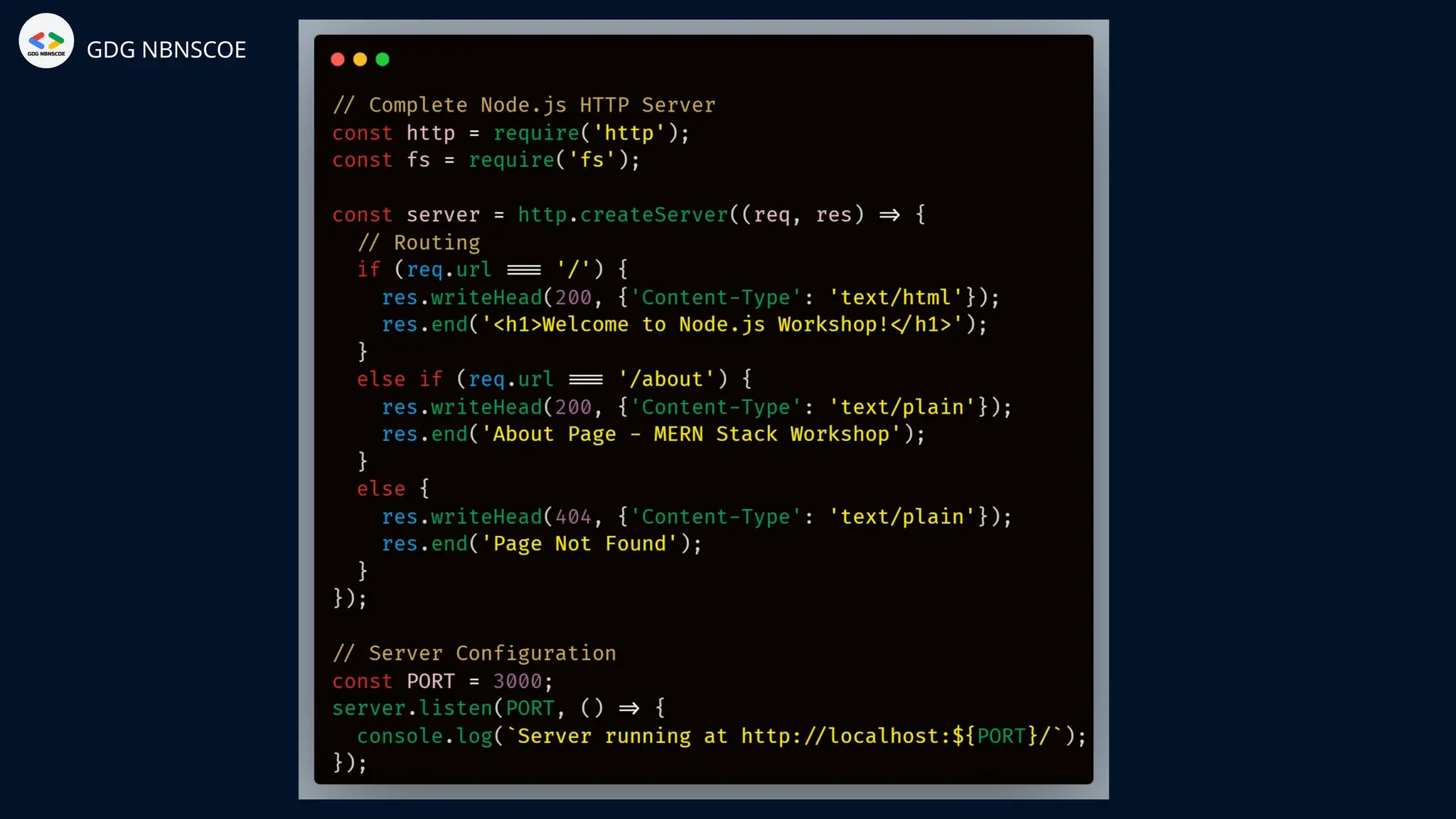
The document is a beginner's guide to MERN stack development, outlining essential components including frontend technologies (HTML, CSS, JavaScript), backend logic (Node.js, Express.js), and database management (MongoDB). It highlights the advantages of using the MERN stack such as a unified language, flexibility, and scalability, making it suitable for a range of applications from startups to large enterprises. The presentation emphasizes the importance of consistent practice and learning to thrive in modern web development.