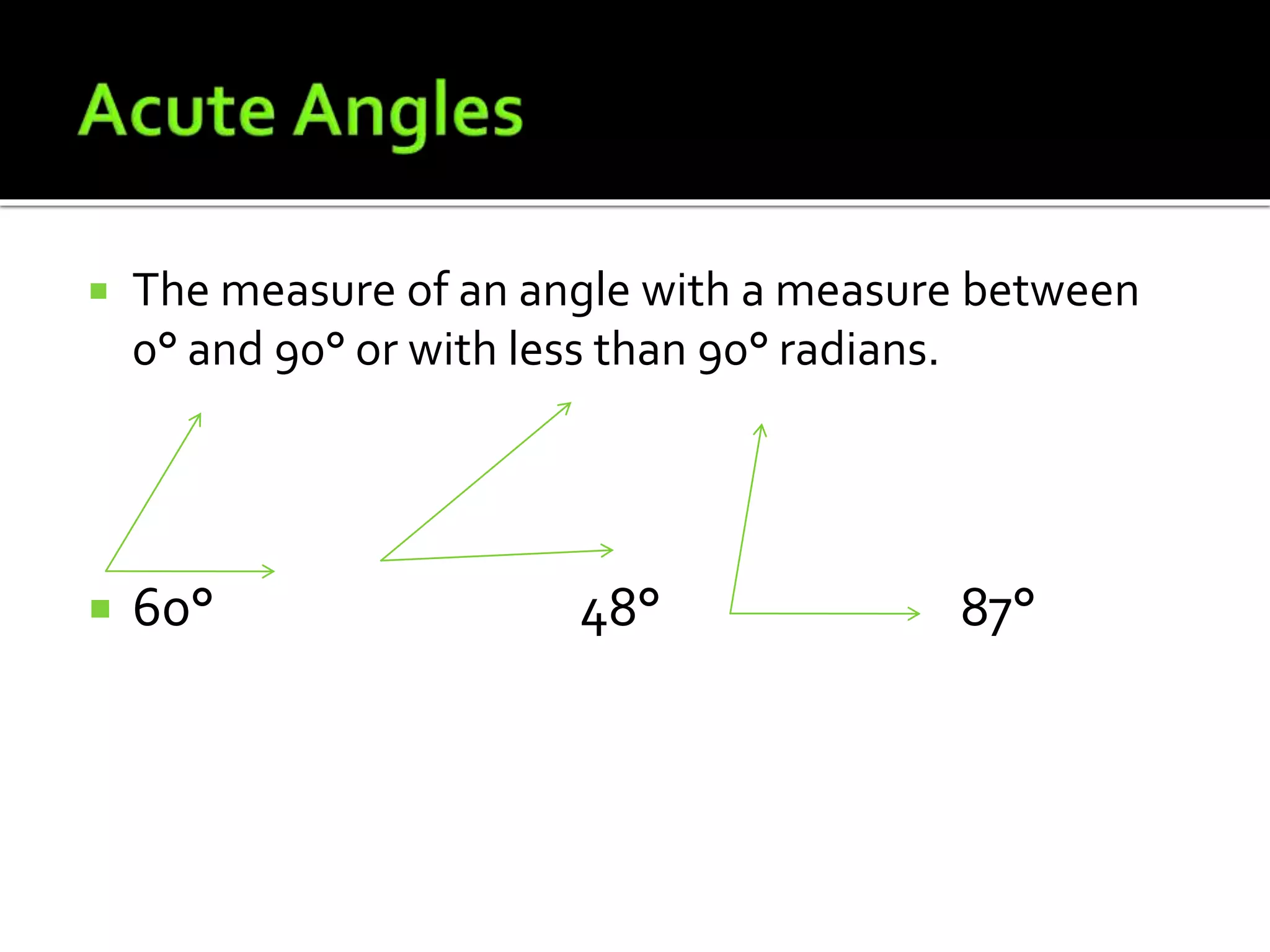
