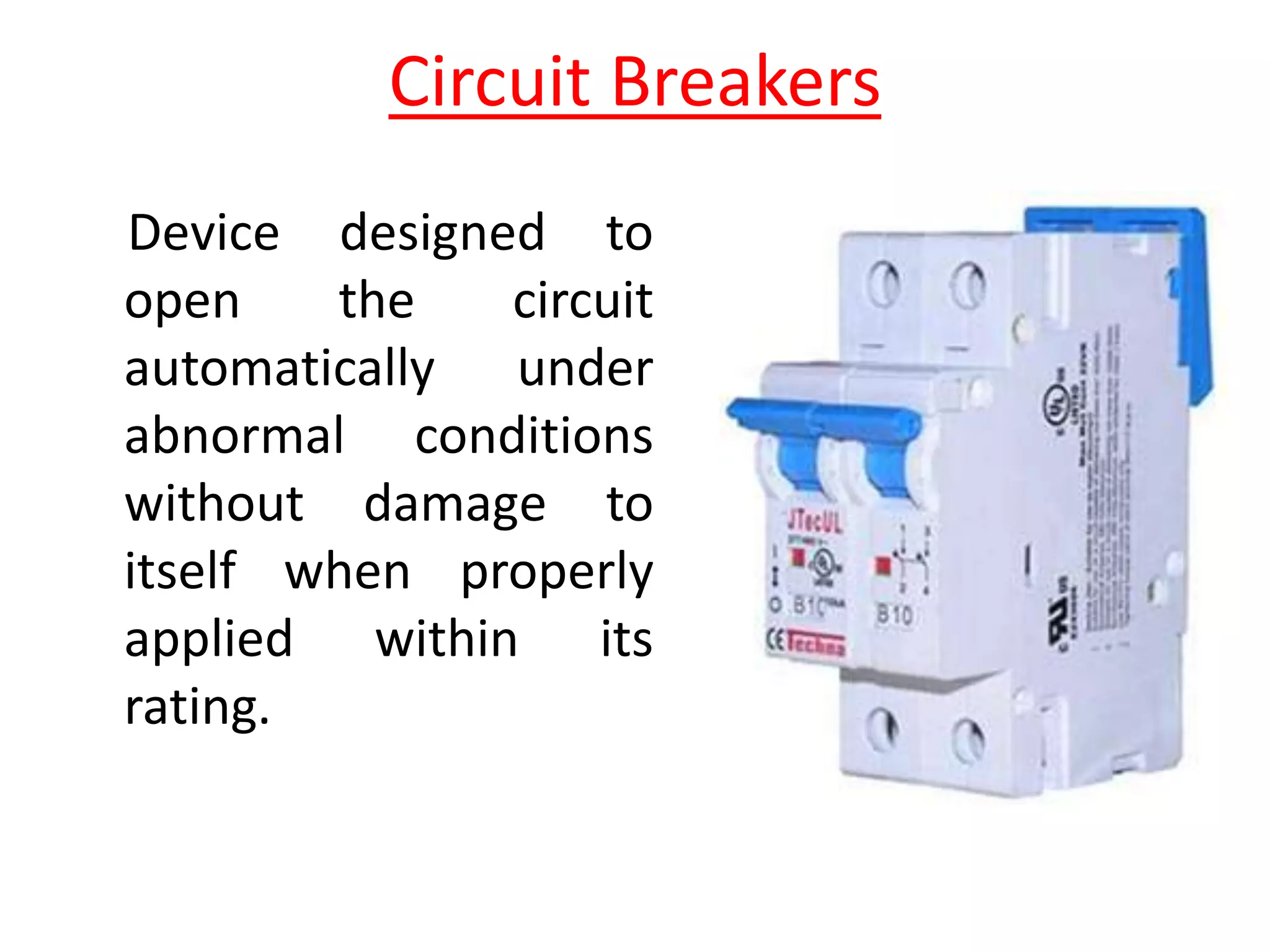
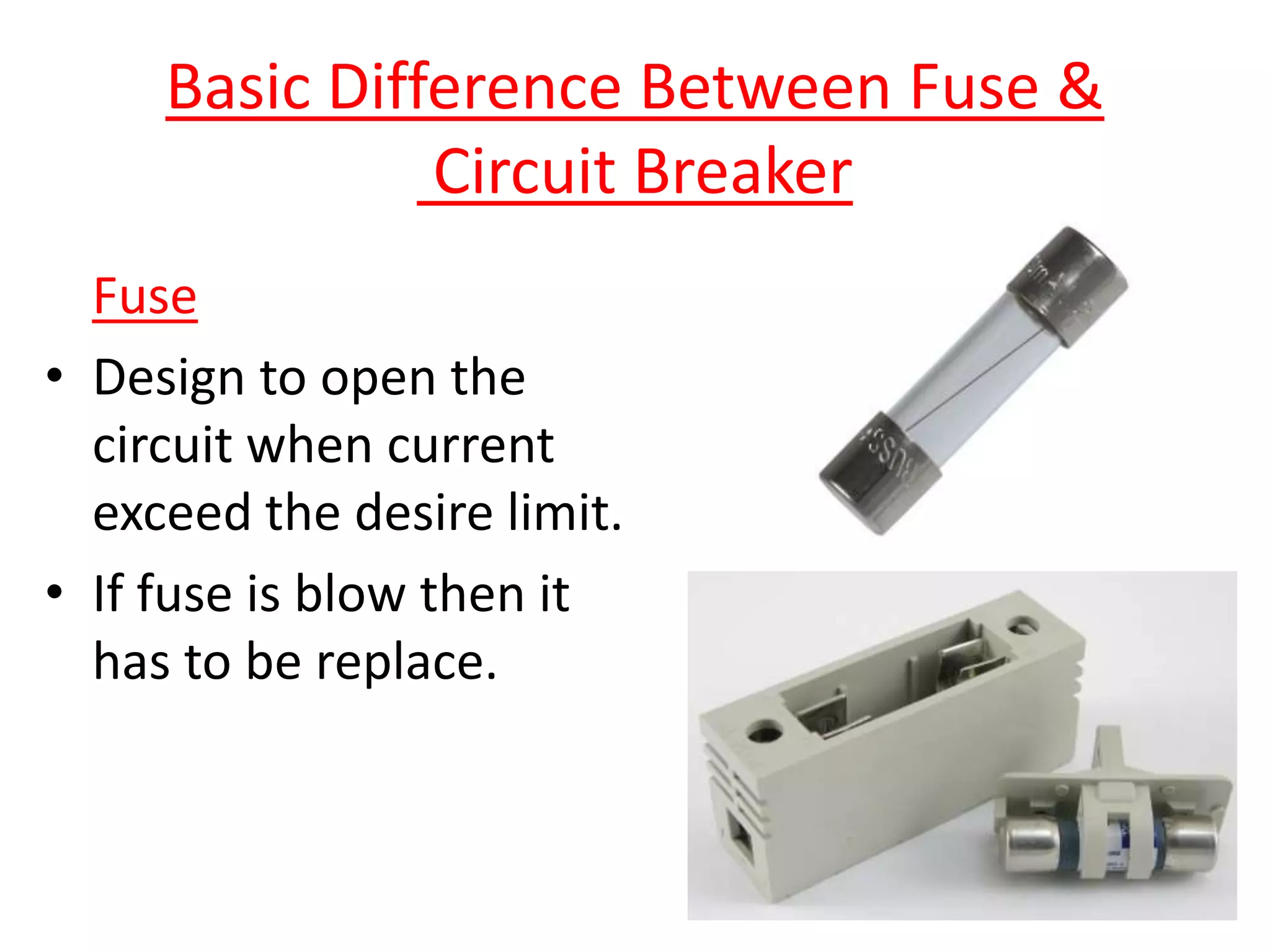
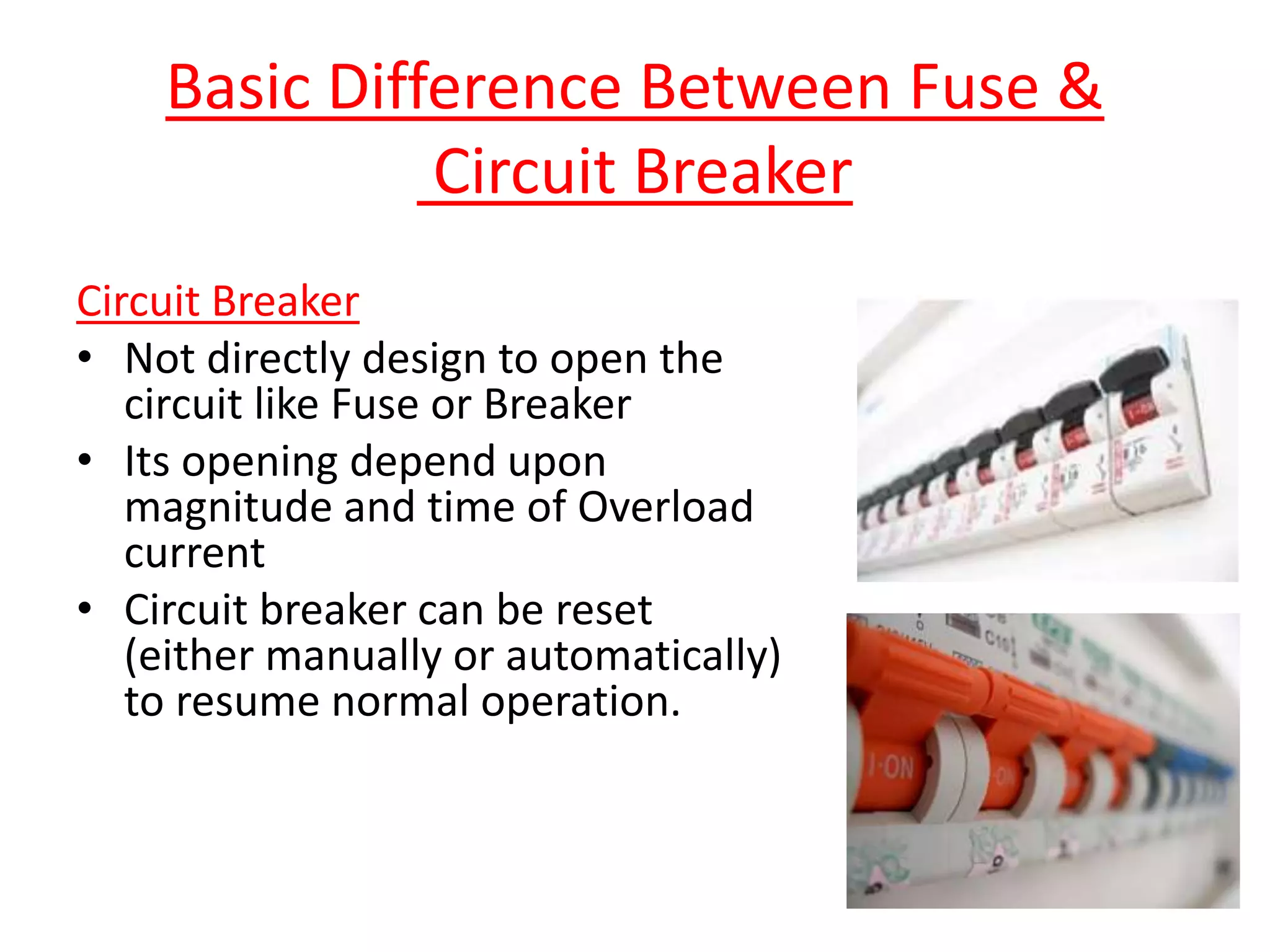
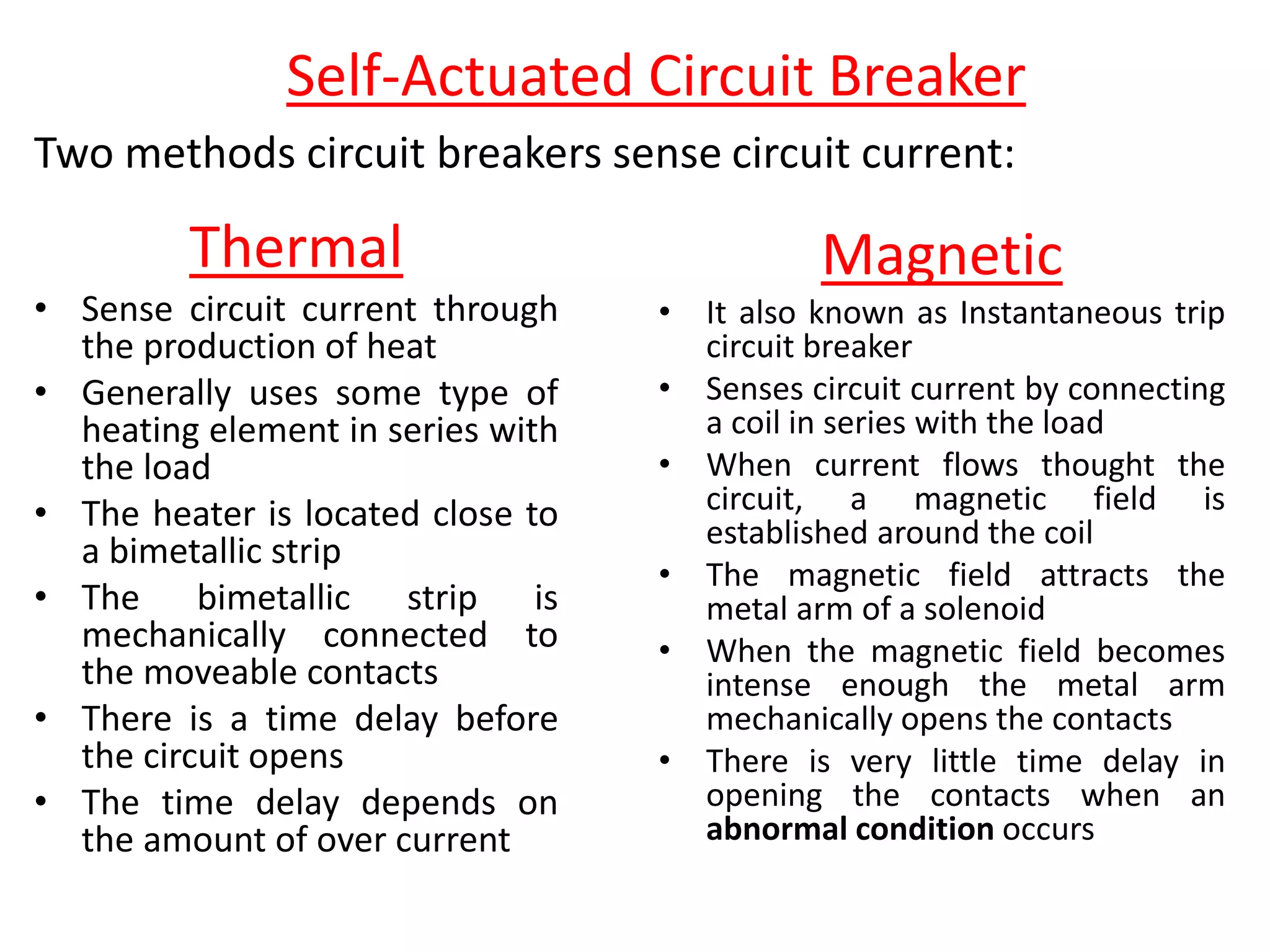
