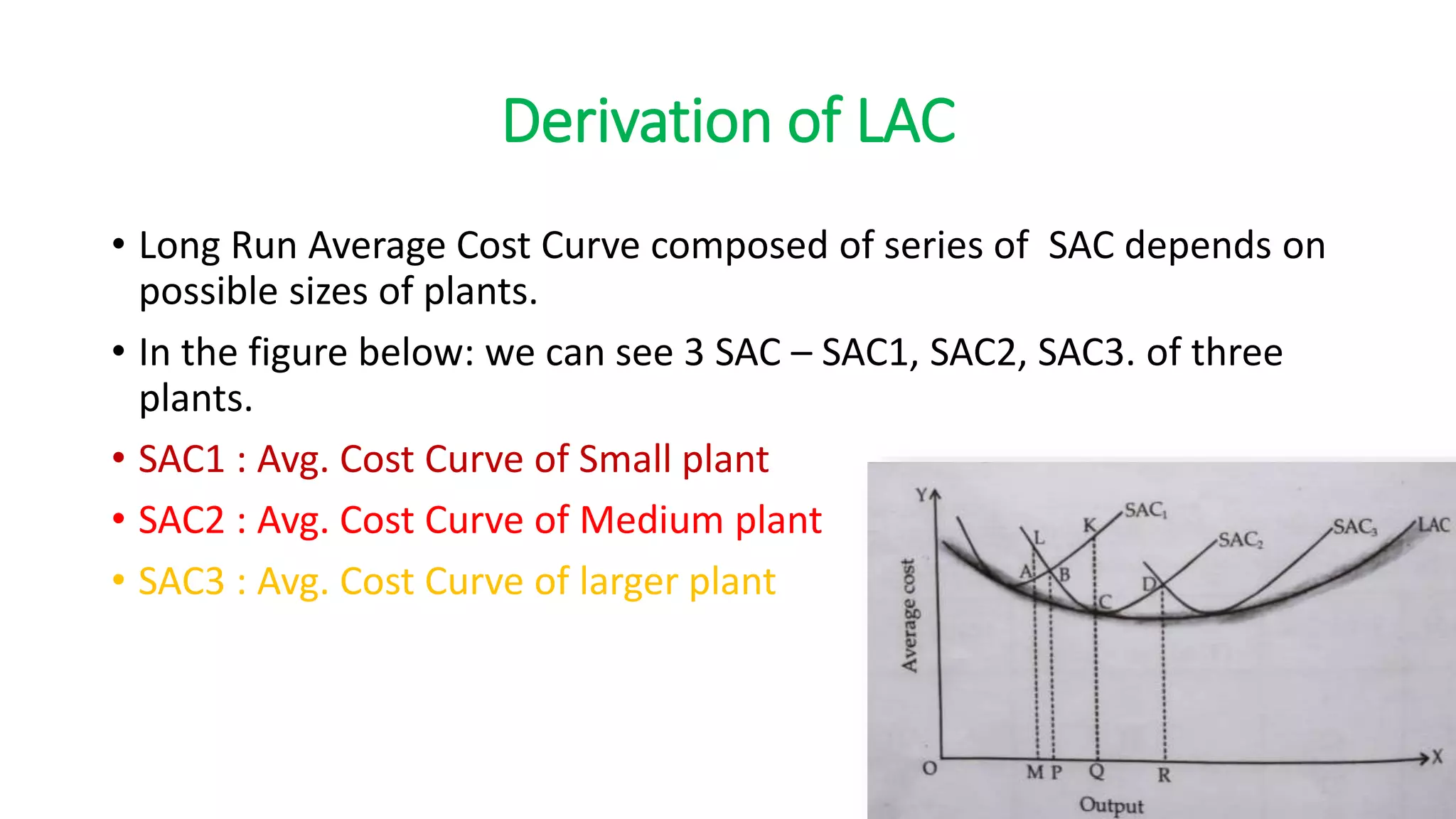
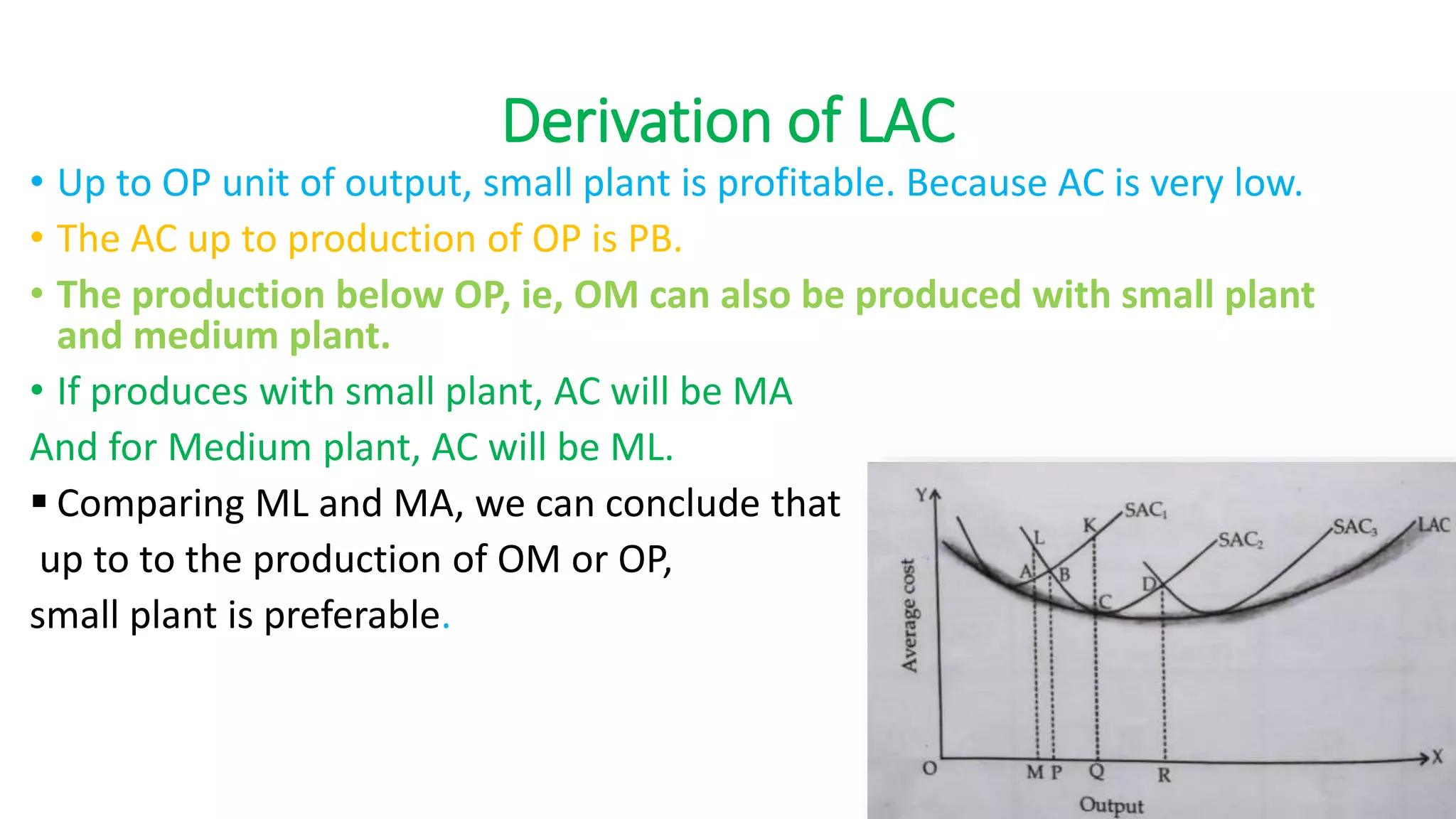
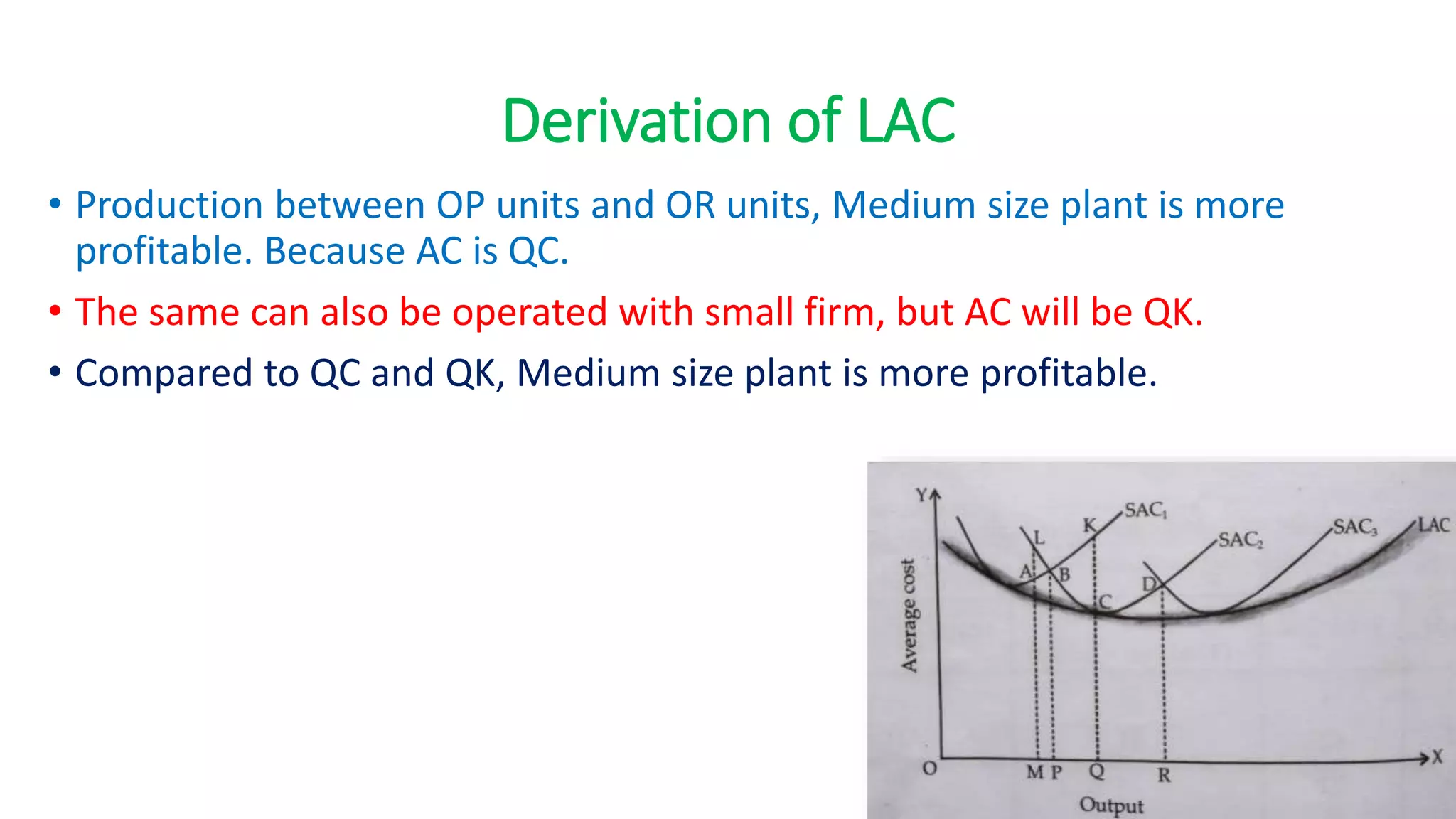
