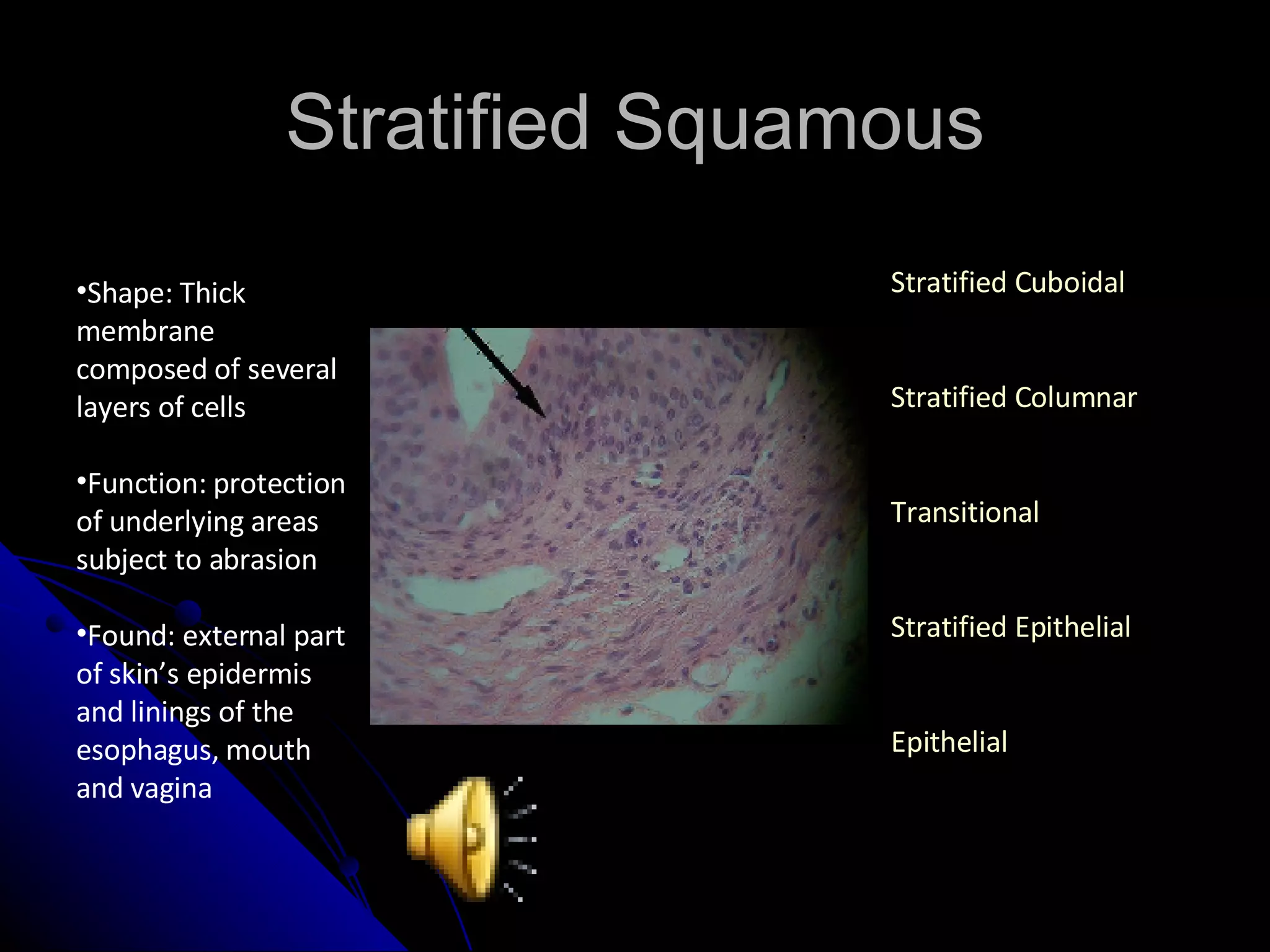
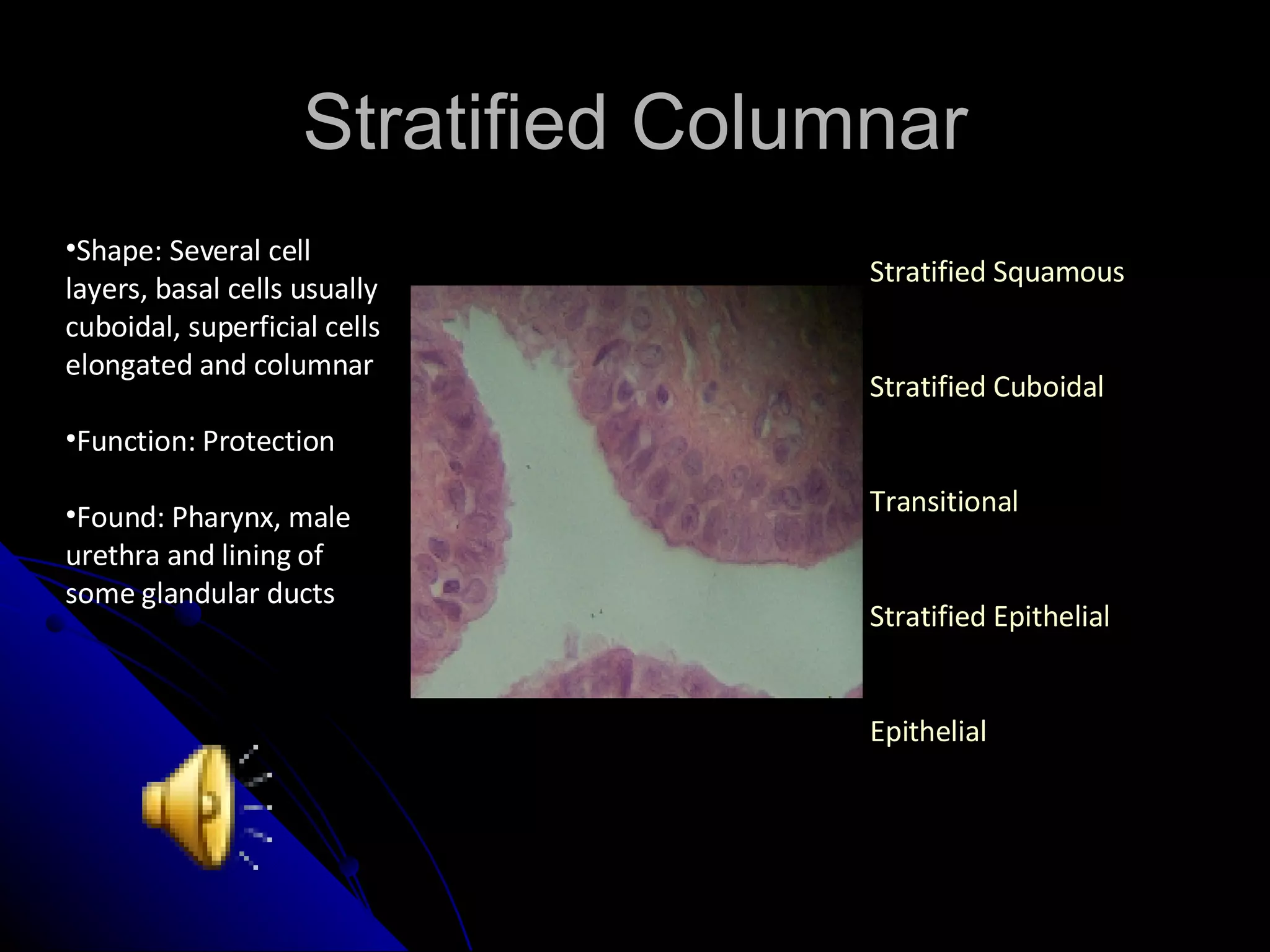
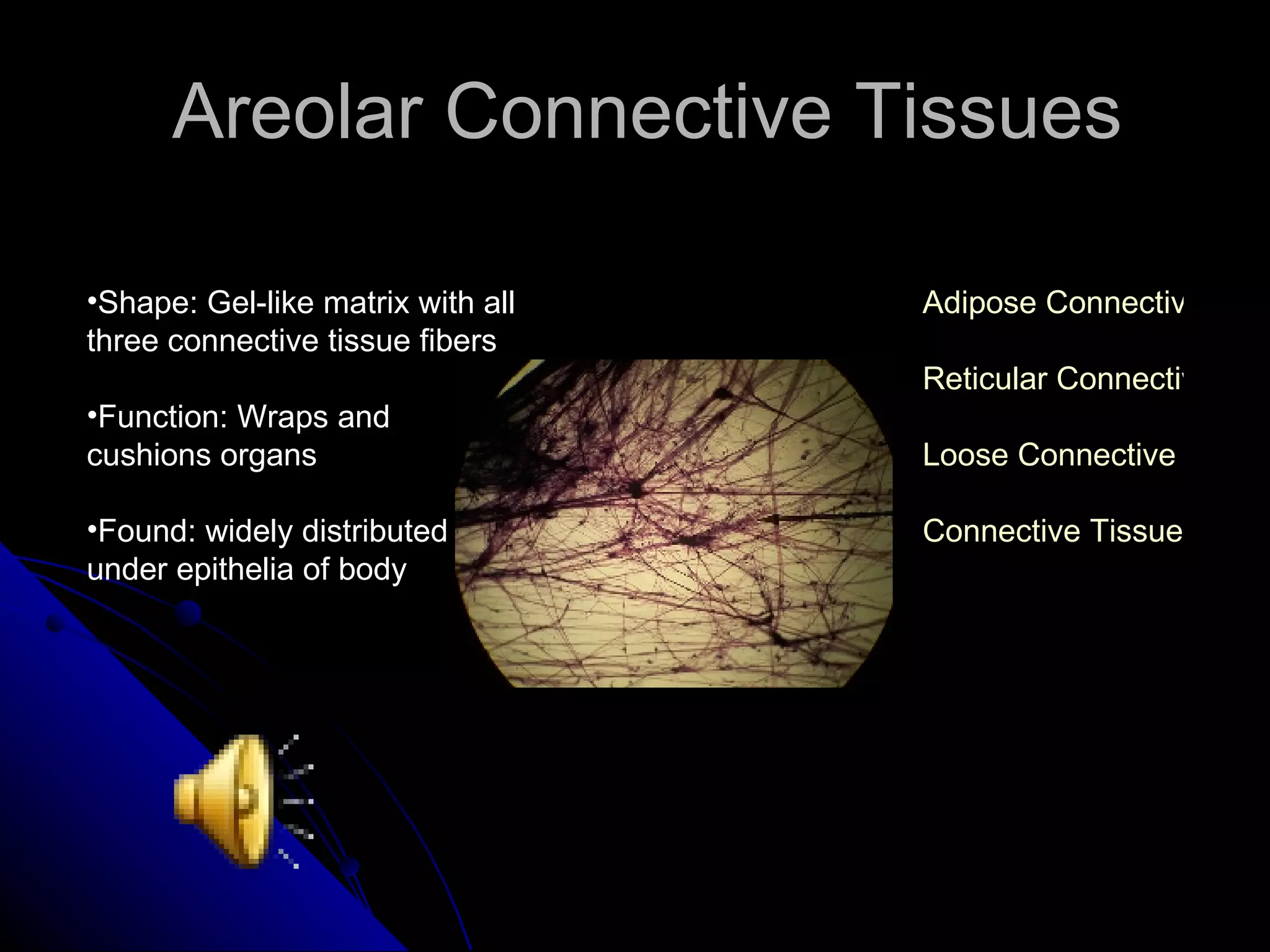