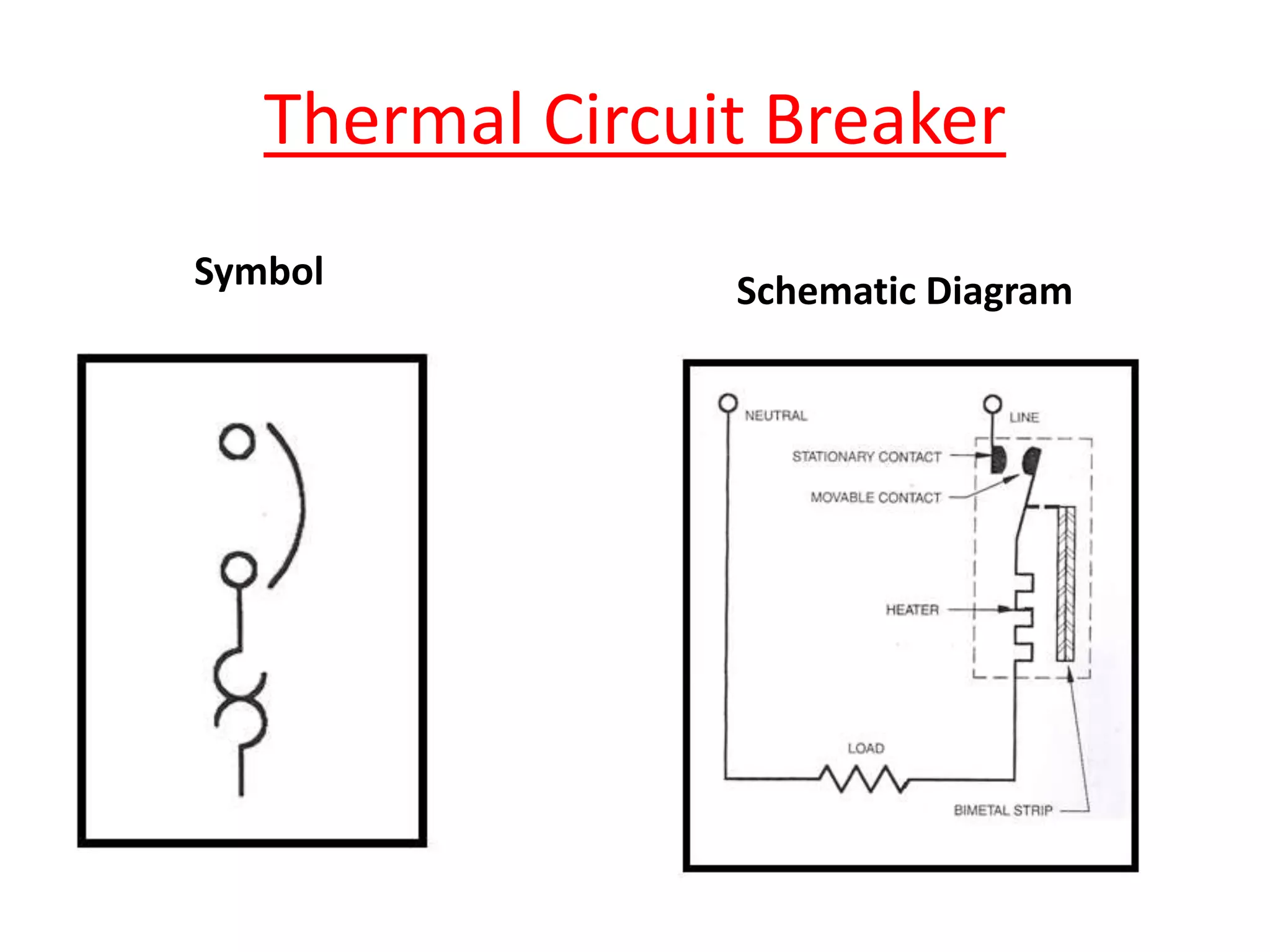
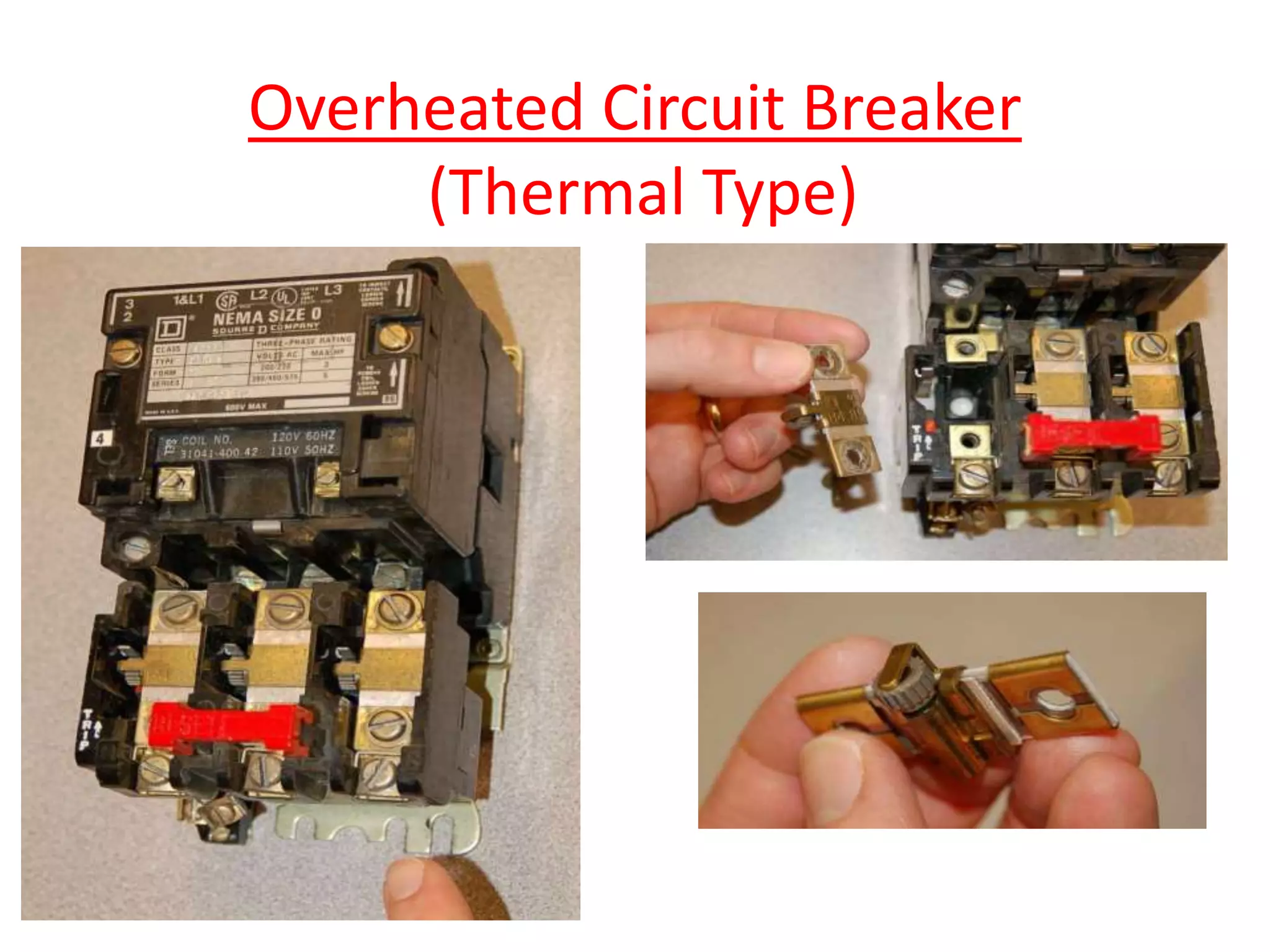
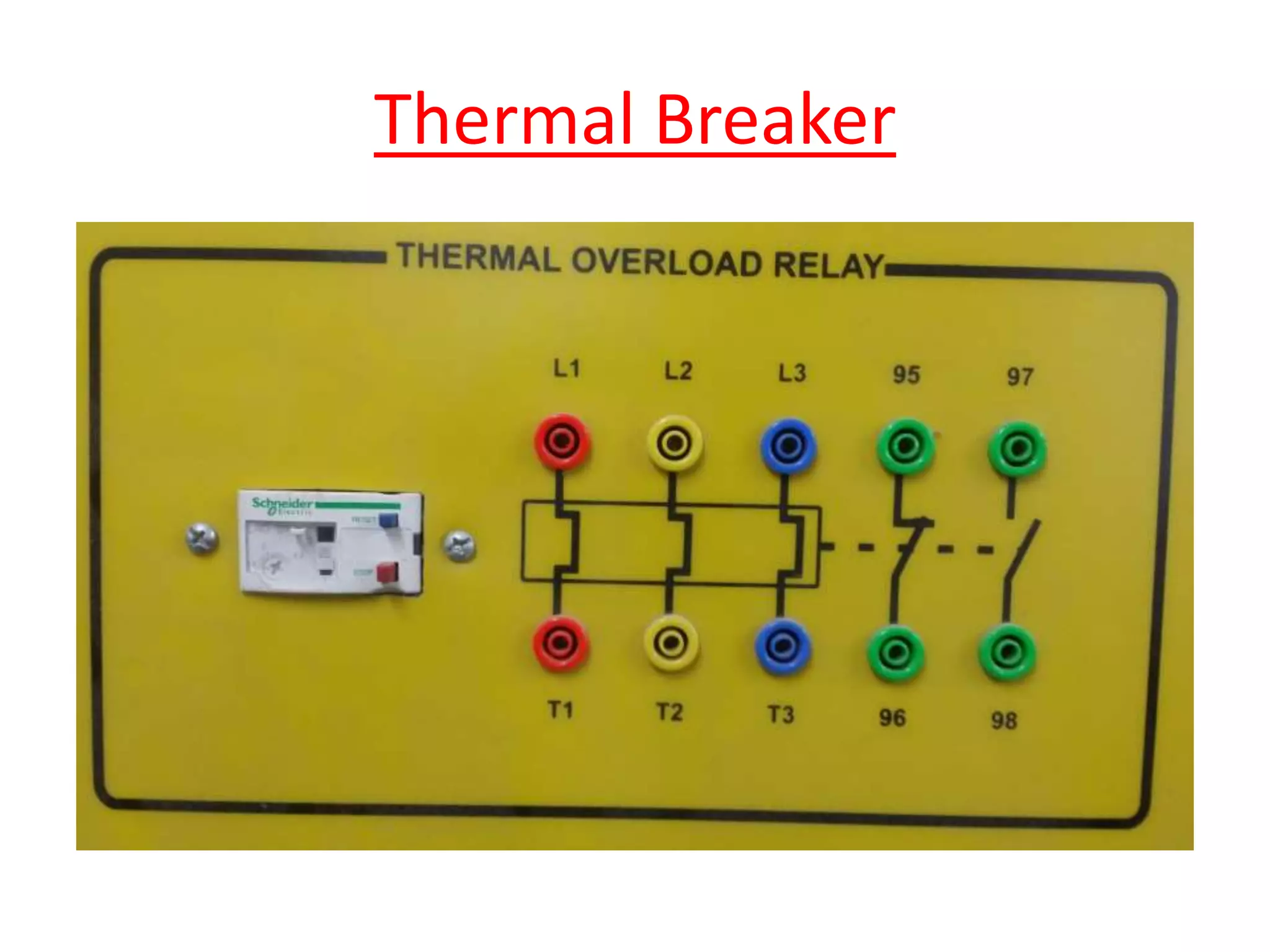
