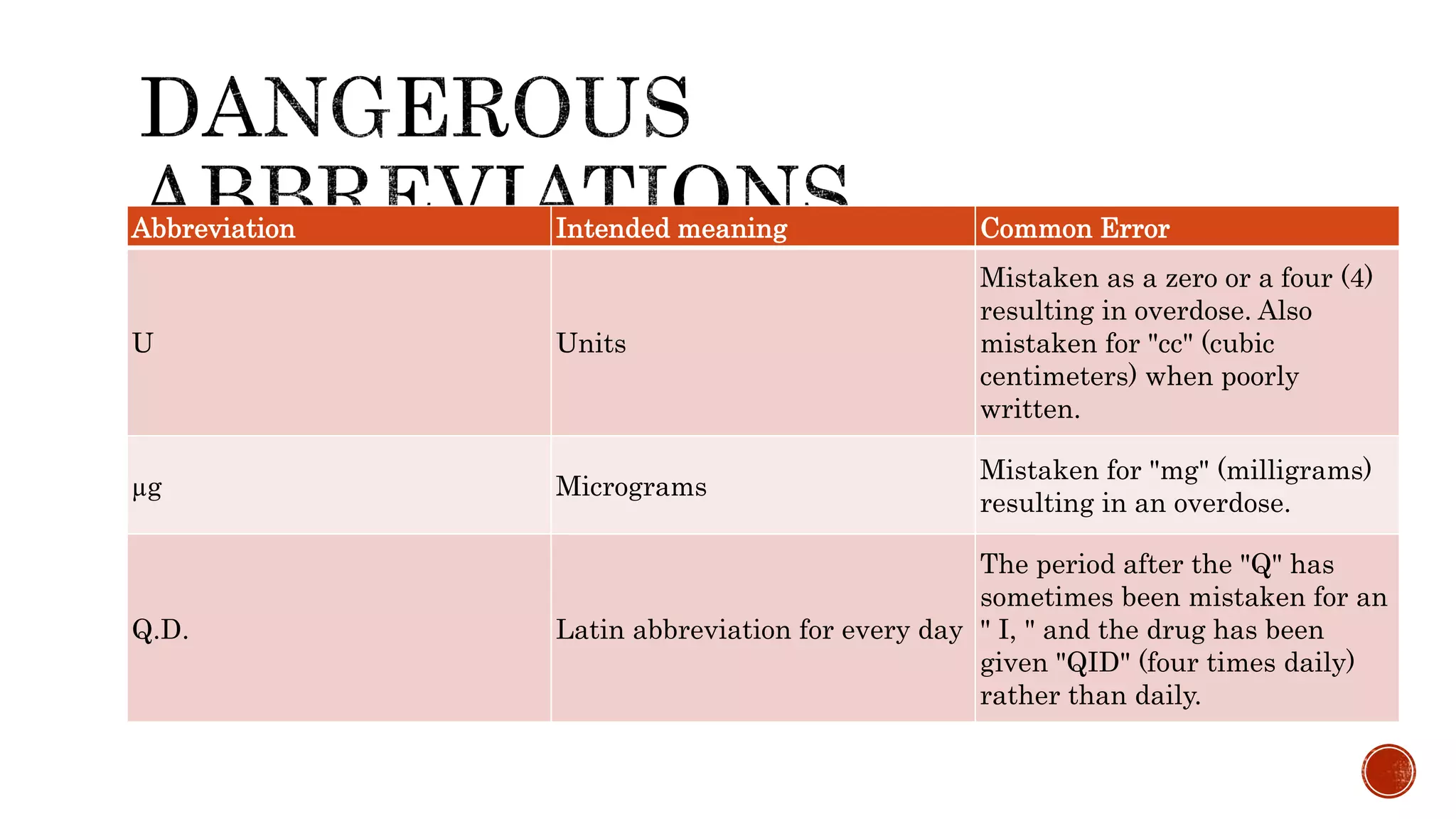
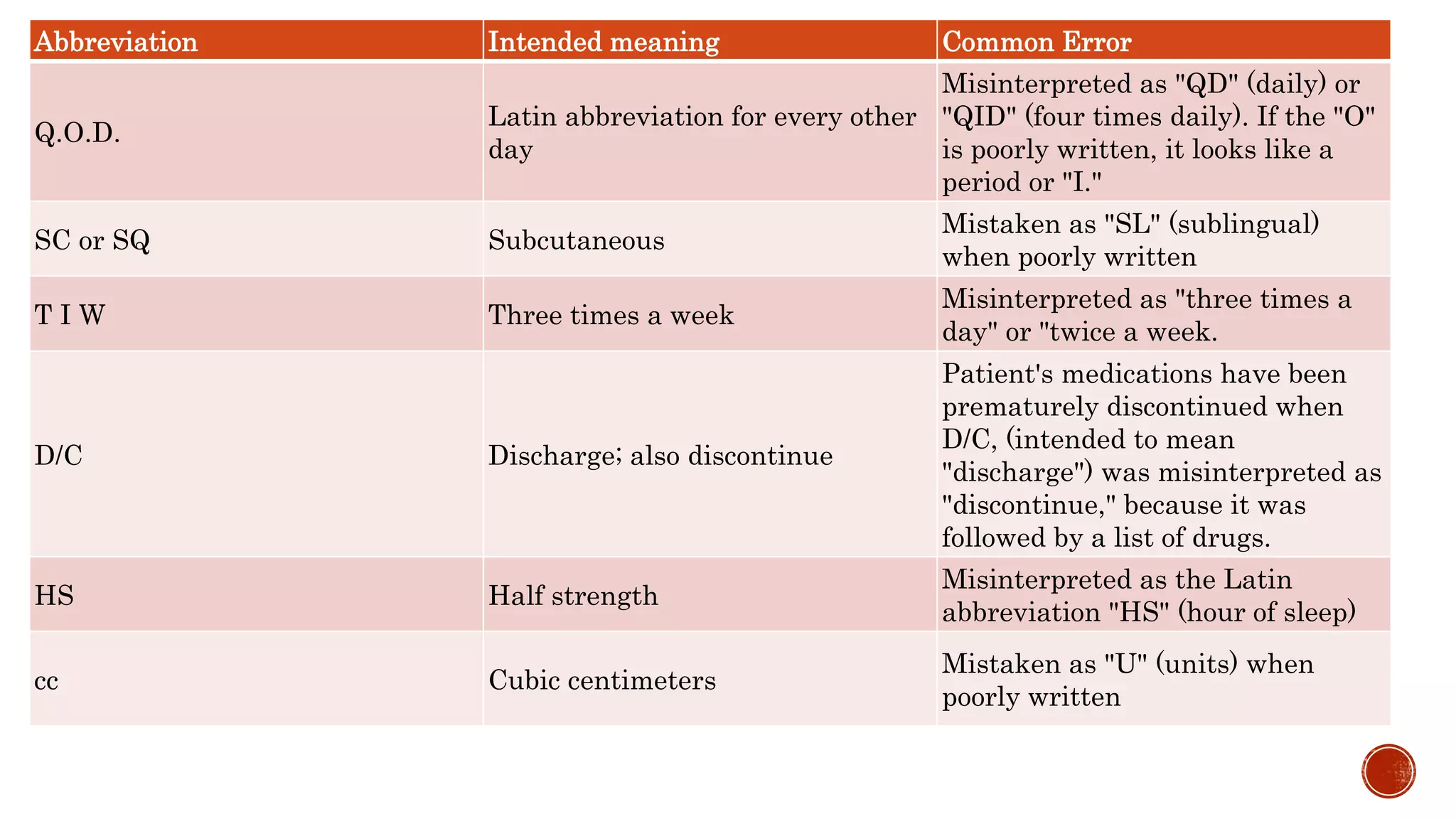
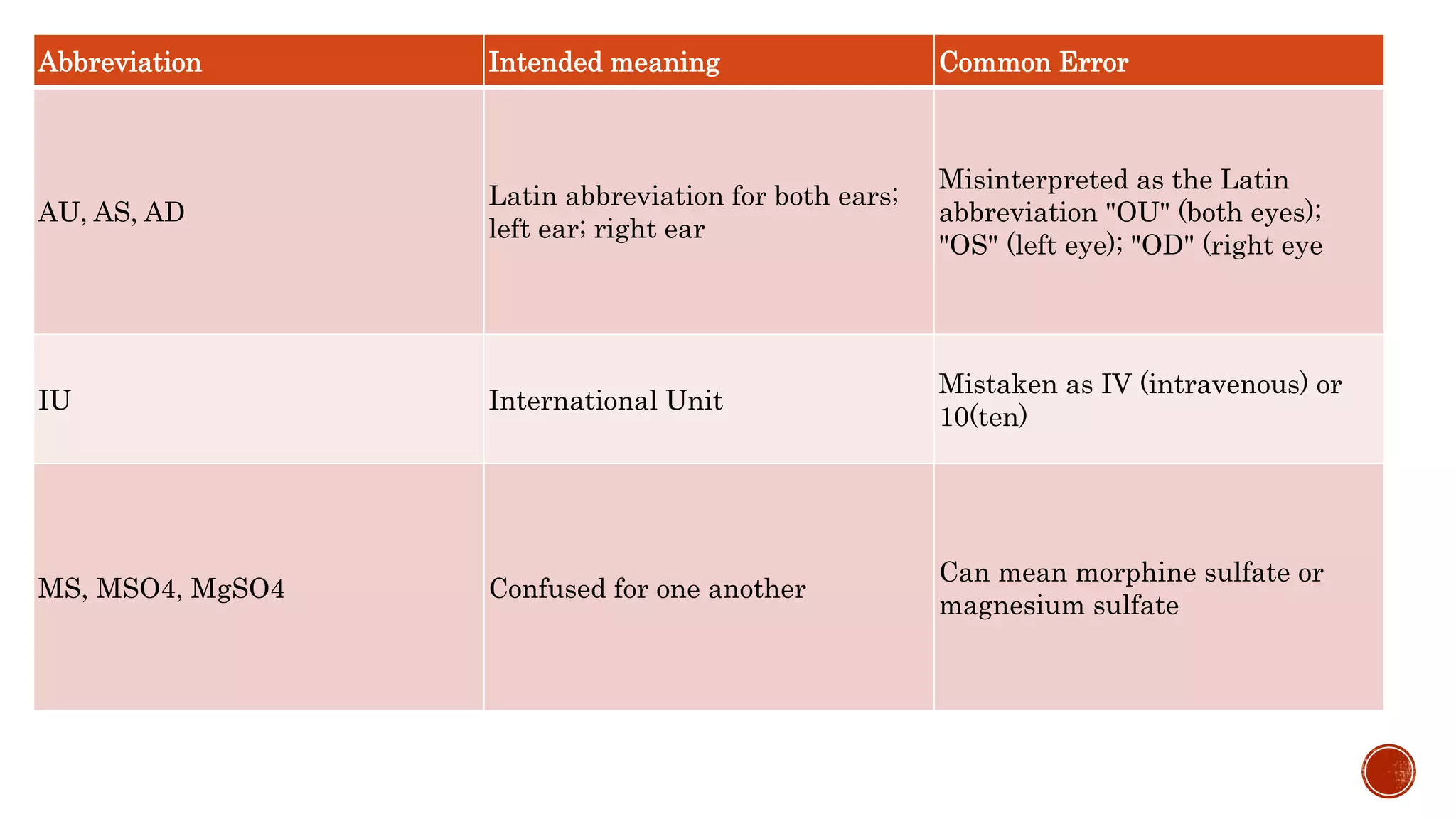