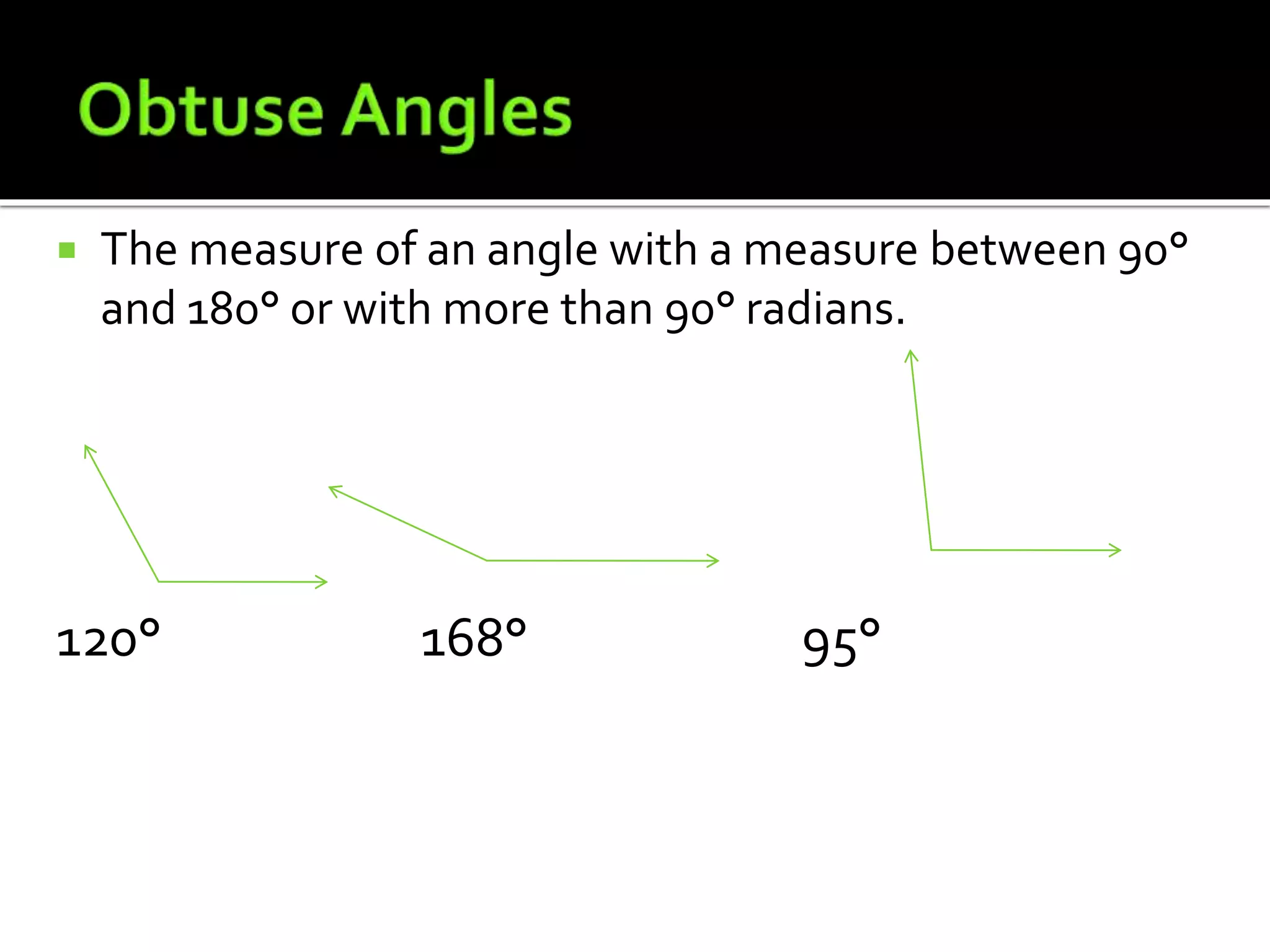