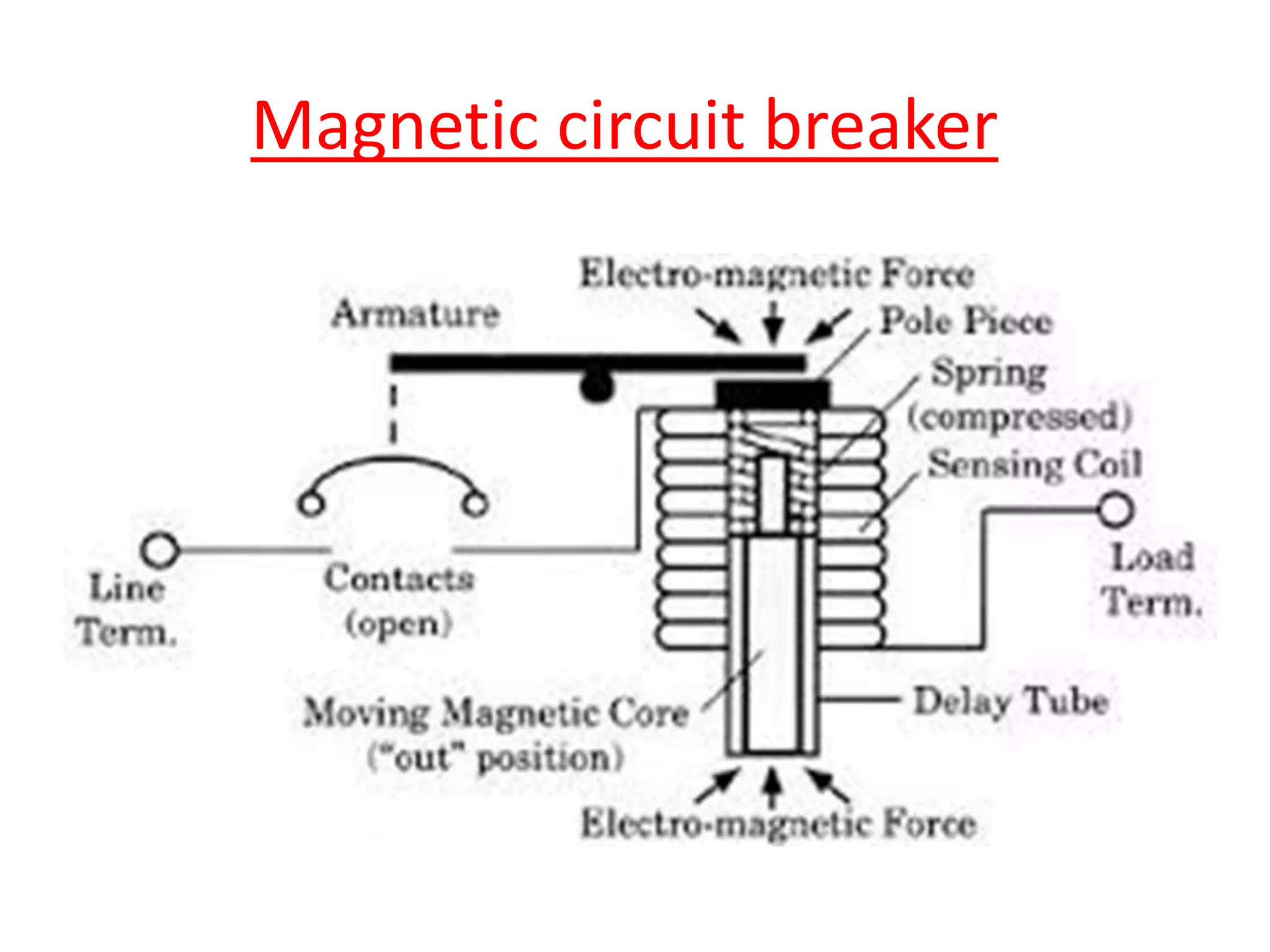
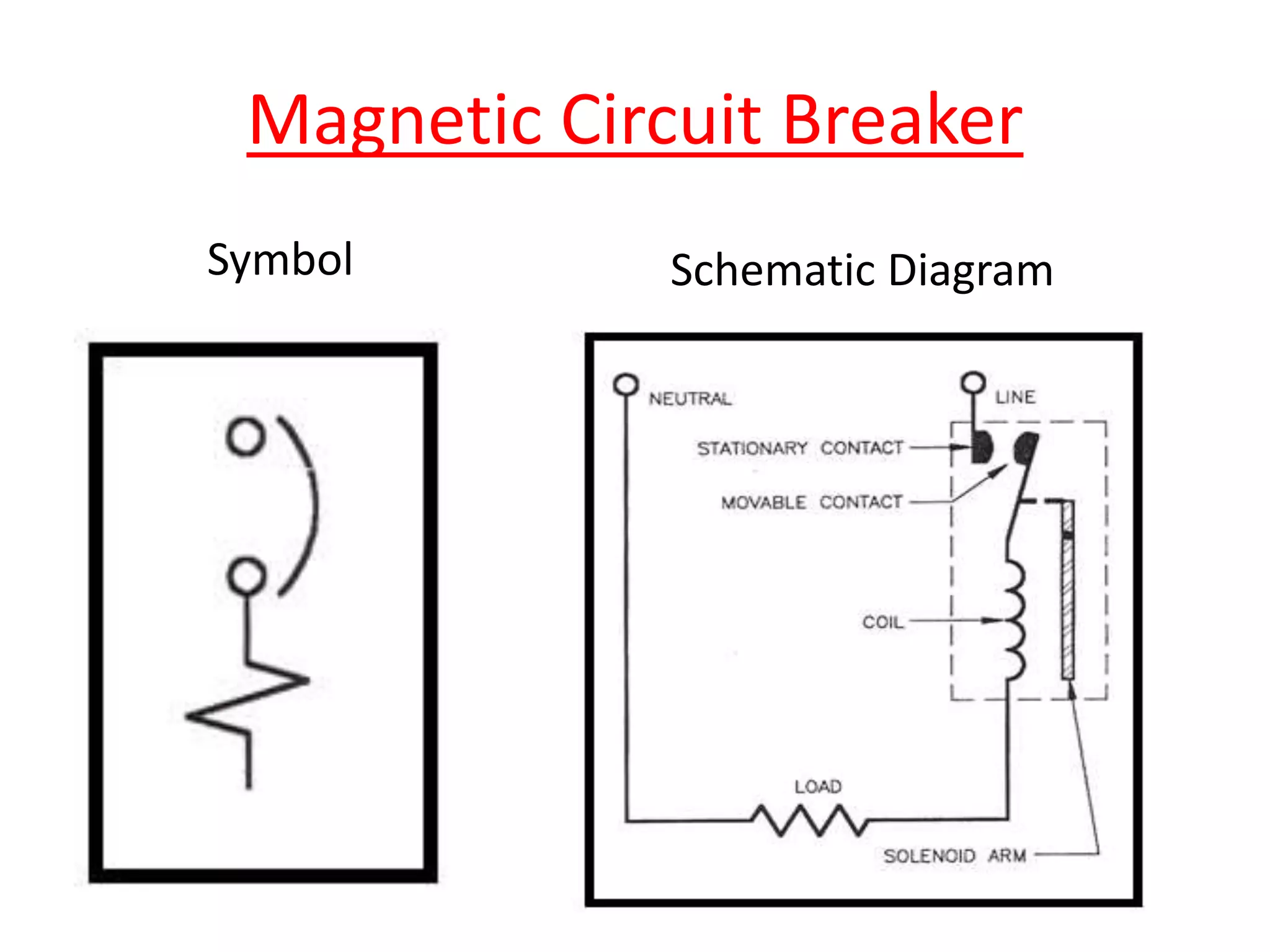
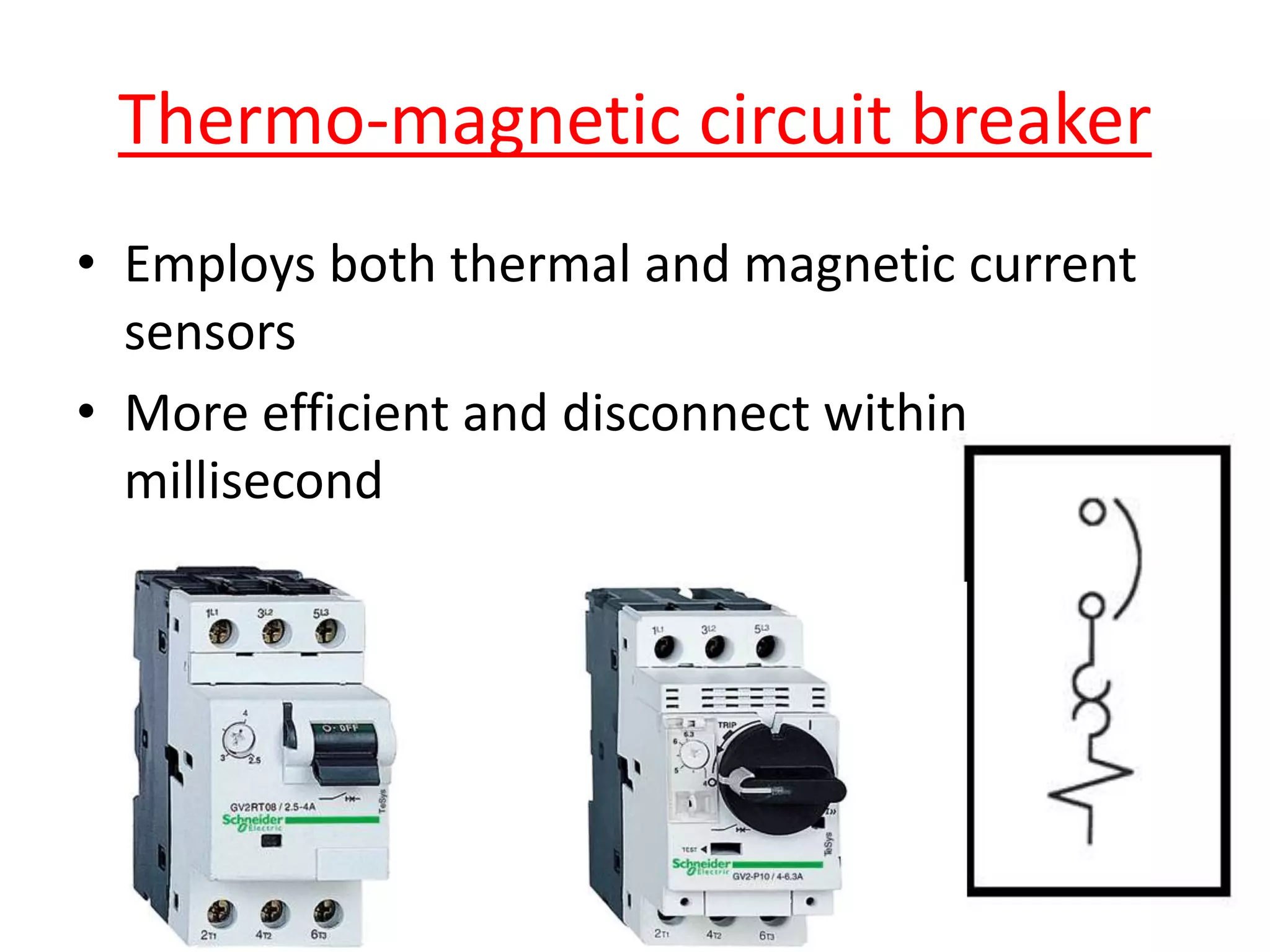
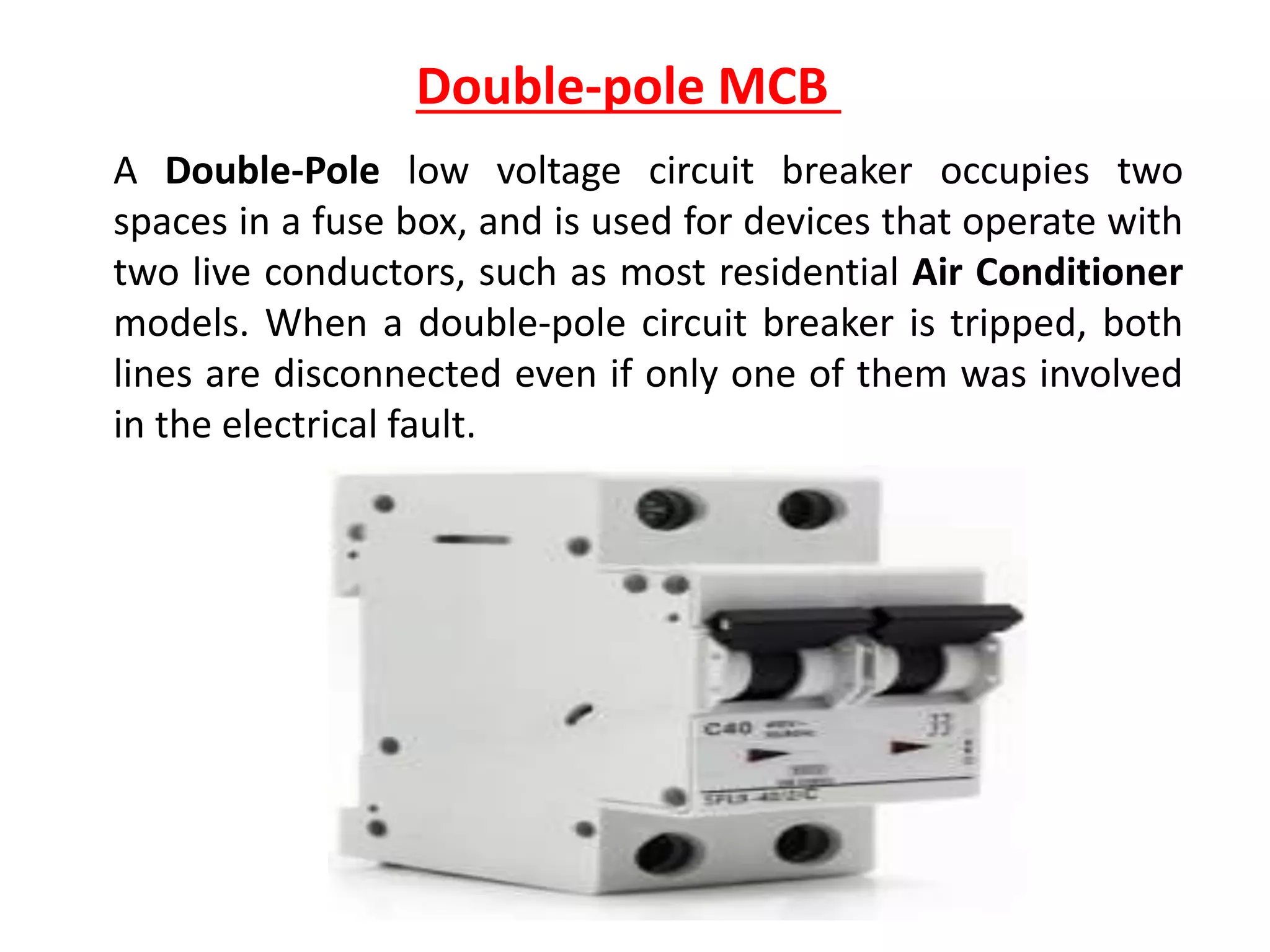
