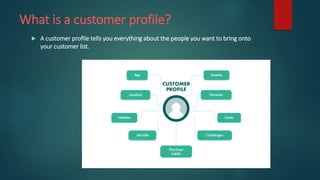
Market research is defined as evaluating the feasibility of new products or services through research with potential consumers. It allows organizations to understand their target market, collect opinions, and make informed decisions. Market research can be conducted directly or outsourced to agencies with expertise. It provides valuable customer information, identifies market trends, and gives competitive advantages to help businesses plan strategies accordingly. The key steps involve defining problems and samples, collecting and analyzing data, and making decisions based on research reports.