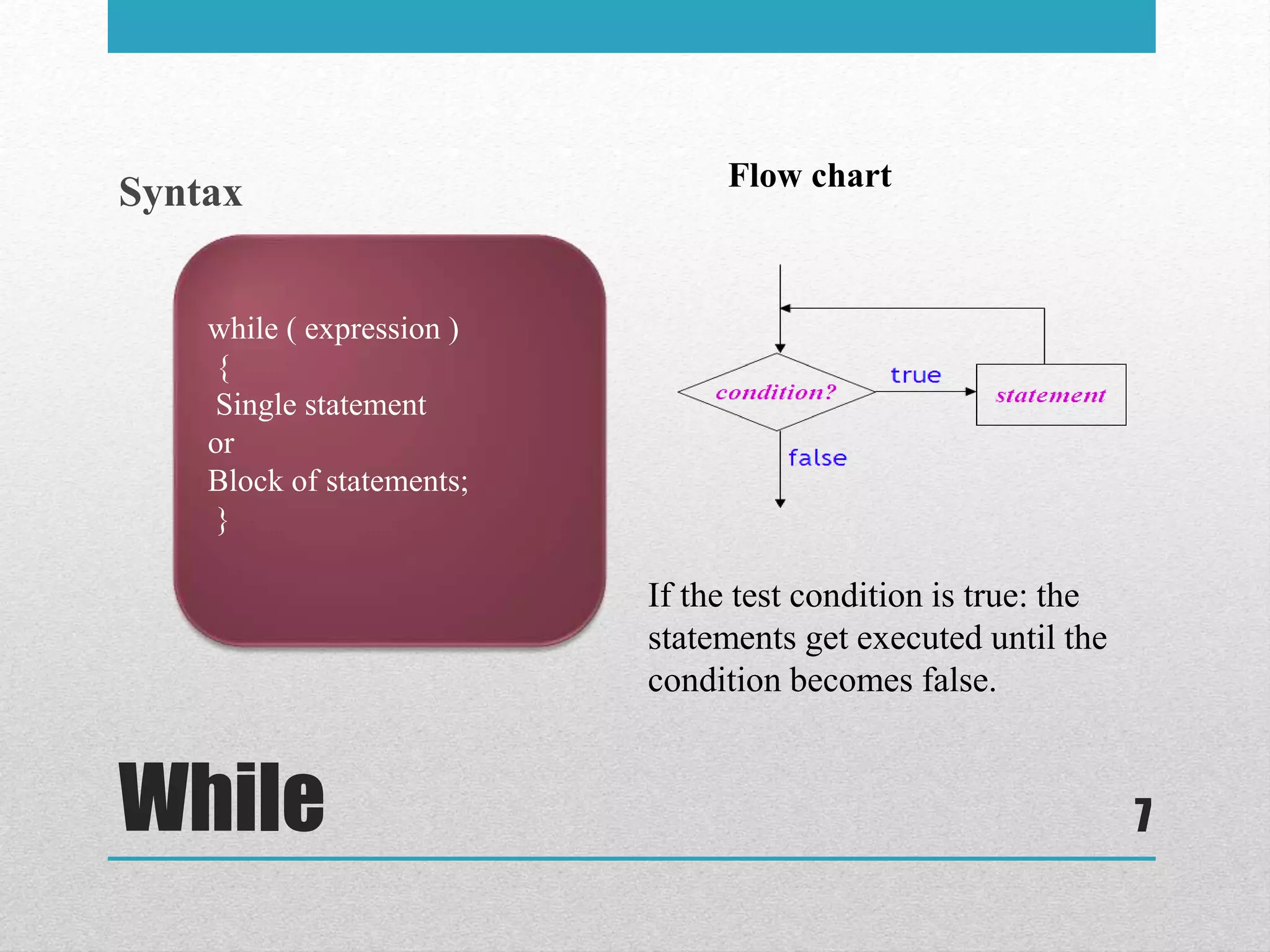
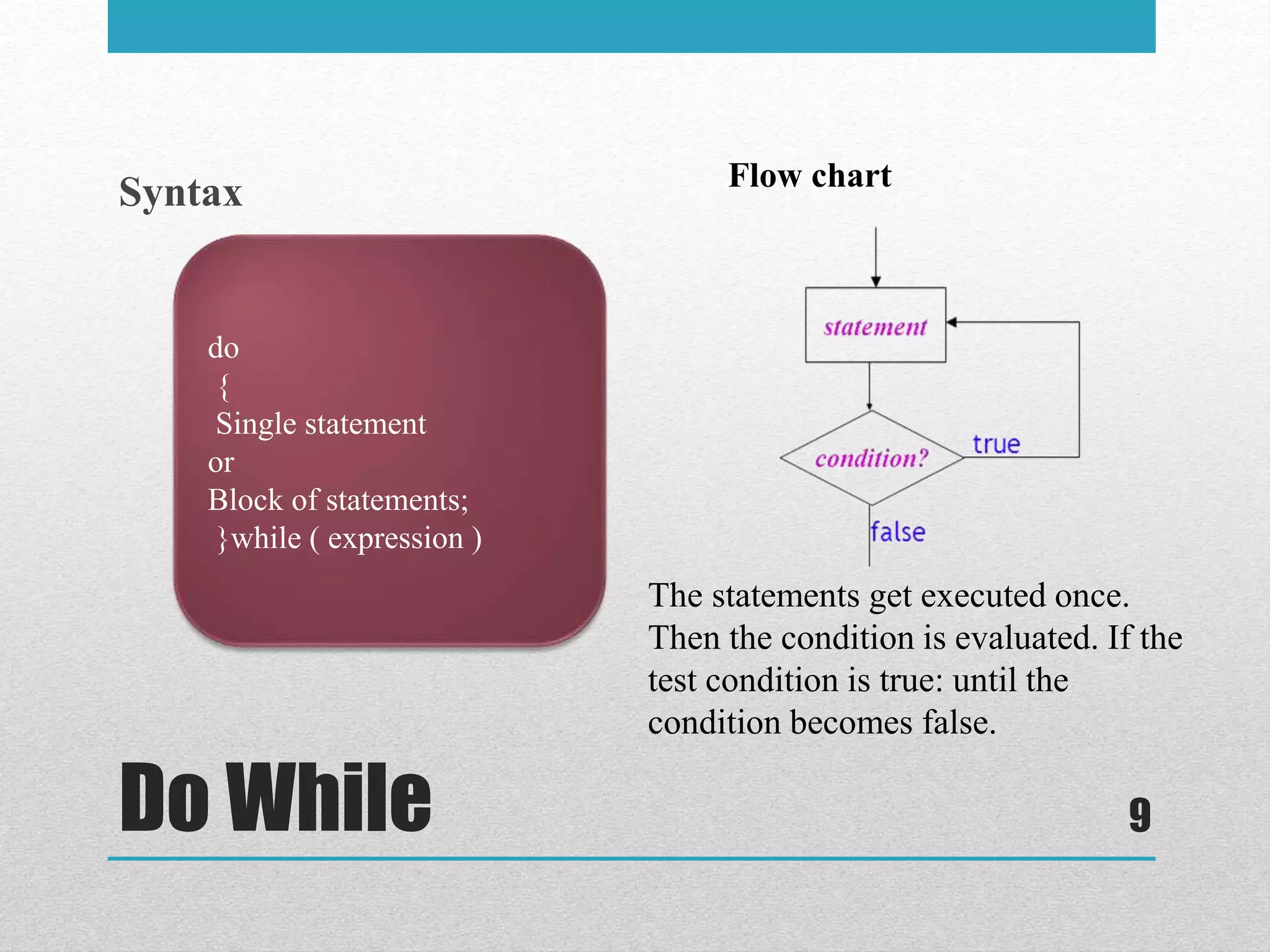
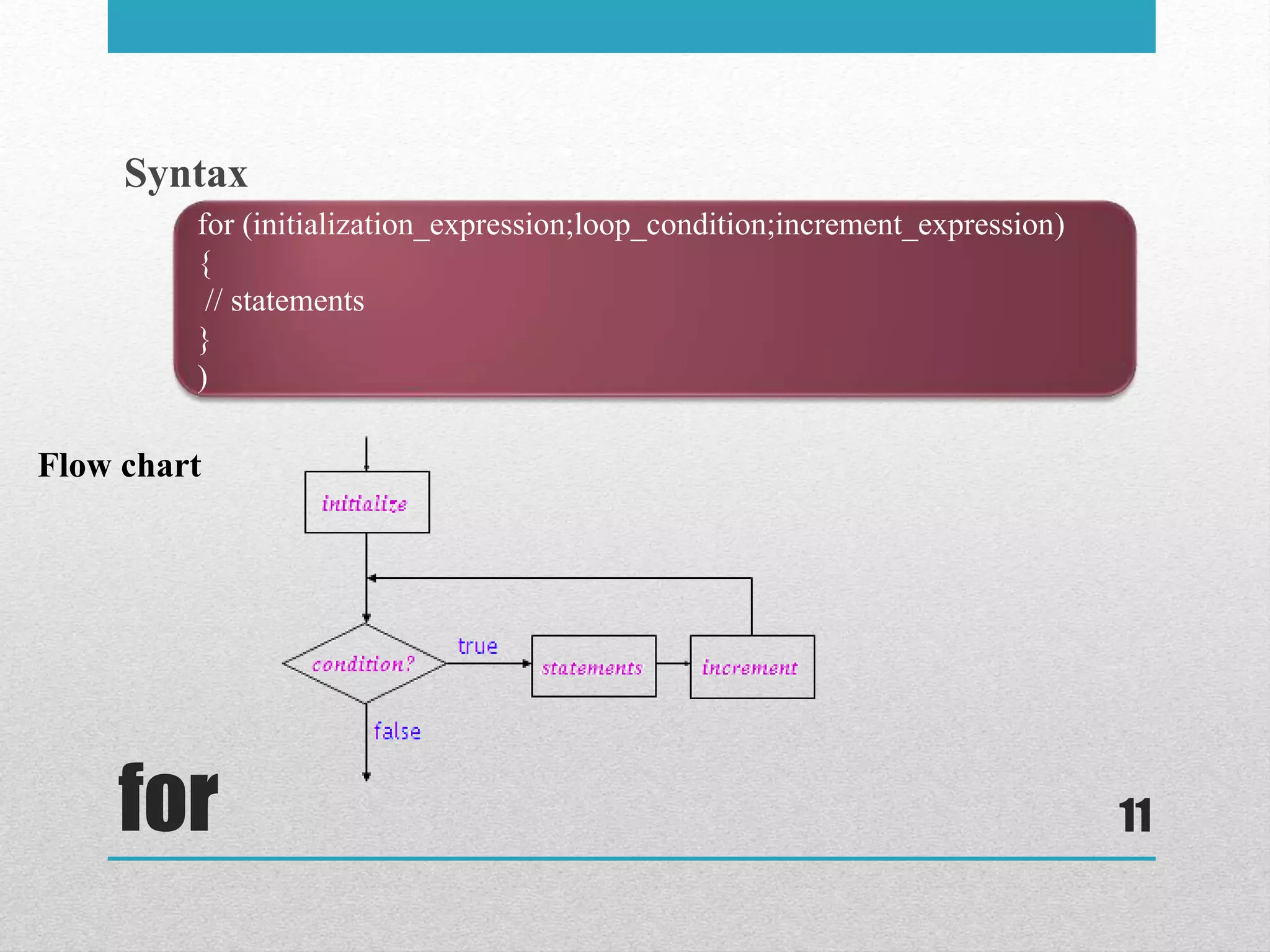
