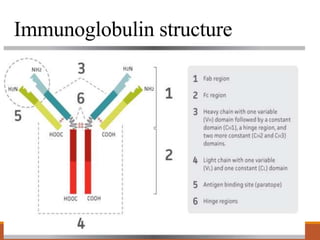
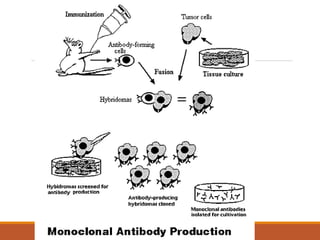
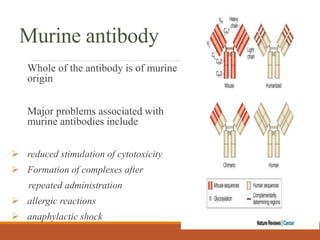
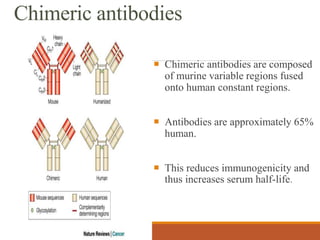
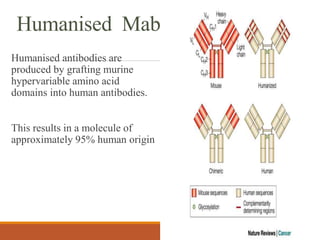
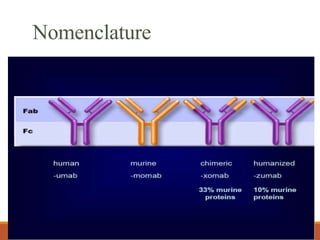
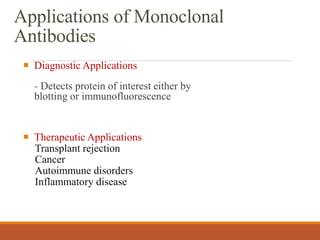
Monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) are identical antibodies produced by a single clone of B cells or hybridoma cell line. Paul Ehrlich first described antibodies as "magic bullets" in search of toxins. Key developments included methods to isolate hybrid cell lines producing mAbs. mAbs can be murine, chimeric, humanized, or human. They have diagnostic applications like pregnancy tests and therapeutic uses like treating cancer, transplants, and autoimmune disorders. Common side effects include allergic reactions and infusion reactions. mAbs have revolutionized biotechnology and improved human health.