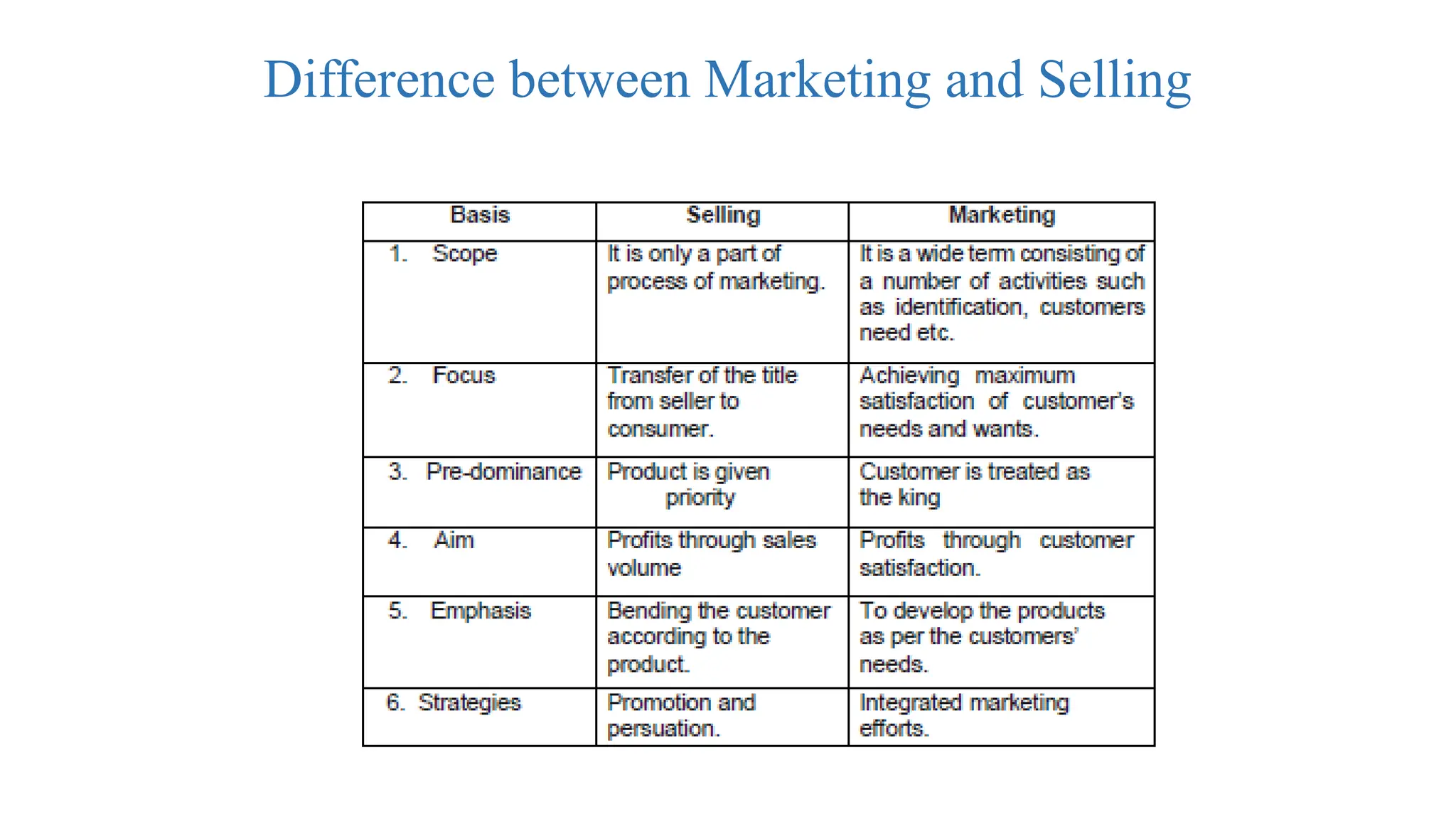
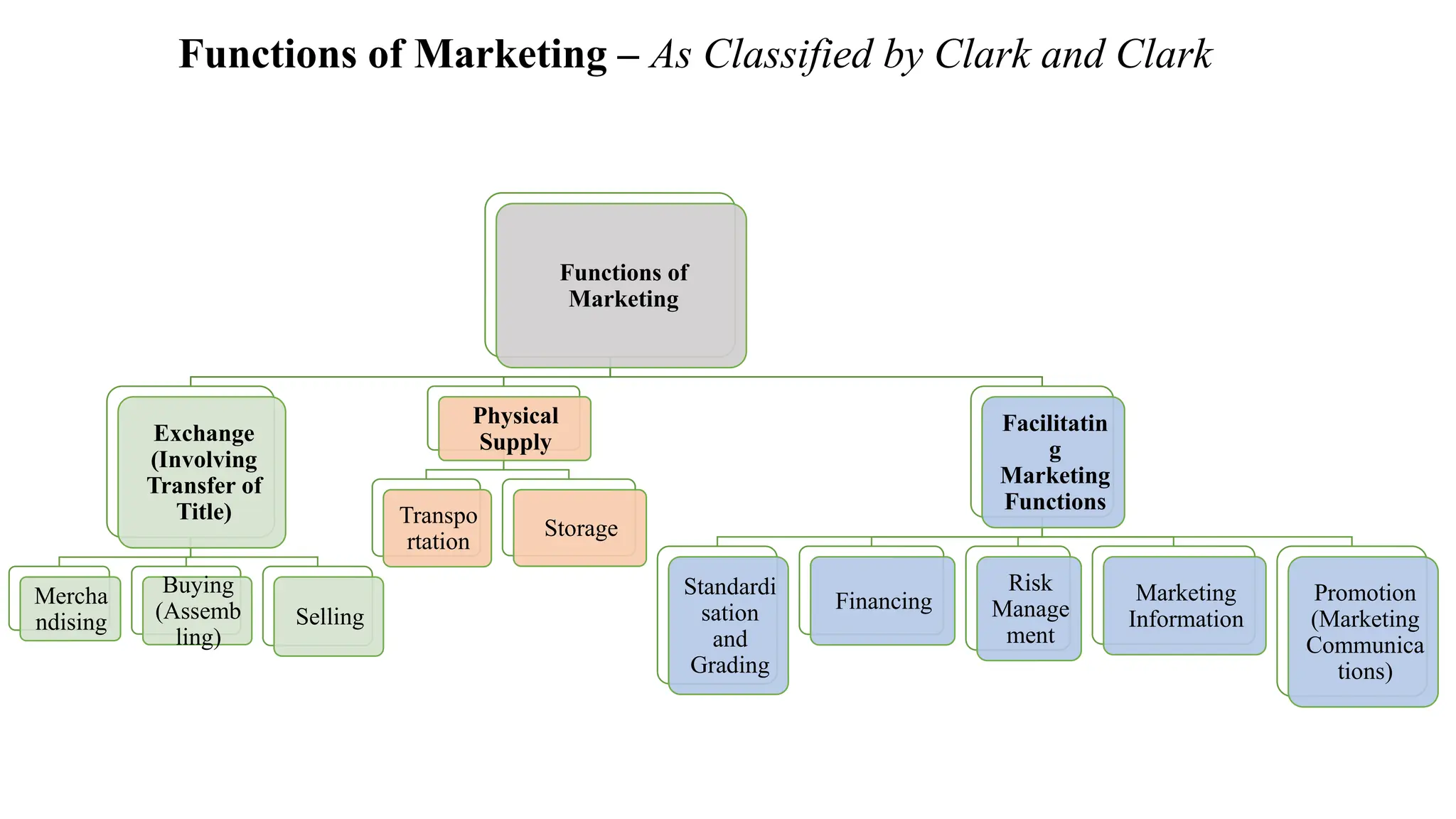
The document provides a comprehensive overview of marketing, including its definitions, objectives, and various approaches to study it, such as the product, institutional, functional, management, system, societal, legal, and economic approaches. It highlights the importance of marketing in understanding market opportunities, customer satisfaction, and profitability, as well as the functions involved in the marketing process. Overall, the content emphasizes the multifaceted nature of marketing and its impact on businesses and society.