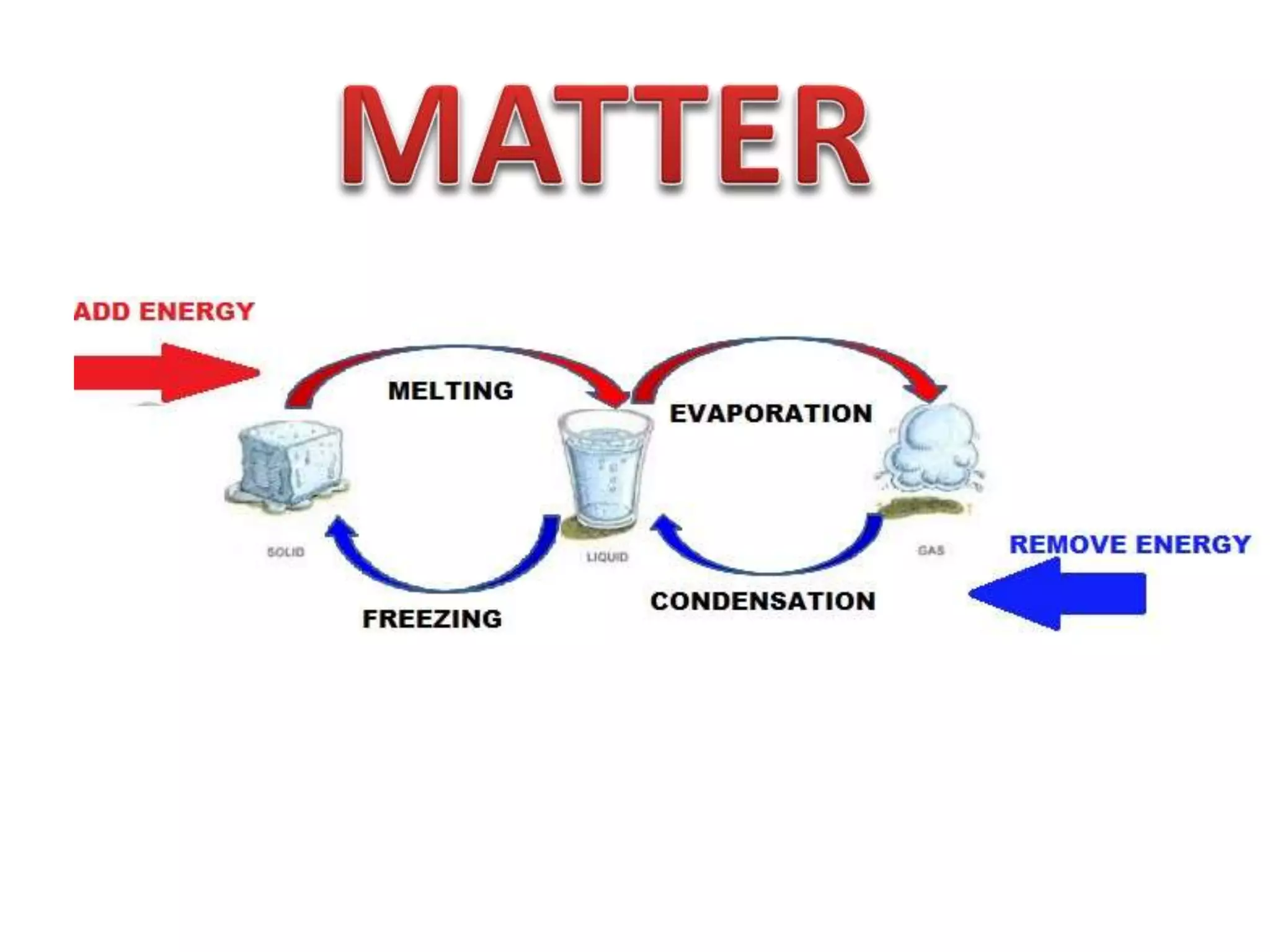
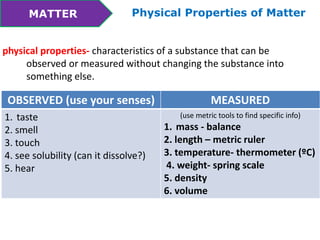
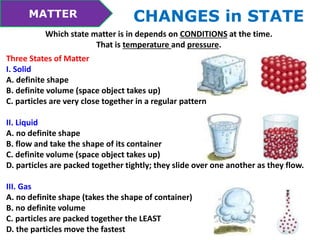
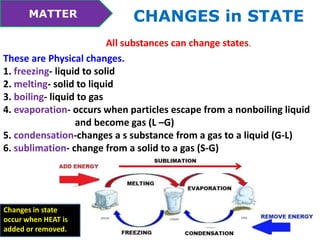
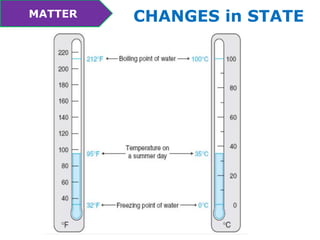
This document discusses the properties and states of matter. It defines matter as anything that takes up space and has mass. Physical properties are characteristics that can be observed or measured without changing the substance, such as mass, volume, density, and state of matter (solid, liquid, gas). A mixture is a combination of two or more substances that keep their own properties, while a solution is a type of mixture where particles are evenly mixed but not easy to separate. The state that matter exists in depends on temperature and pressure - it can change states between solid, liquid and gas through physical processes like melting, freezing, boiling, evaporation and condensation that involve adding or removing heat.