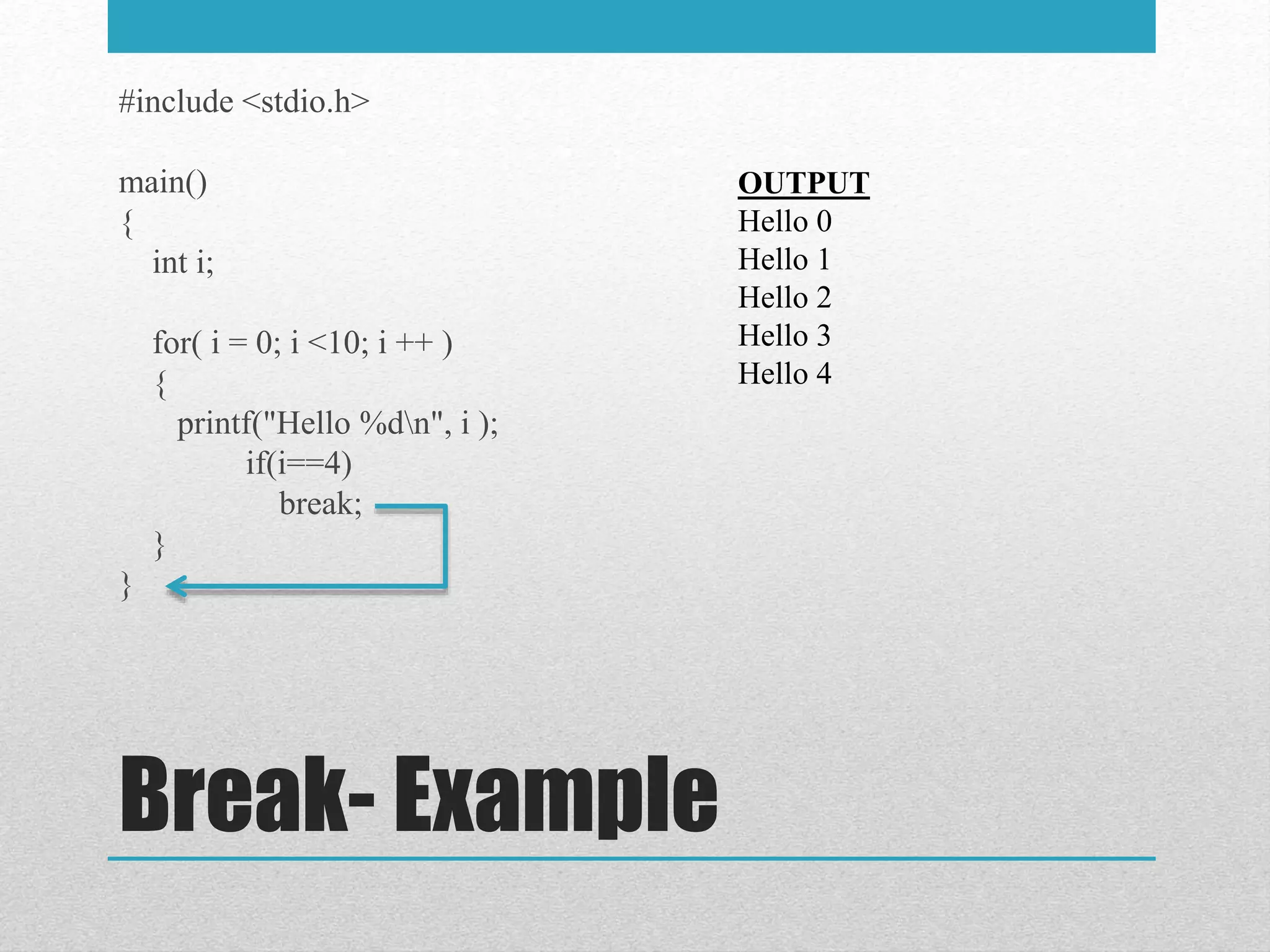
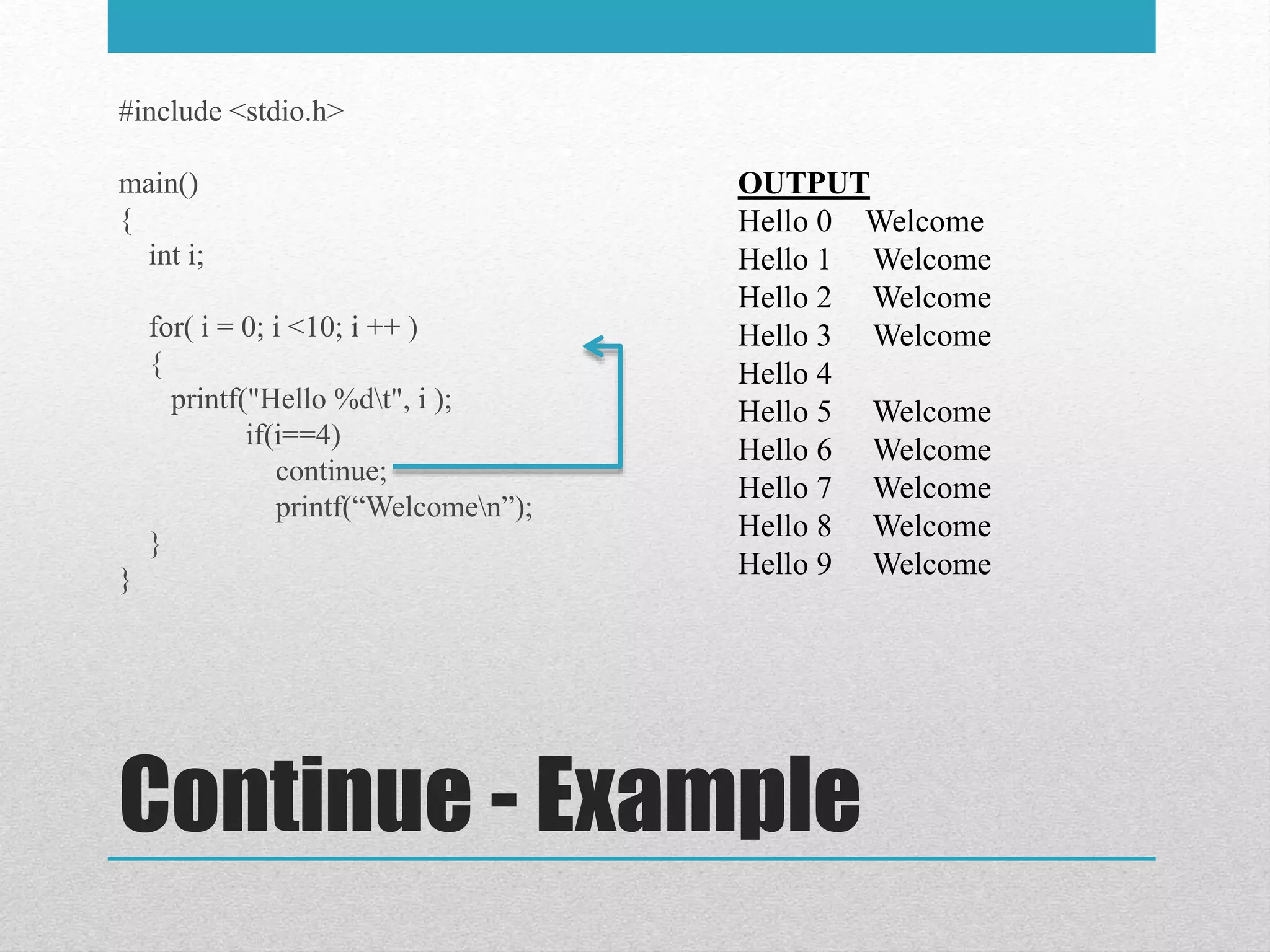
The document discusses looping statements in C. It explains that loops allow code to be repeated without having to rewrite the code multiple times. It describes three types of loops: while, do-while, and for. It provides the syntax and an example for each loop type. It also discusses the break and continue statements that can be used within loops to terminate the loop early or skip iterations.