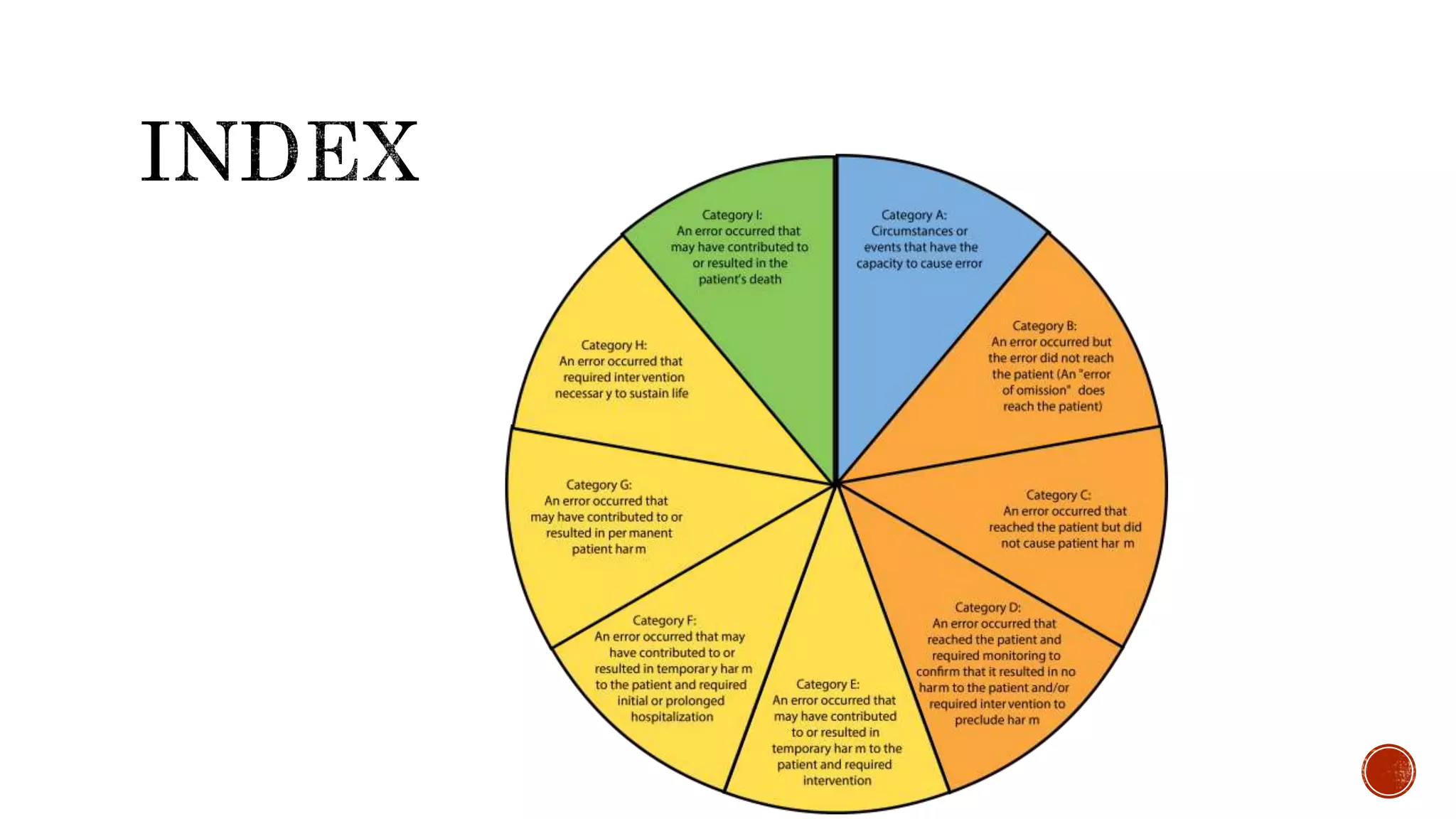
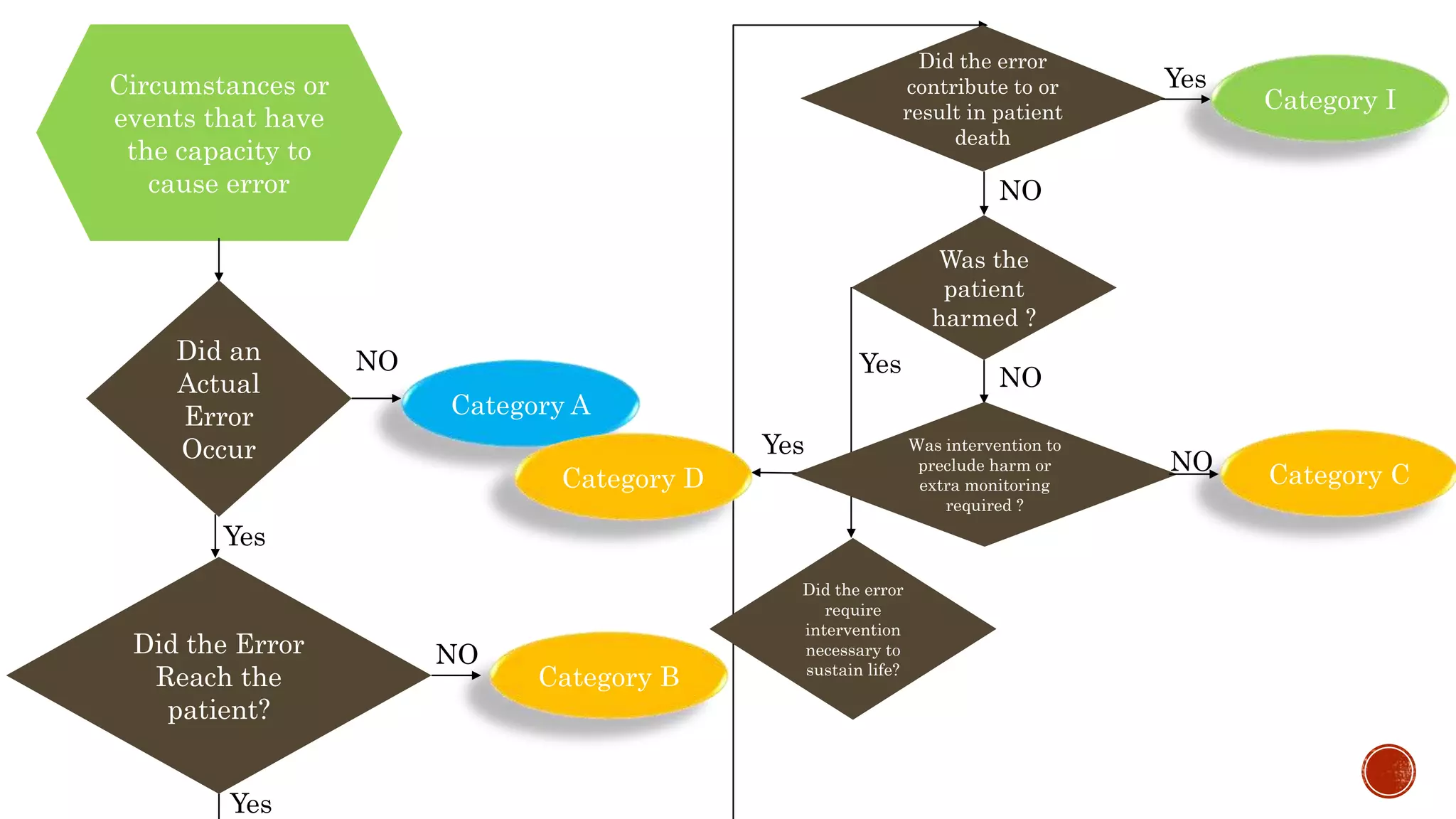
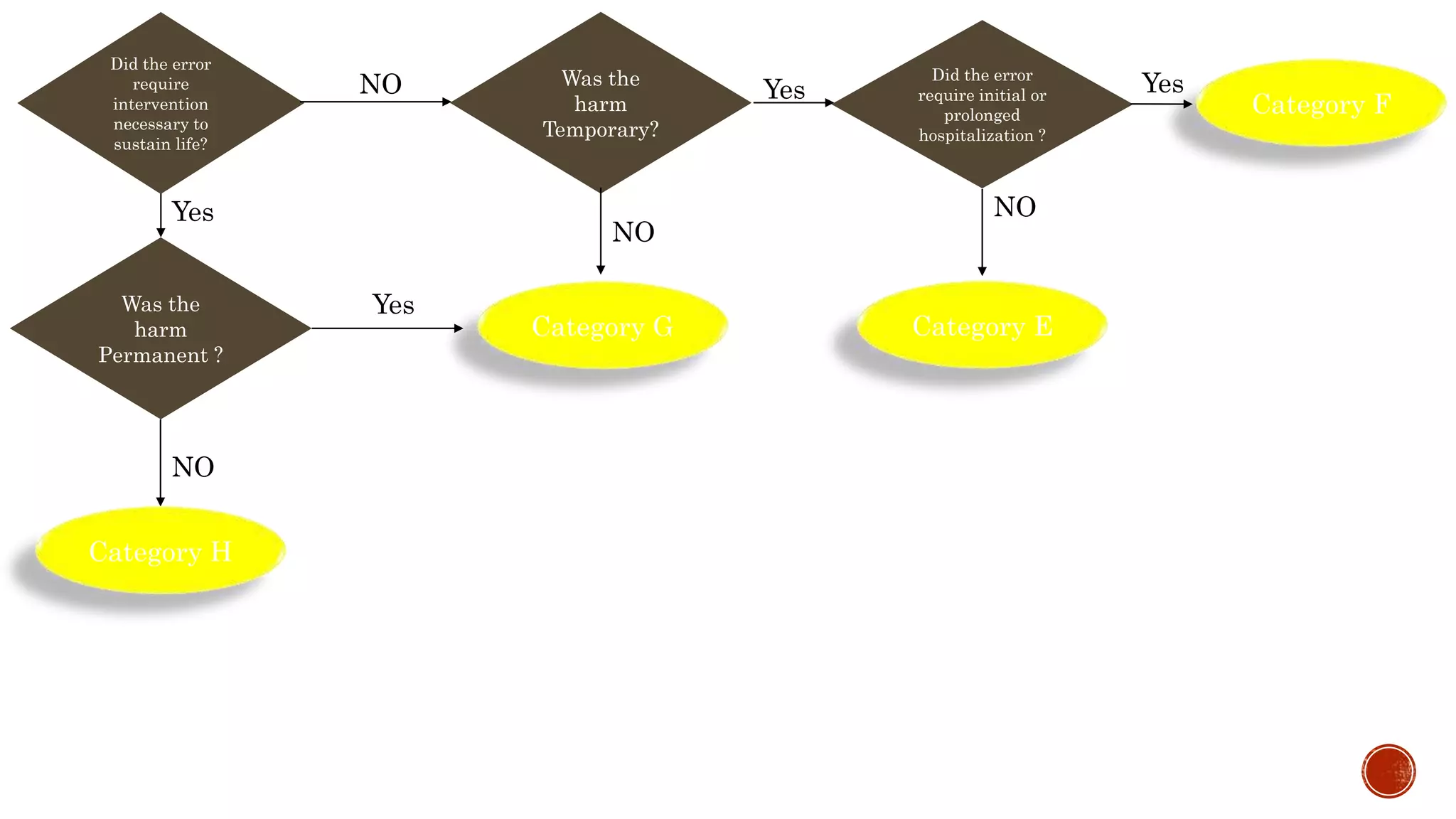
The document discusses medication errors, defining them as preventable events that may harm patients during their medication use, and outlines common causes such as ordering mistakes and illegible handwriting. It emphasizes the significance of healthcare professionals in identifying these errors and introduces concepts like medication transcription errors and the five rights of medication administration. The document also highlights the importance of accurate communication and documentation to minimize risks associated with medication errors.