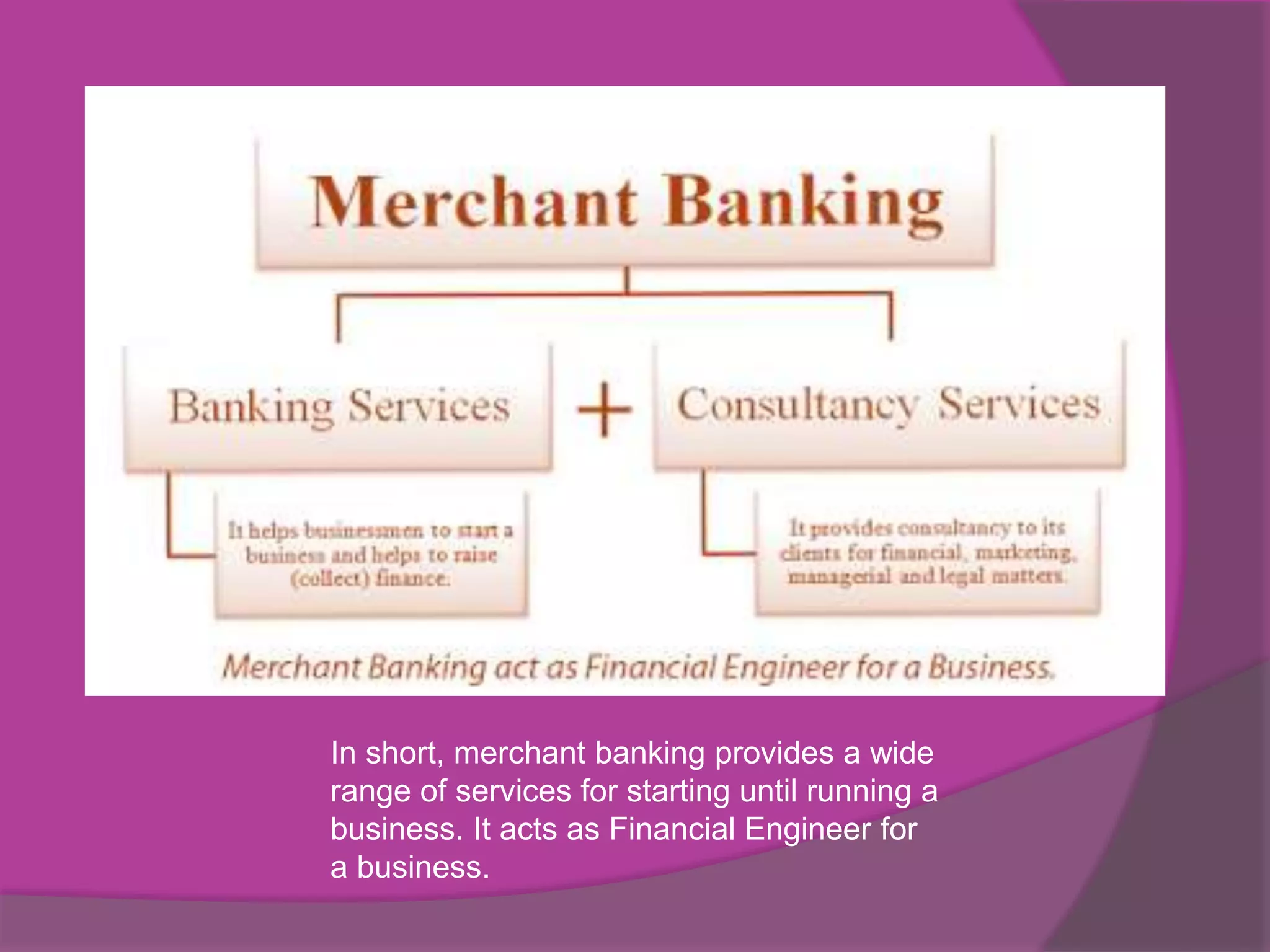
Merchant banking is a specialized financial service that combines banking and consultancy, focusing on large corporations and wealthy individuals to provide advice on finance, marketing, and legal matters. Originating in Europe and making its way to India in the late 20th century, merchant banks offer services such as issue management and mergers and acquisitions, possessing unique access to financial markets and institutions. While advantageous for large clients, merchant banking carries risks and is not suited for general public banking needs.