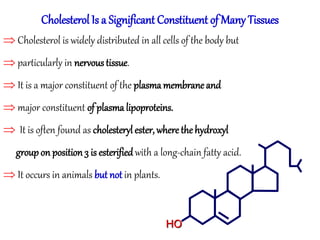
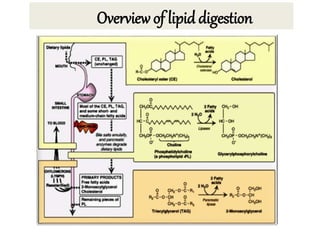
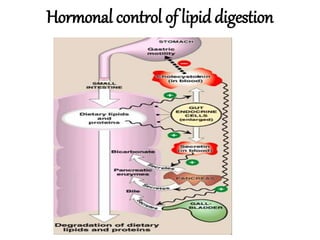
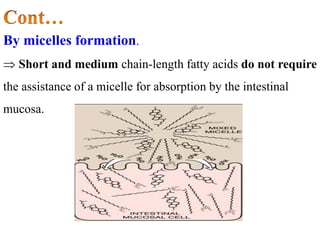
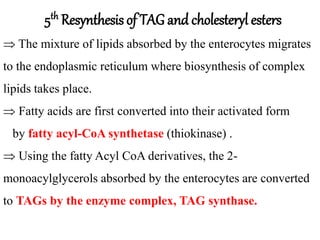
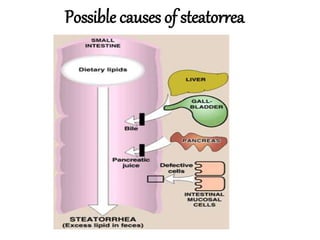
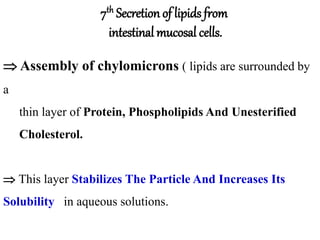
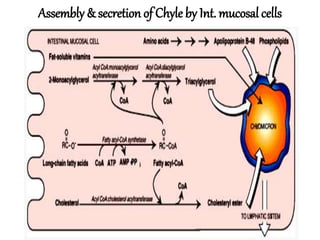
This document discusses lipids, their digestion, absorption, and utilization. It defines lipids and their classifications. Key points include: lipids are insoluble in water but soluble in nonpolar solvents. Dietary lipids are emulsified and hydrolyzed by pancreatic lipases in the small intestine. Bile salts and hormones like cholecystokinin and secretin regulate digestion. Lipids are absorbed via micelle transport across the intestinal epithelium and enter the lymphatic system. Cholesterol is an important precursor for bile acids, steroid hormones, vitamin D, and structural membranes.




































![Short answer Questions
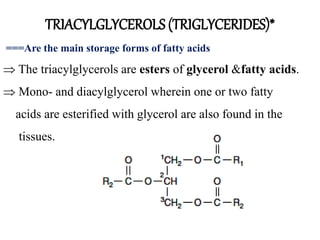
1.Triacylglycerols are
A. soluble in water B. partiallysoluble in water
C. Insoluble in water D. None
2.What are the components of a triacylglycerols?
3.What are the sources of fattyacids?
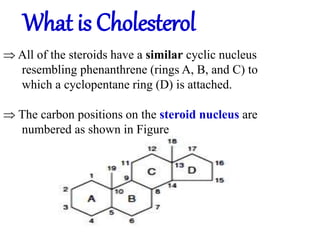
4.At whichposition is the fattyacidattached to the cholesterol ring,?
5.which fatty acid should havethe least melting point out of the followings?
Steric acid[0db] Arachidonic acid[4db], Timnodonic acid [5db]
6.Name a fatty acid with18 carbonatoms and a single double bond in trans
configuration
.7. Numbercarbons of cholesterol is -------------------](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lipiddigestionmd1-230325222623-3ad32a8d/85/lipid-digestion-MD-1-pptx-51-320.jpg)