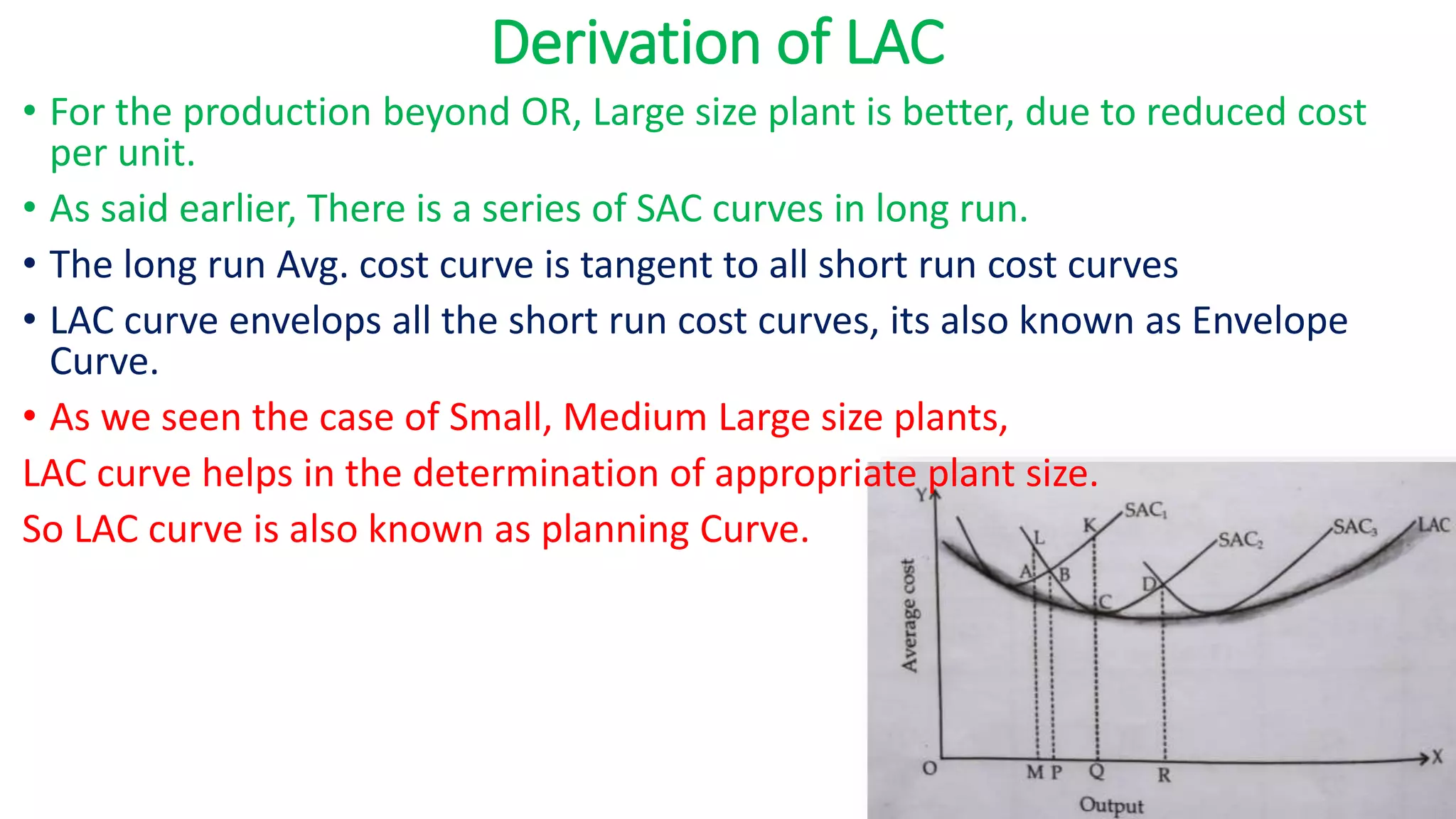
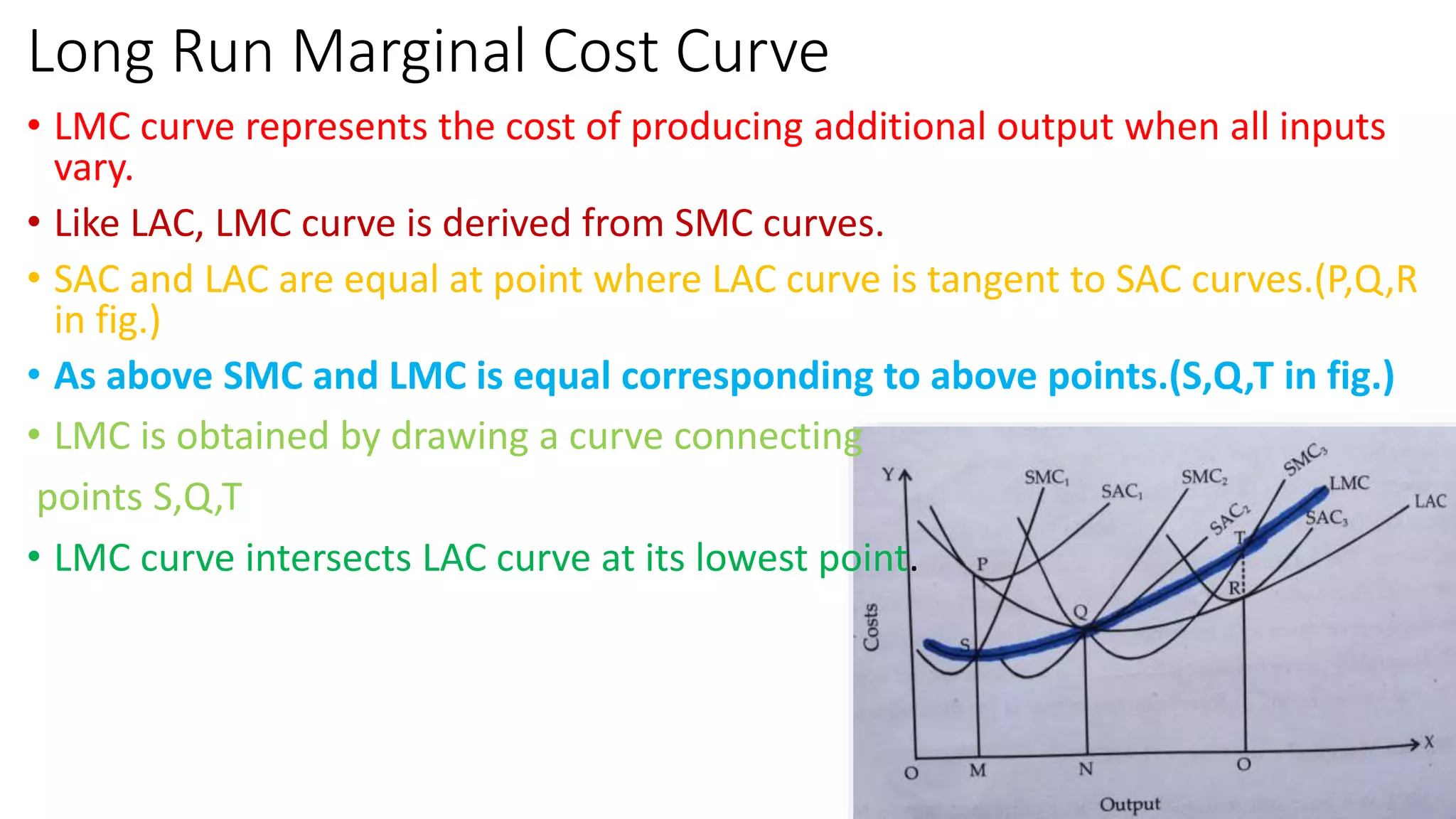
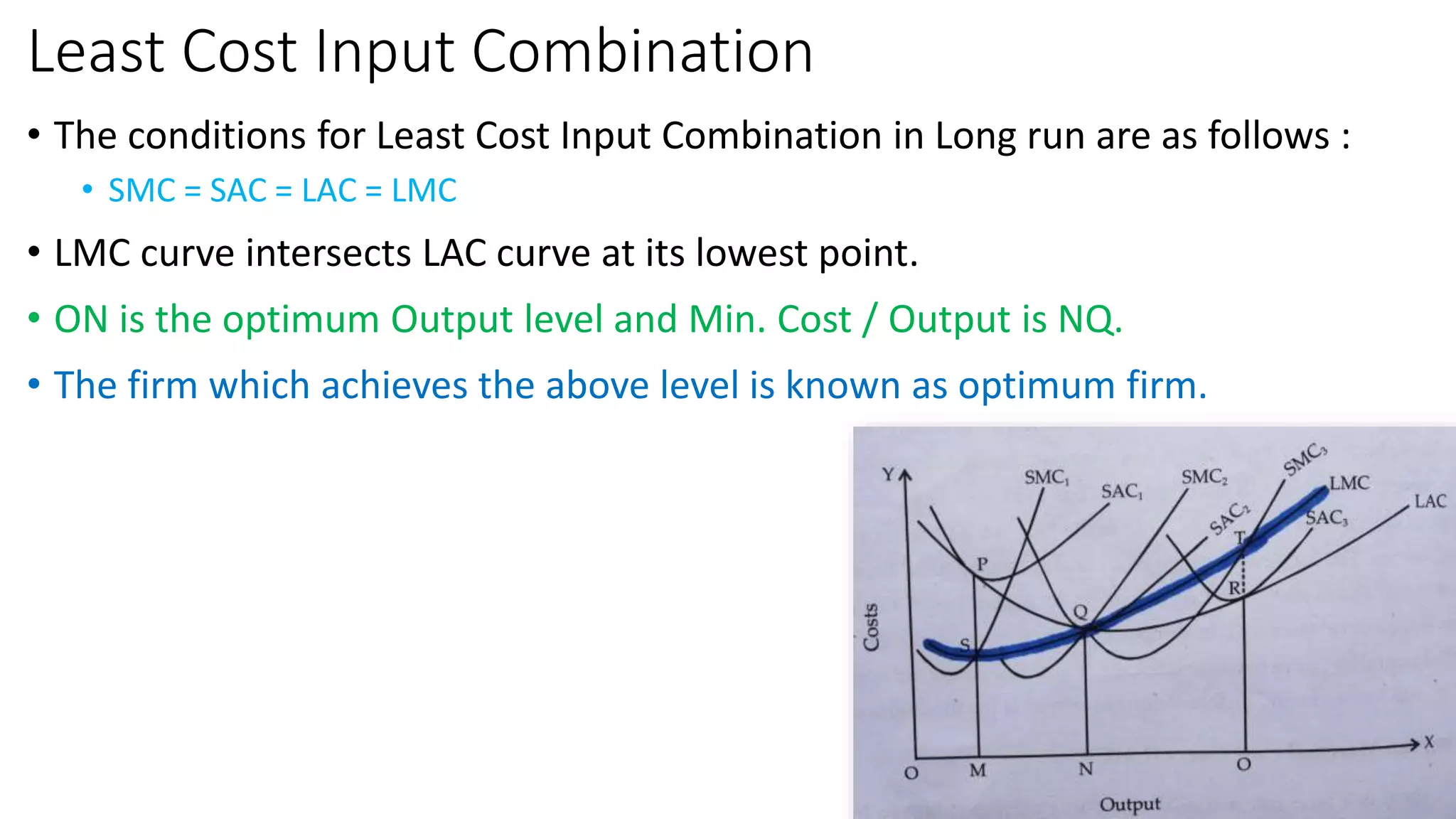
The document discusses long run cost functions in economics, covering determinants of cost, the cost-output relationship, and features of long run production. It emphasizes that in the long run, all factors are variable and firms can adjust production by varying plant size, leading to distinct average cost curves for each size. The long run average cost curve is derived from short-run average cost curves and helps determine the optimum firm size for cost minimization.