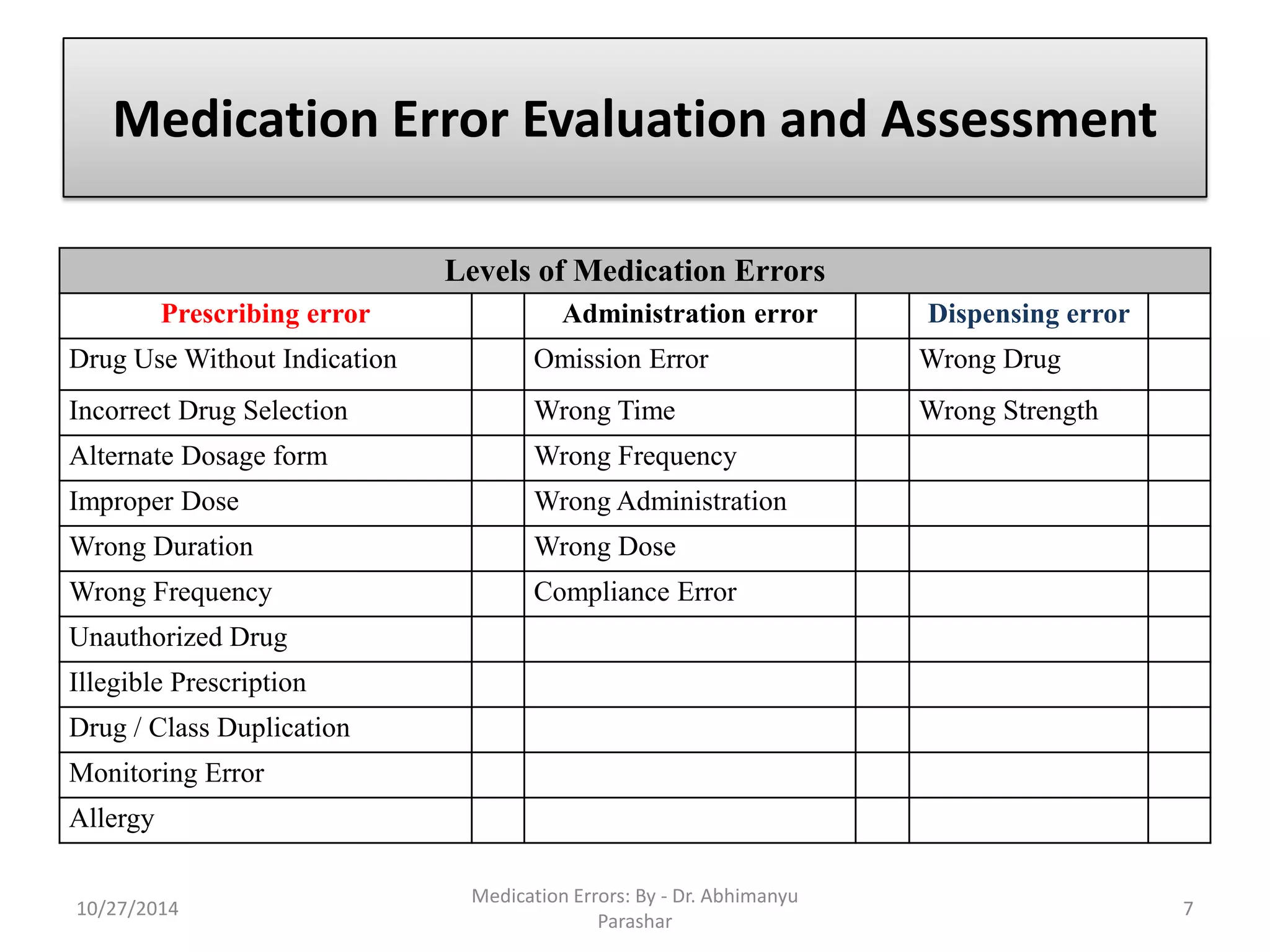
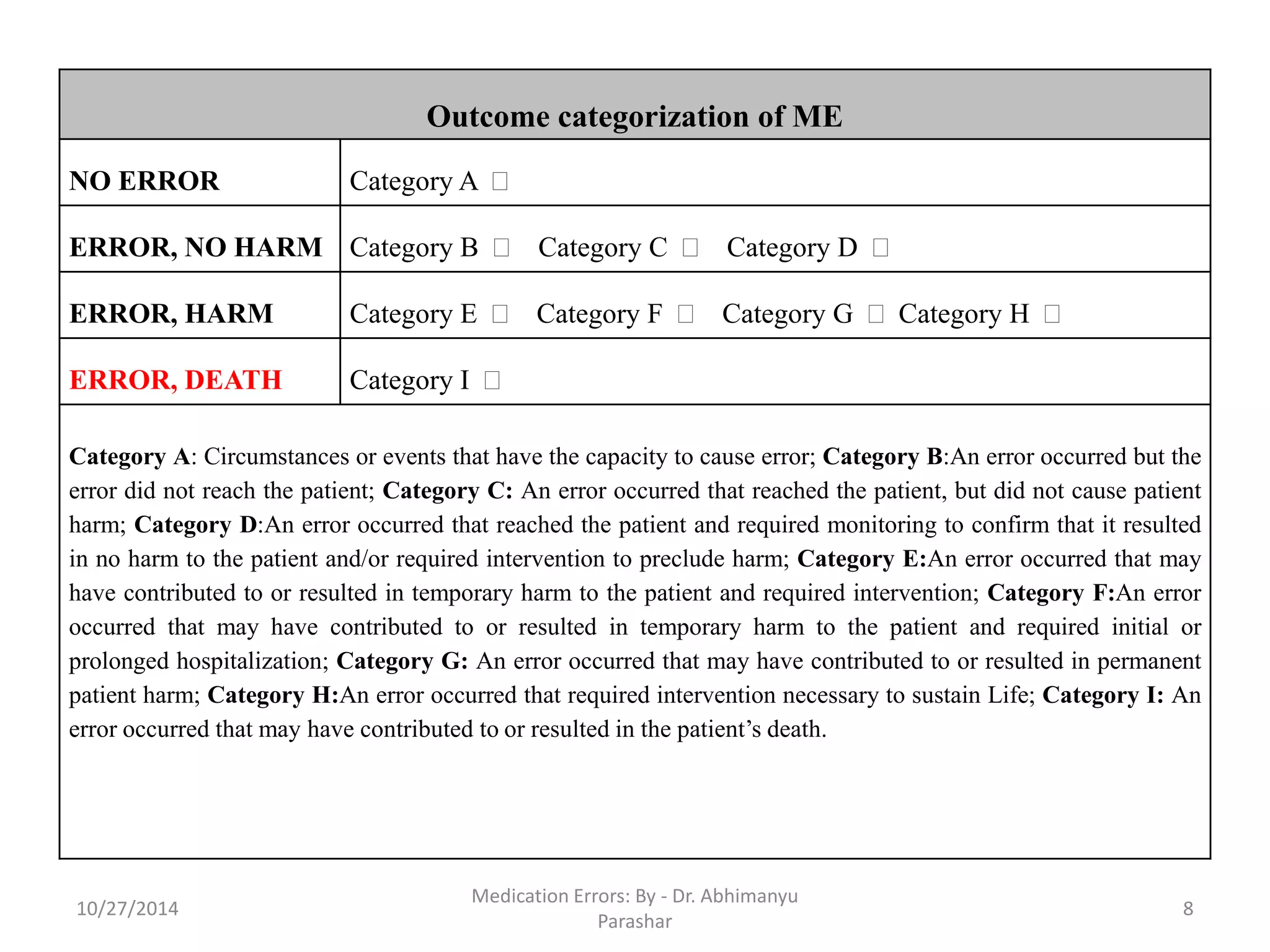
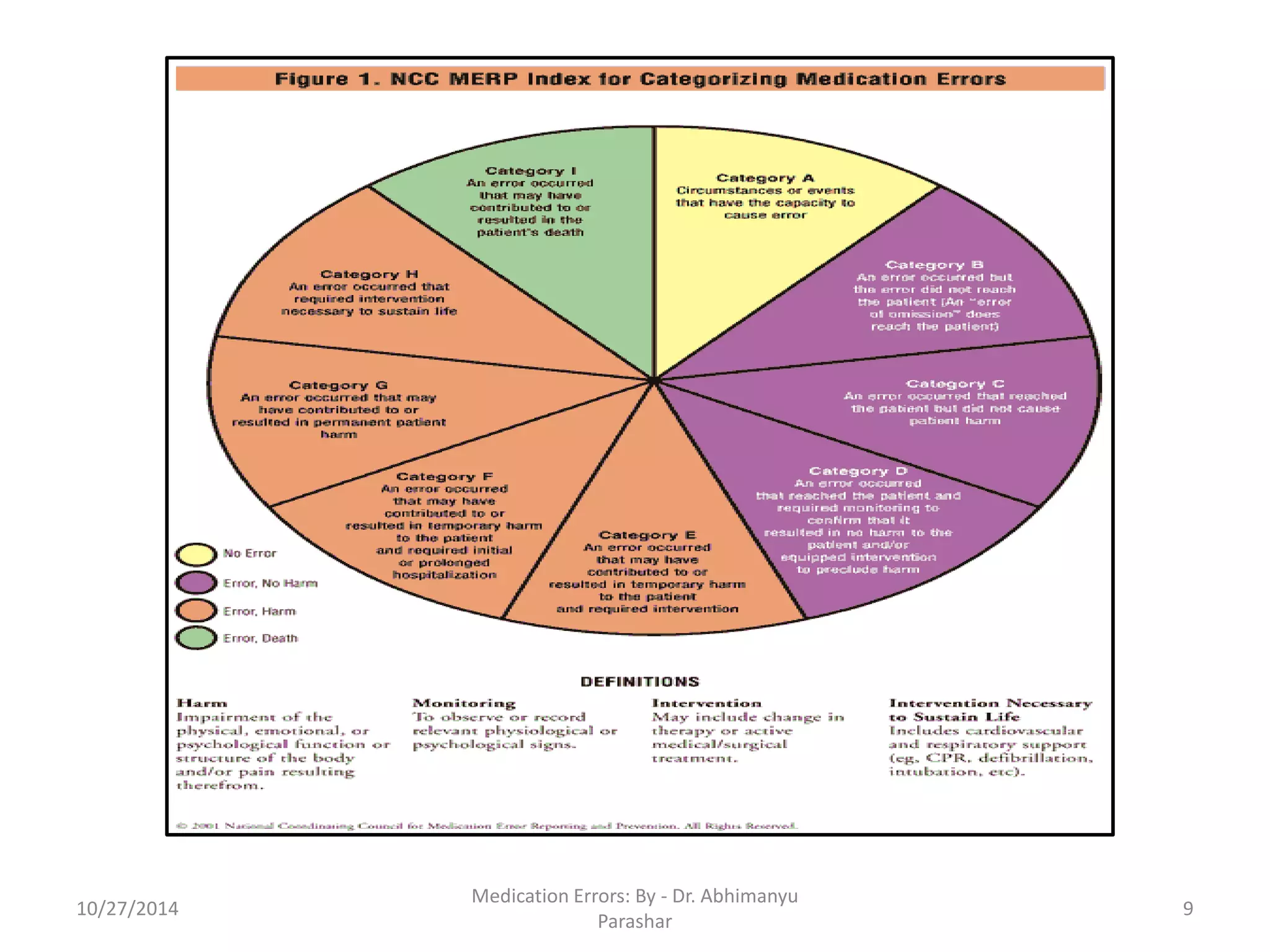
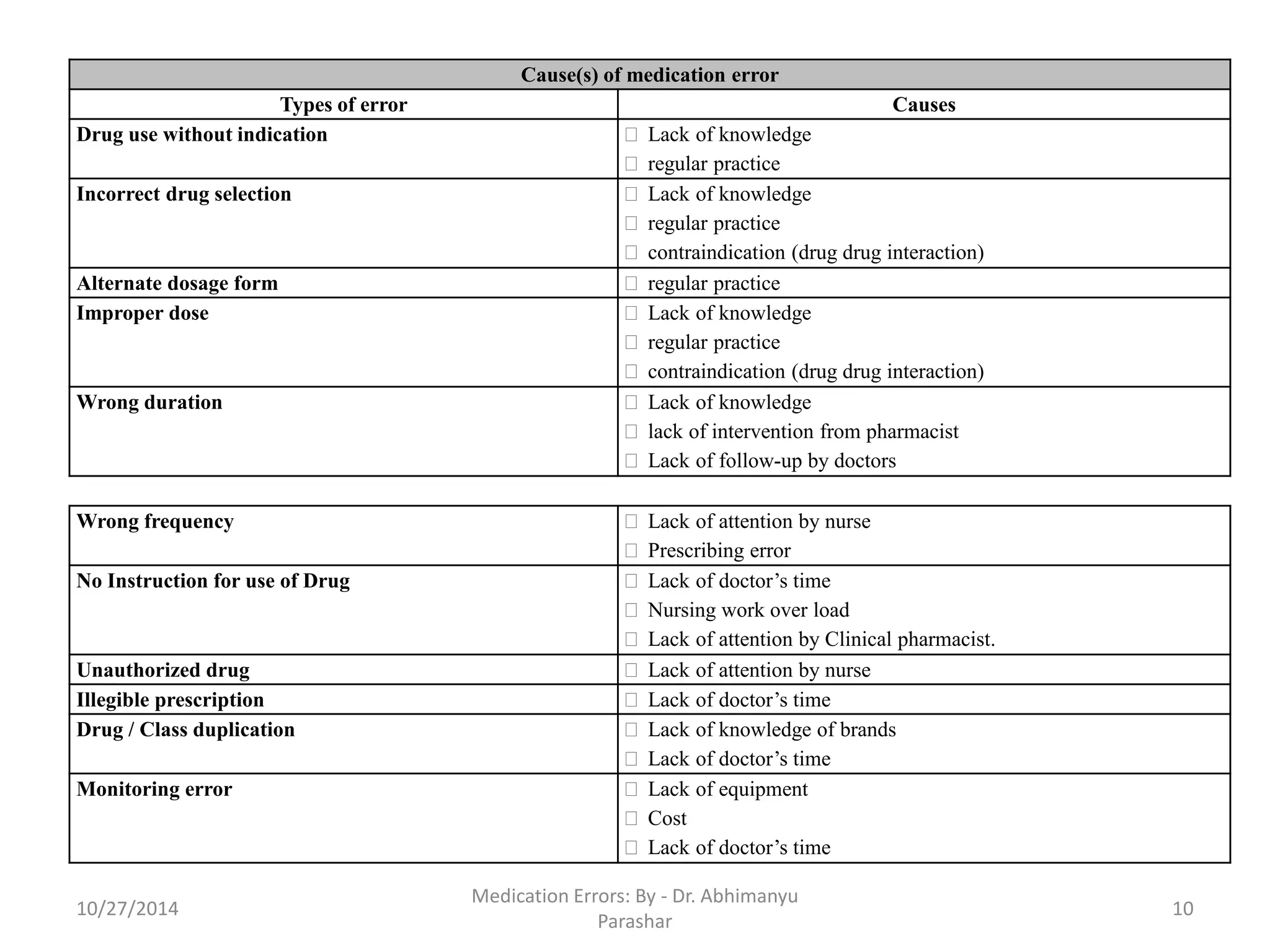
Medication errors are preventable events that can cause inappropriate medication use or harm to patients, occurring during various stages including prescribing, dispensing, and administration. Common causes include poor communication, illegible prescriptions, and incorrect drug information, which can lead to different types of errors. Prevention strategies focus on patient education, proper documentation, and leveraging electronic technologies.