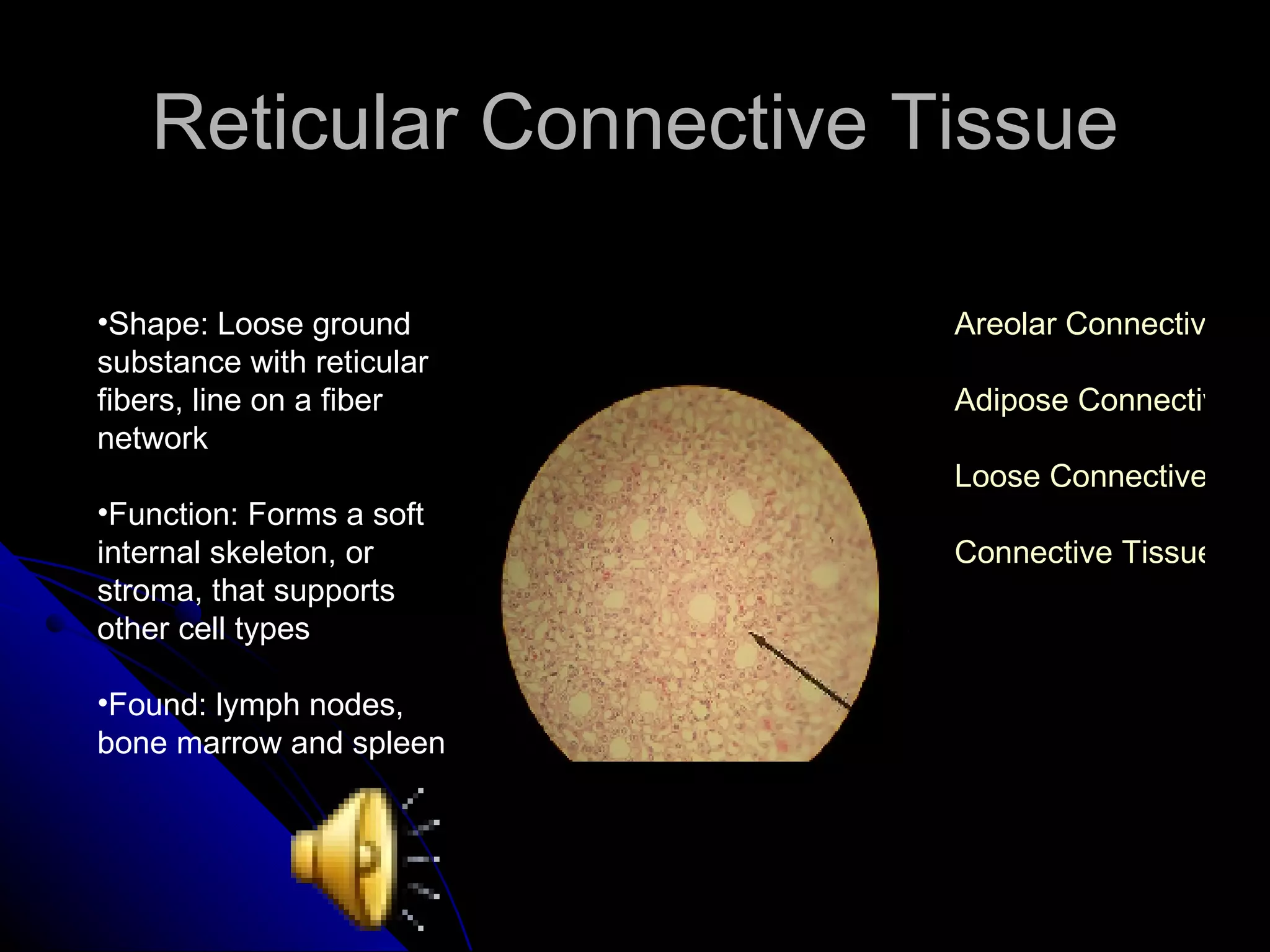
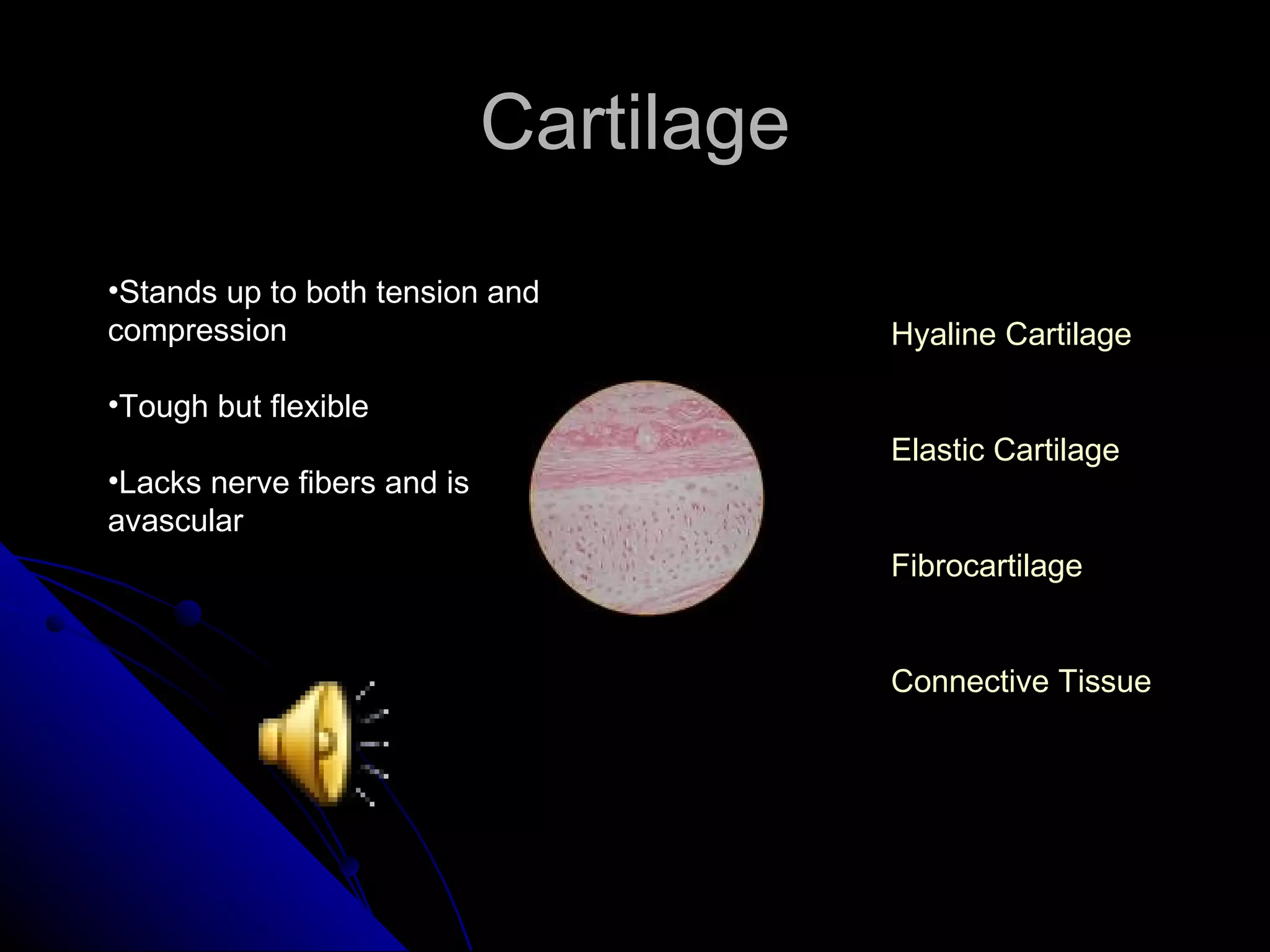
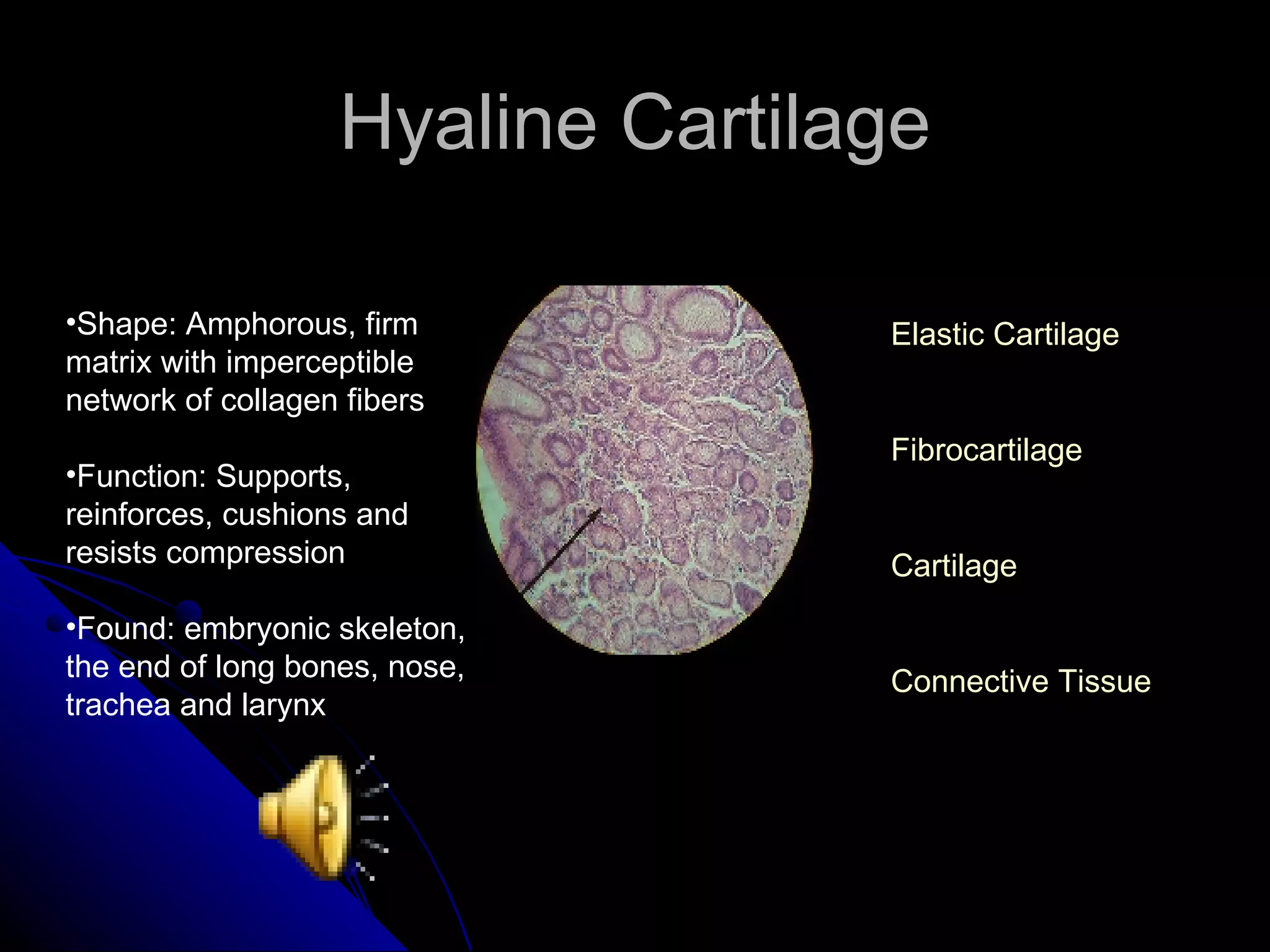
