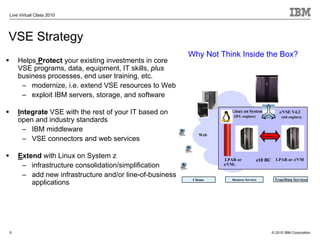
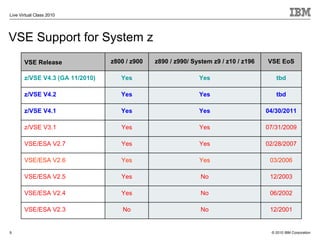
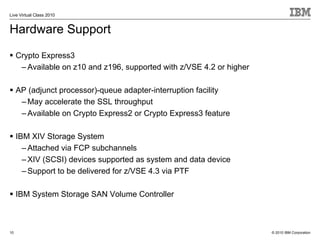
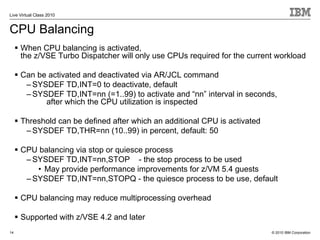
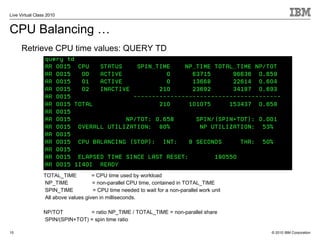
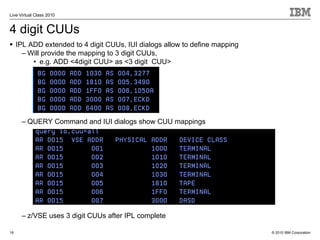
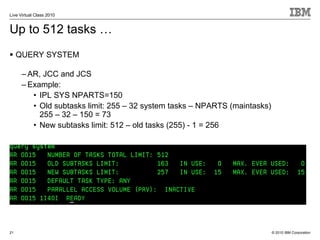
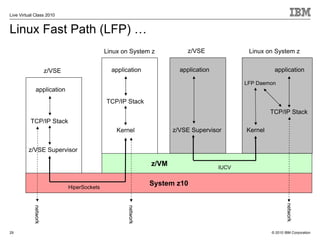
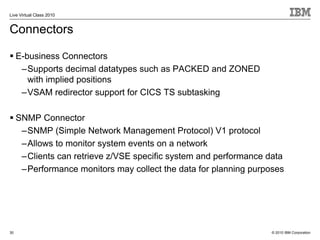
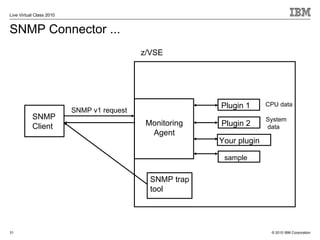
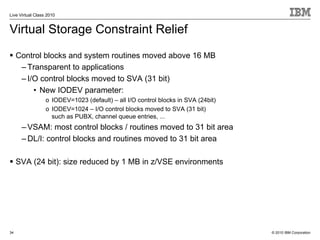
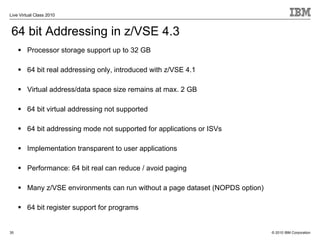
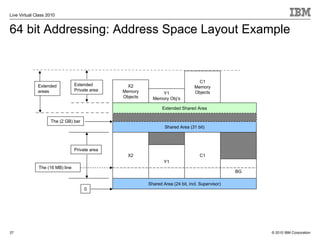
The document outlines the features and updates of IBM's z/VSE version 4.3, including enhanced capacity for growth, support for 64-bit virtual addressing, and improved performance capabilities. Key updates include new hardware support, CPU balancing for improved workload management, and the introduction of four-digit device addresses for simplified infrastructure integration. The document also discusses the strategy to modernize and extend z/VSE resources, as well as compliance with various IBM and third-party trademarks.