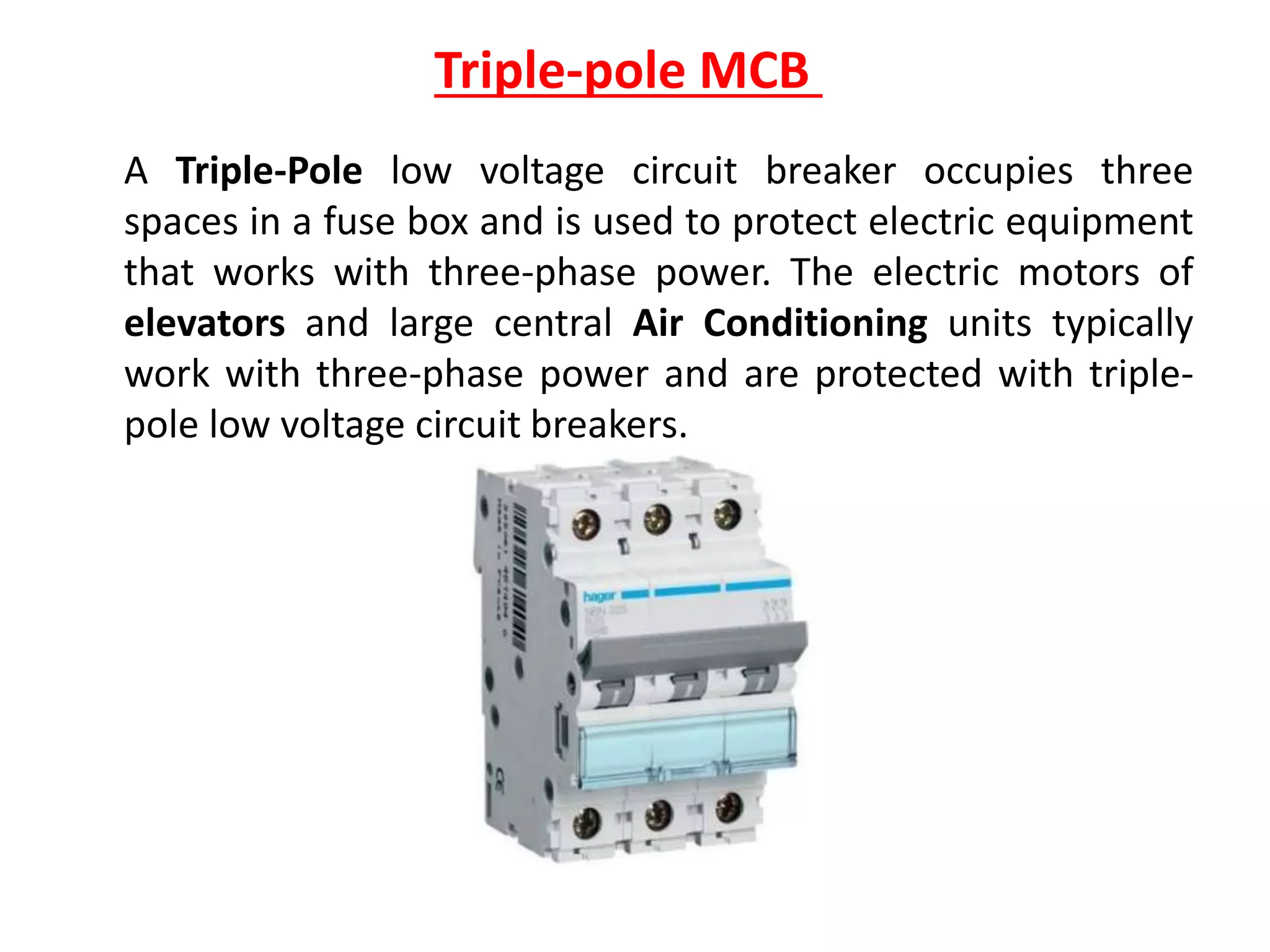
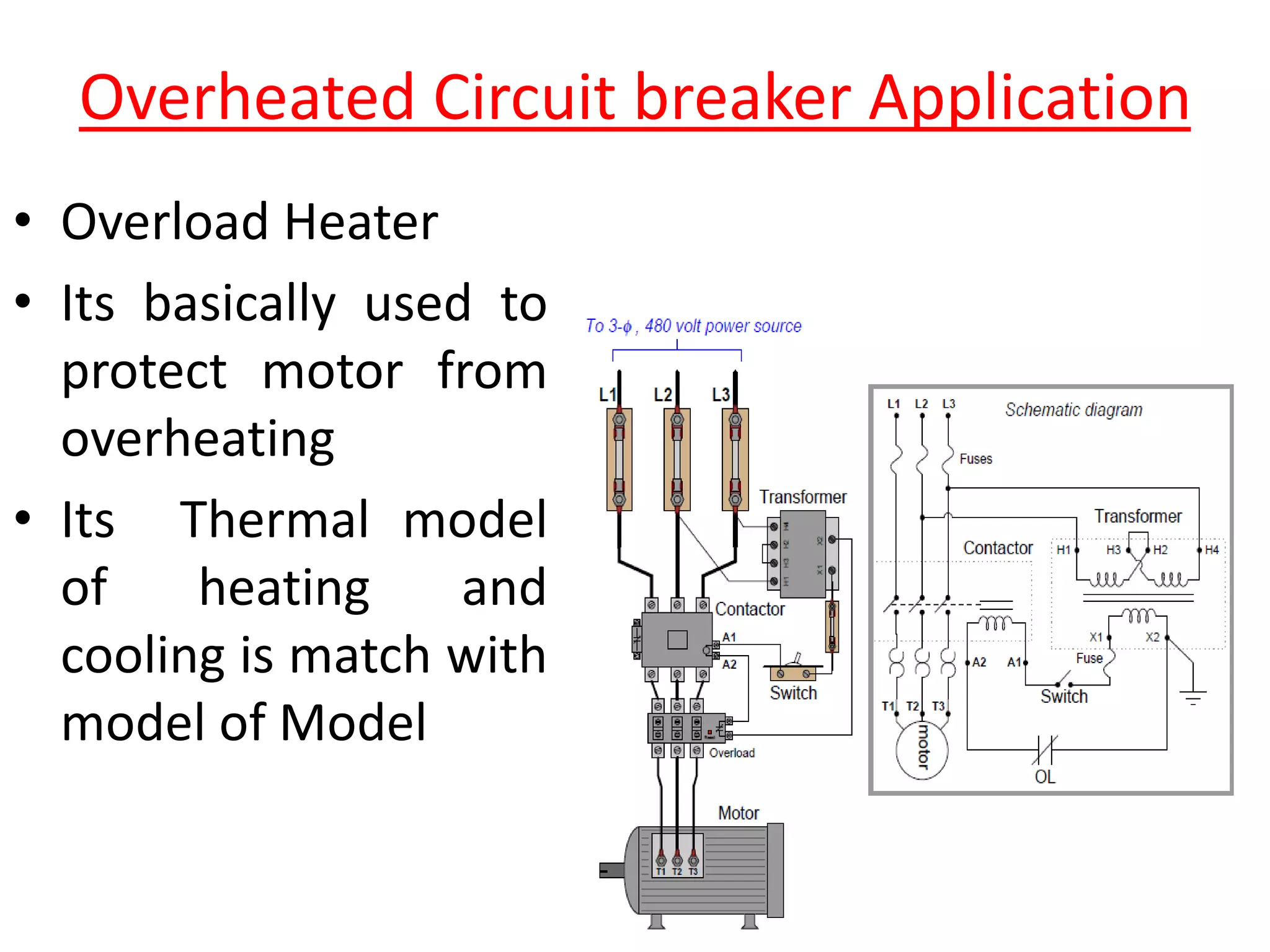
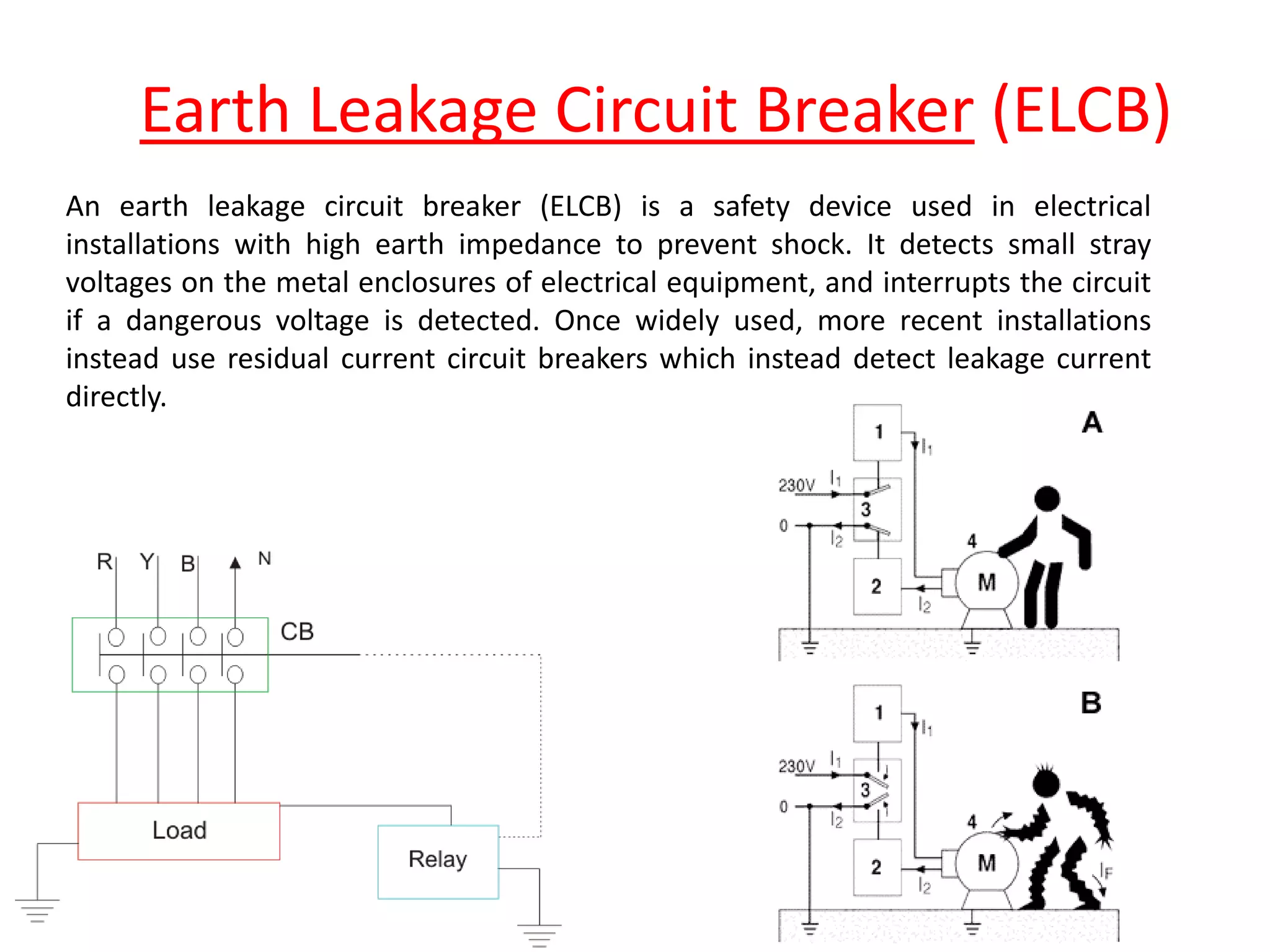
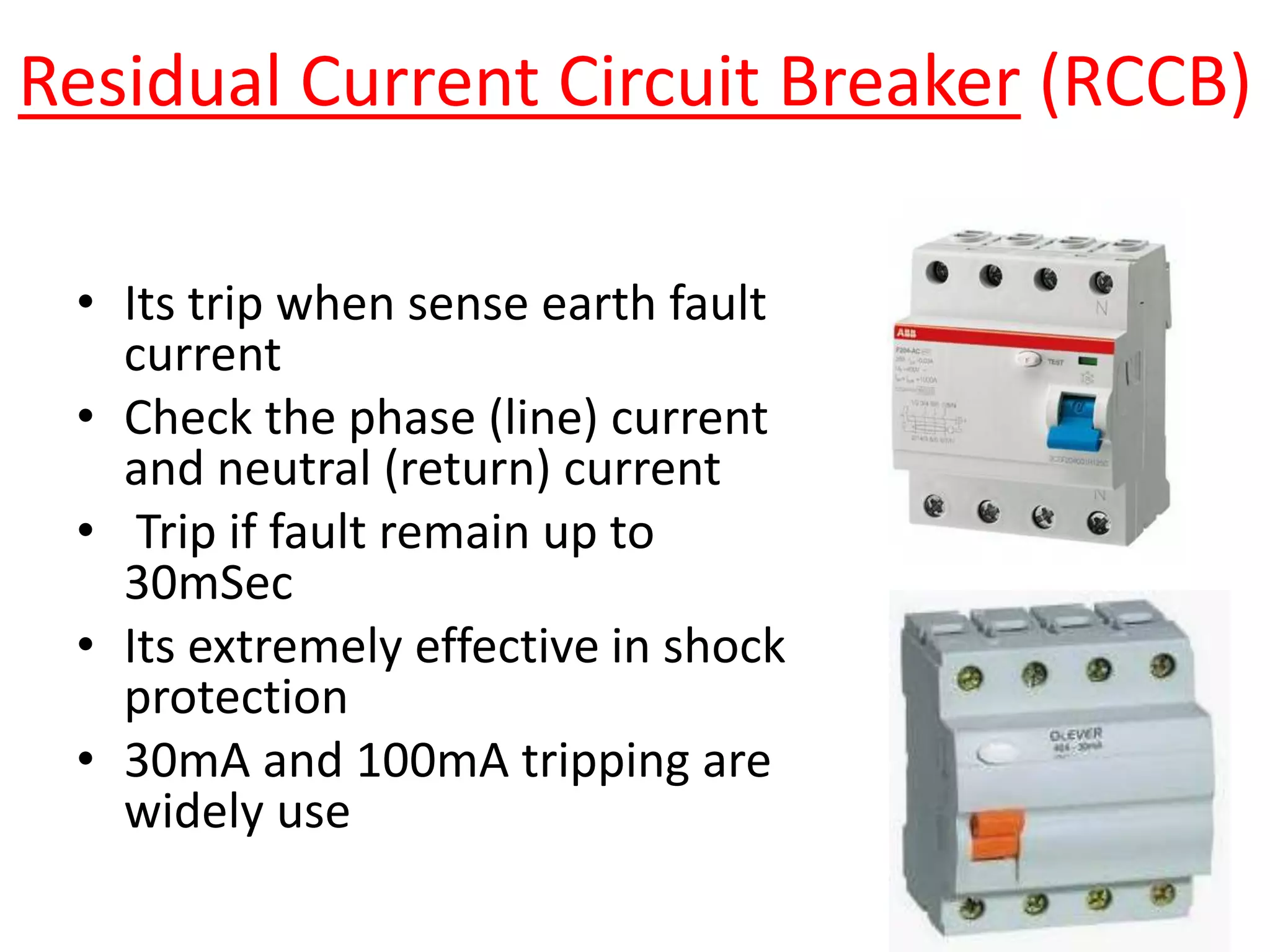