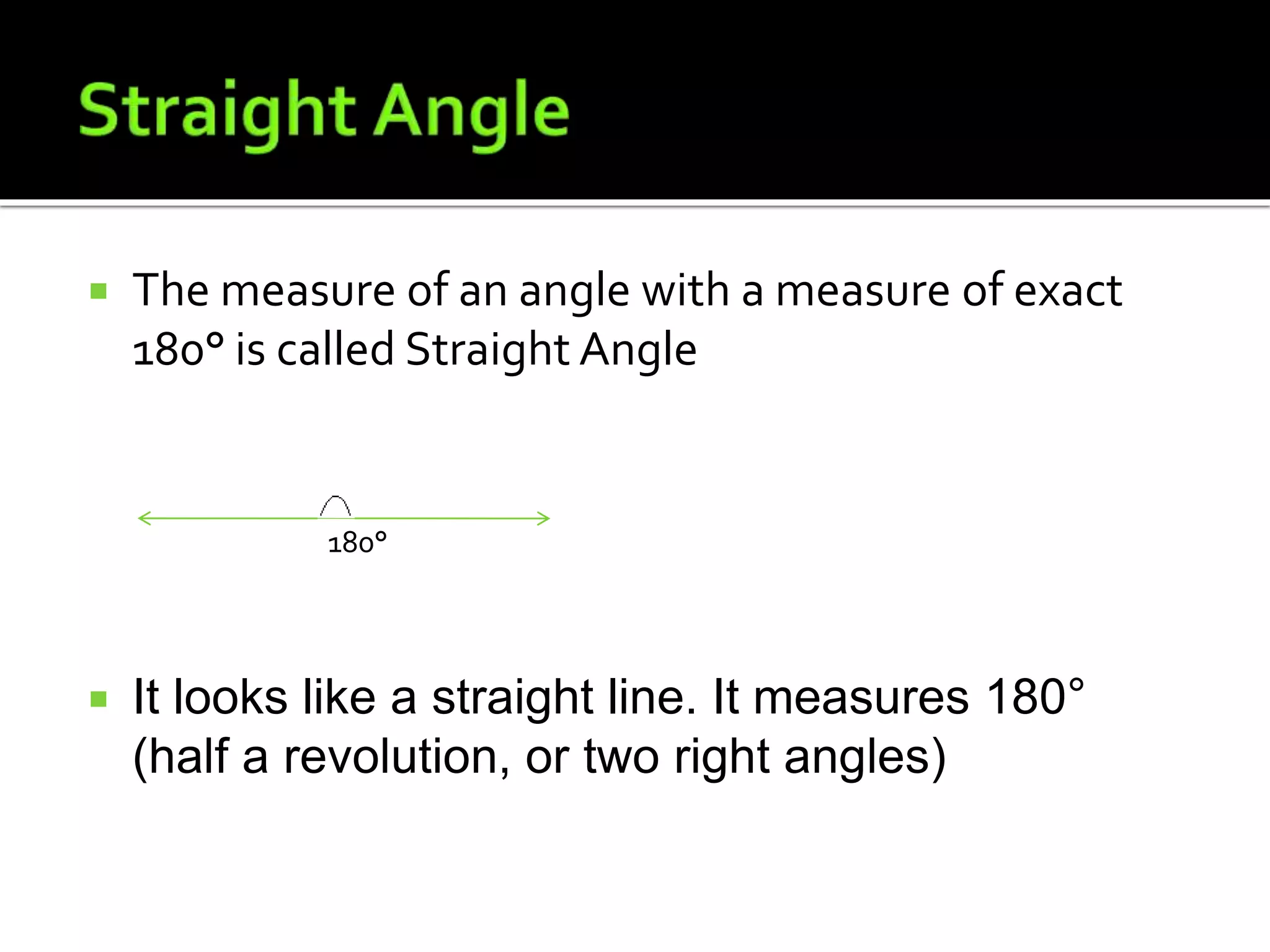