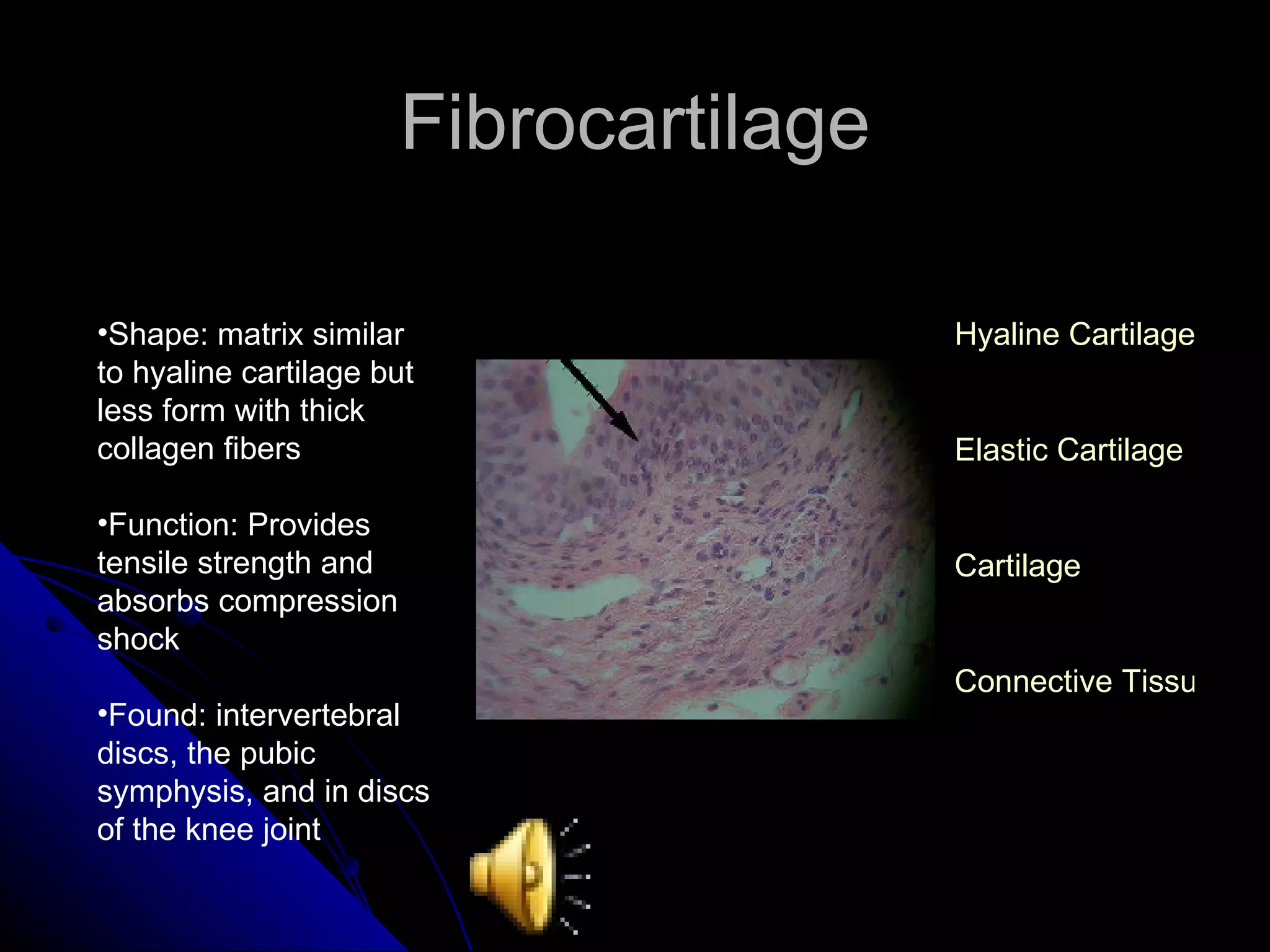
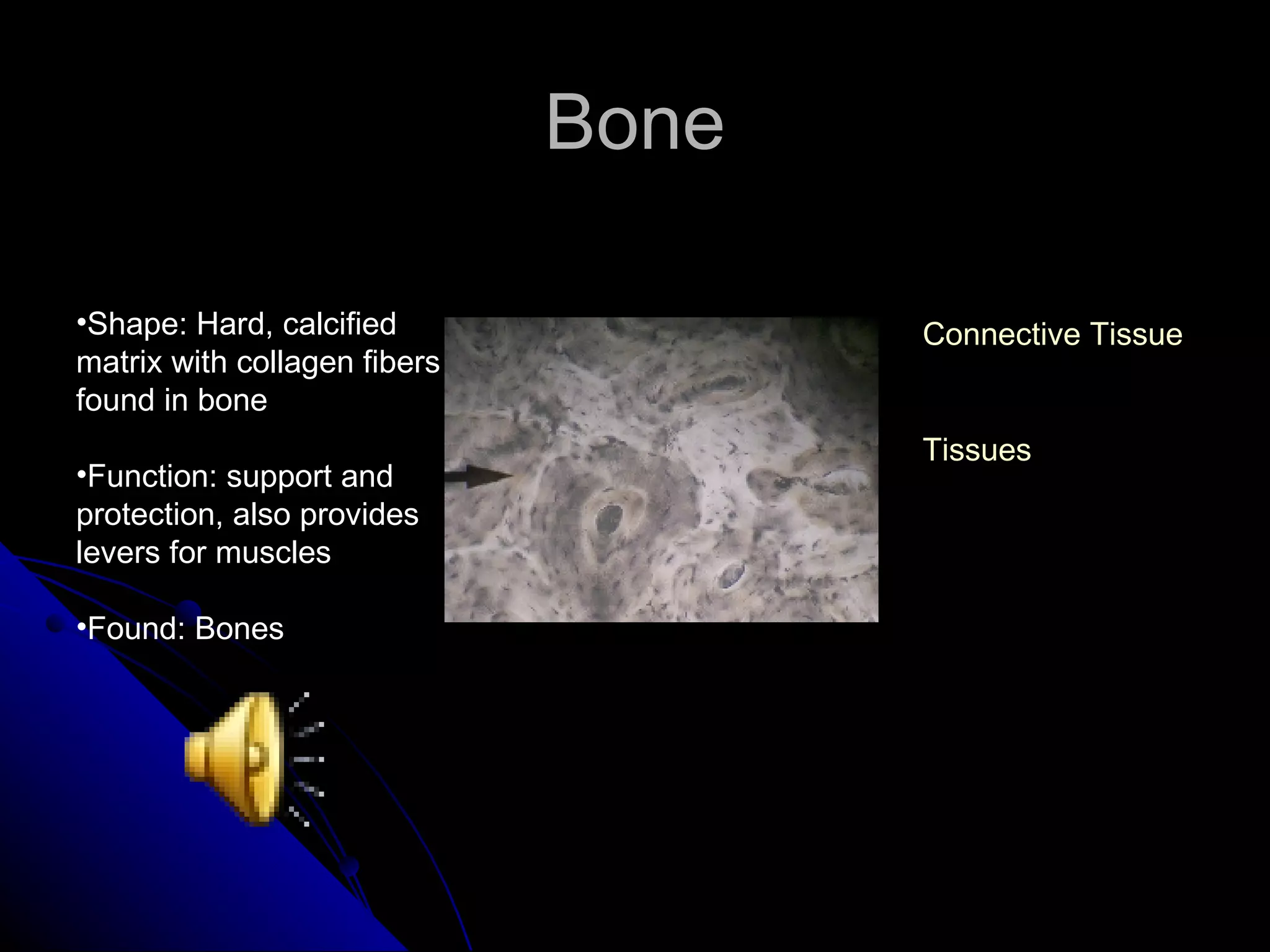
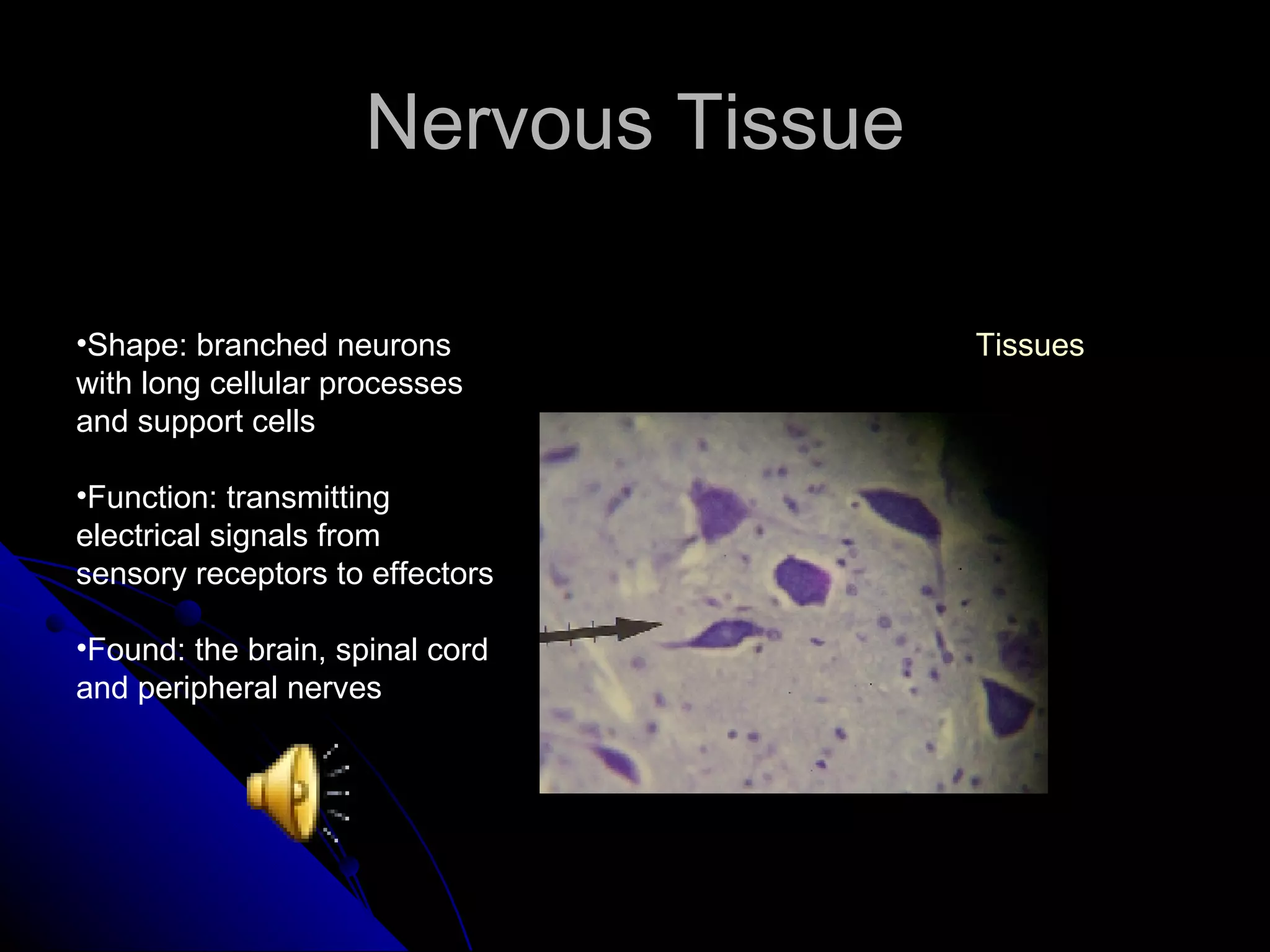
There are four main types of tissues in the body: epithelial, connective, muscle and nervous. Epithelial tissue covers surfaces and forms glands. It is classified as simple or stratified. Connective tissue is found throughout the body and includes connective tissue proper, cartilage, bone and blood. It has roles like binding, supporting and protecting. Muscle tissue includes skeletal, cardiac and smooth muscle that allow for voluntary movement, pumping of blood and involuntary movement like digestion. Nervous tissue transmits electrical signals through neurons in the brain, spinal cord and nerves.