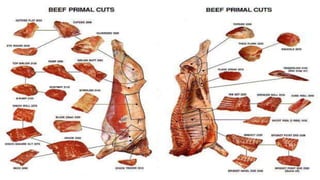
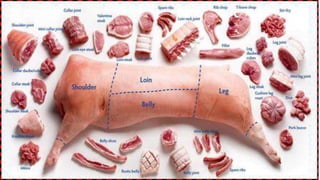
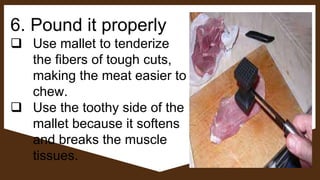
Meat refers to the edible flesh of animals that is eaten as food. It provides nutrients like protein, iron, and B vitamins. Meat consists mainly of water, protein, and fat. Various knives, cutting boards, and thermometers are used to process meat. Common market forms include fresh, chilled, cured, frozen, canned, and dried meats. Meats come from animals like pigs, cattle, sheep, carabao, deer, and goats. Cooking meat is important for tenderness, palatability, and safety by destroying microorganisms.