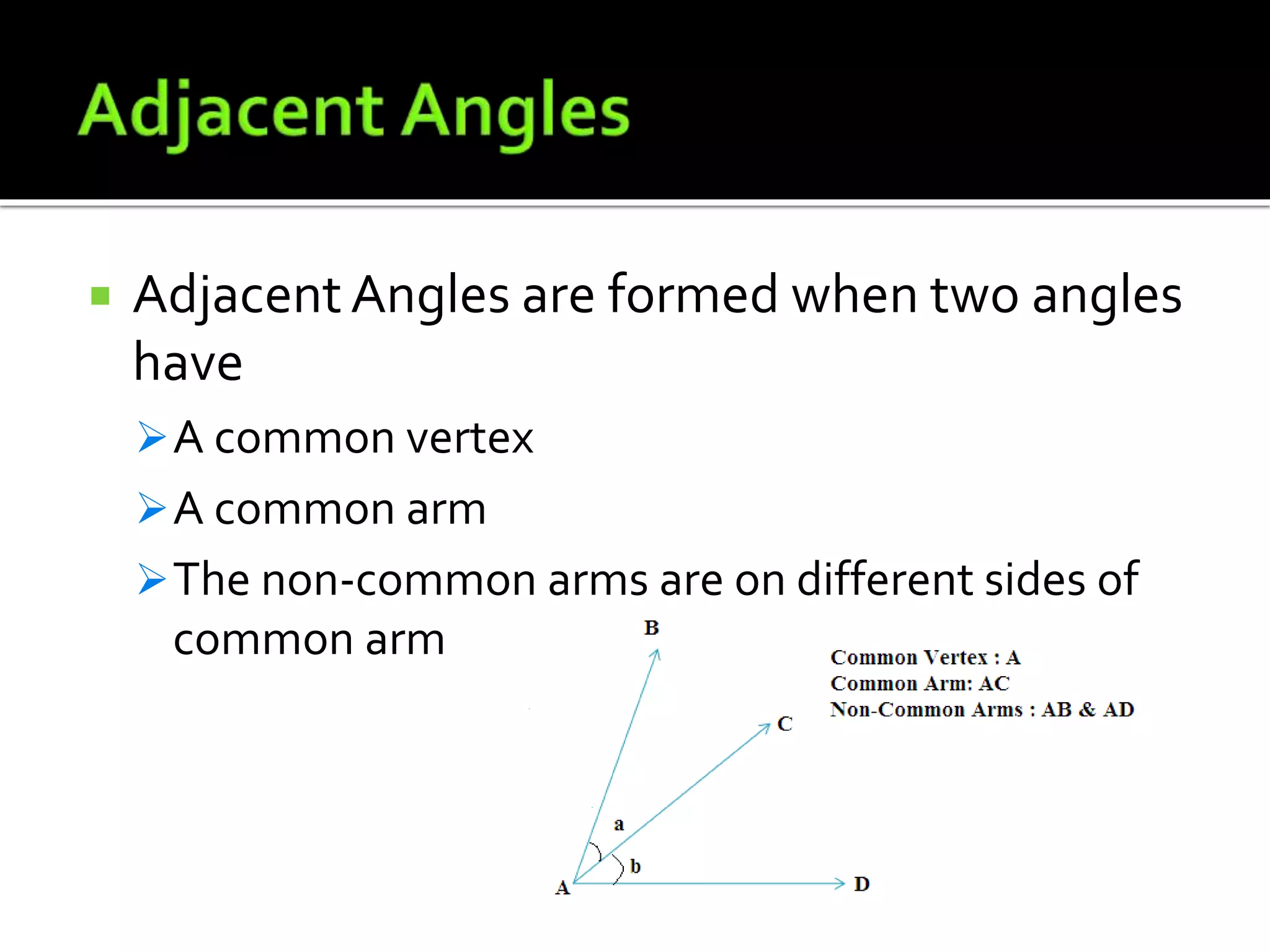
