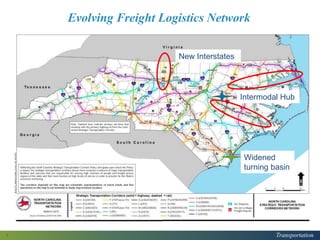
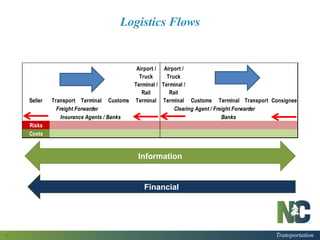
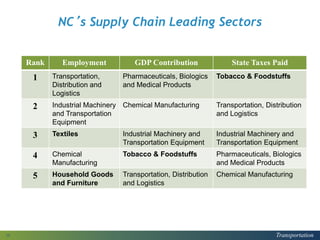
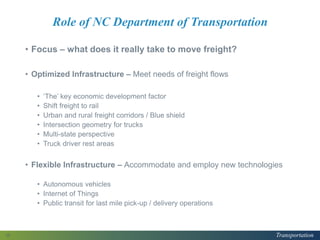
This document provides a logistics overview for North Carolina. It discusses the evolving freight logistics network in the state, including new interstates, widened turning basins, and intermodal hubs. Logistics and transportation are important as each North Carolinian generates or consumes 20 tons of freight per year. The document also summarizes a recent report on North Carolina's supply chain, finding that the transportation, distribution, and logistics sector employs over 105,000 workers and has an economic impact of over $5.7 billion in labor income. It identifies challenges like e-commerce, truck driver shortages, and the need for optimized and flexible infrastructure to accommodate changing technologies and freight flows.