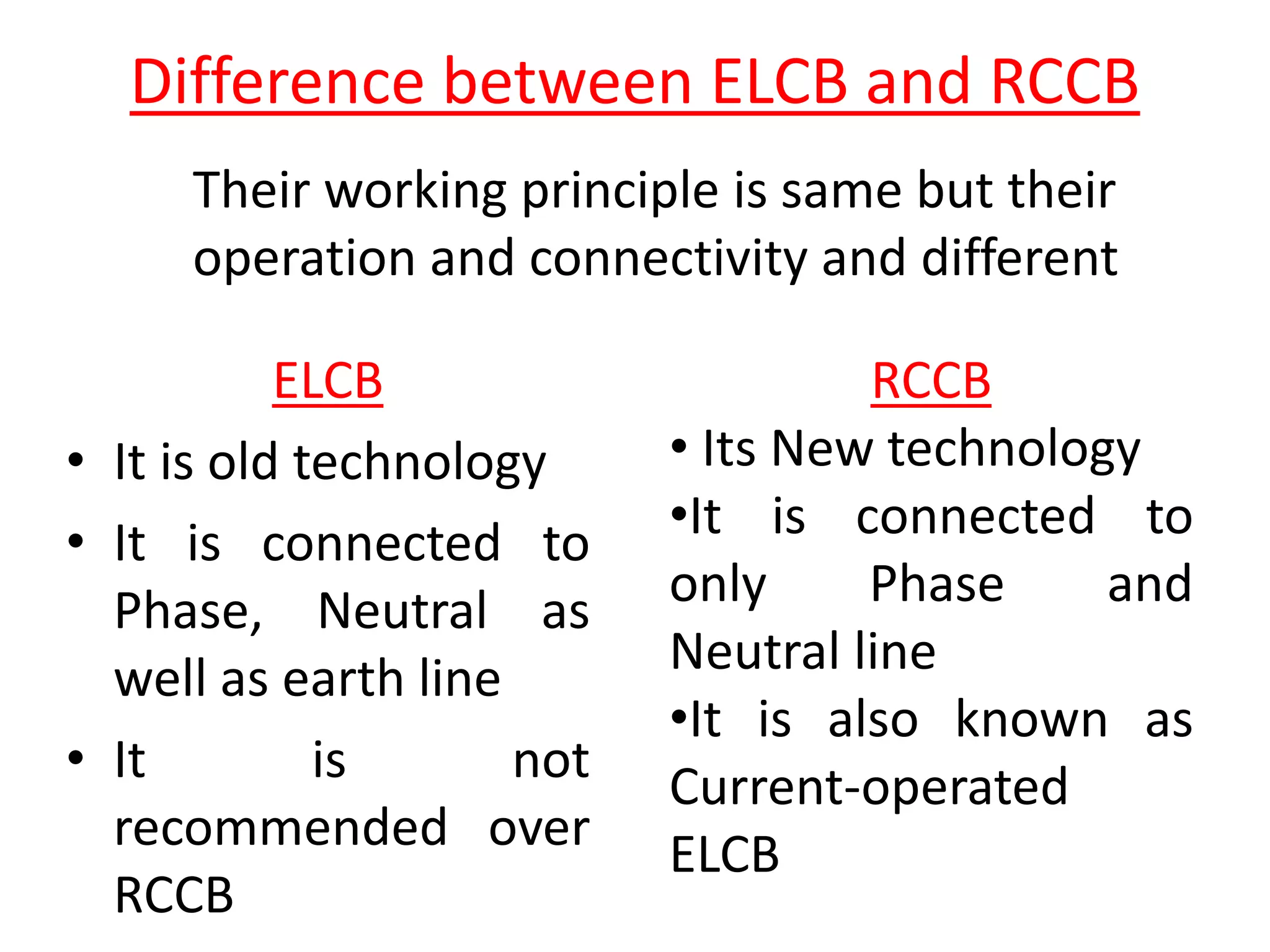
Circuit breakers are devices designed to automatically open an electrical circuit under abnormal current conditions without being damaged. They can be reset to resume normal operation, unlike fuses which must be replaced. There are different types of circuit breakers including oil, air, SF6, and vacuum. Circuit breakers can sense overcurrent through either thermal or magnetic methods and operate on either a time delay or instantaneous basis. Common circuit breakers used in buildings include miniature circuit breakers and molded case circuit breakers.