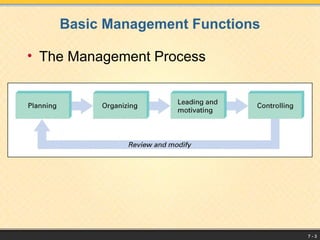
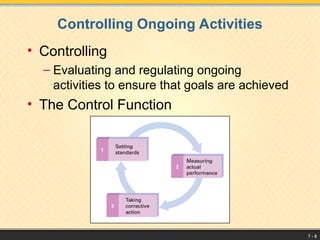
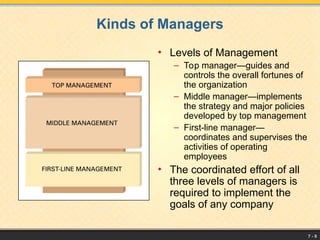
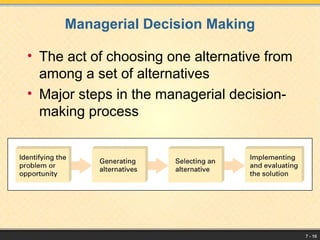
The document outlines the management process, defining management as coordinating resources to achieve organizational goals, which include material, human, financial, and information resources. It details basic management functions such as planning, organizing, leading, and controlling, and emphasizes the importance of goal-setting and strategic planning. Additionally, it highlights the various levels of management, essential managerial skills, decision-making processes, and the significance of leadership styles in effective management.