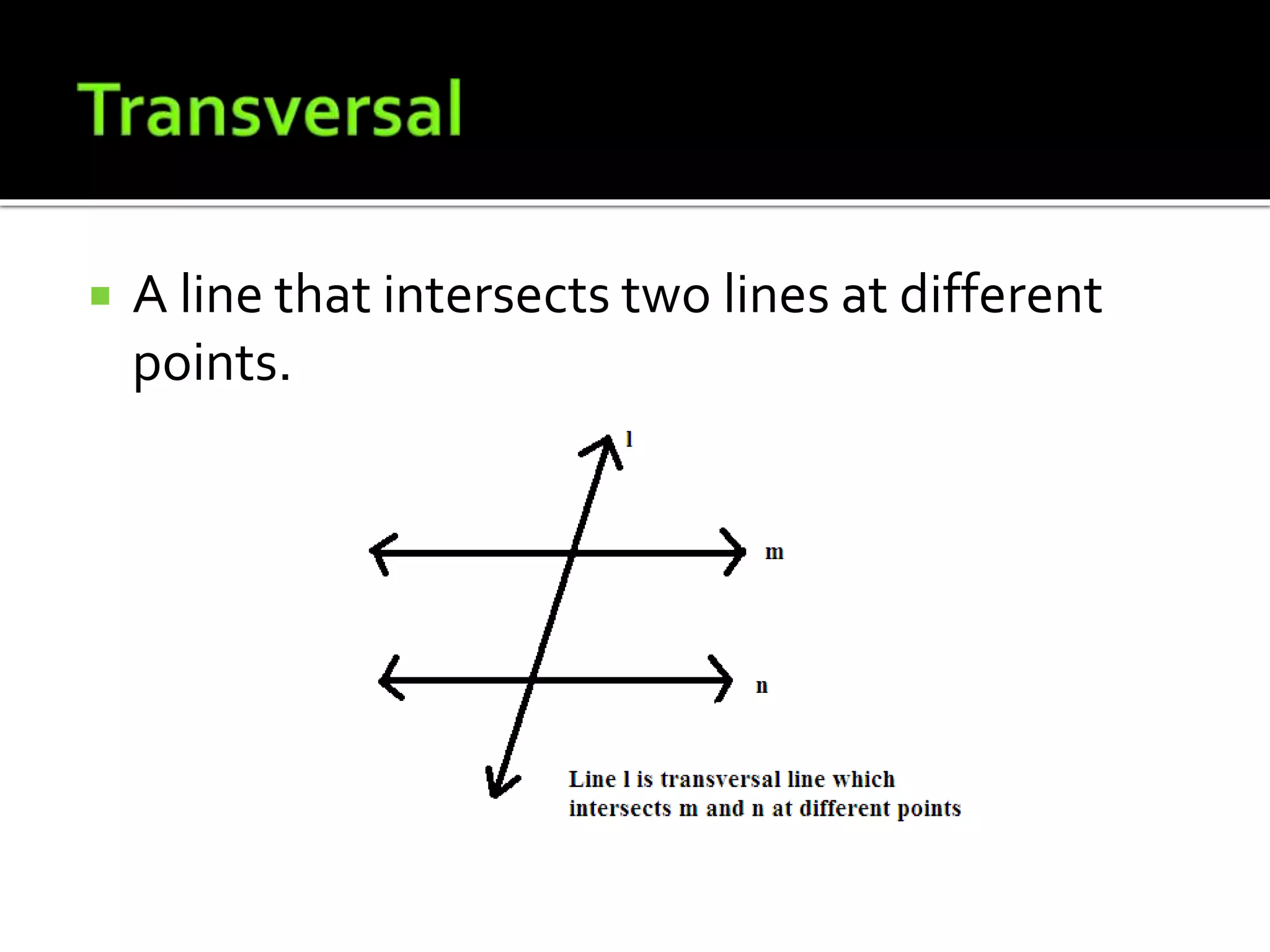
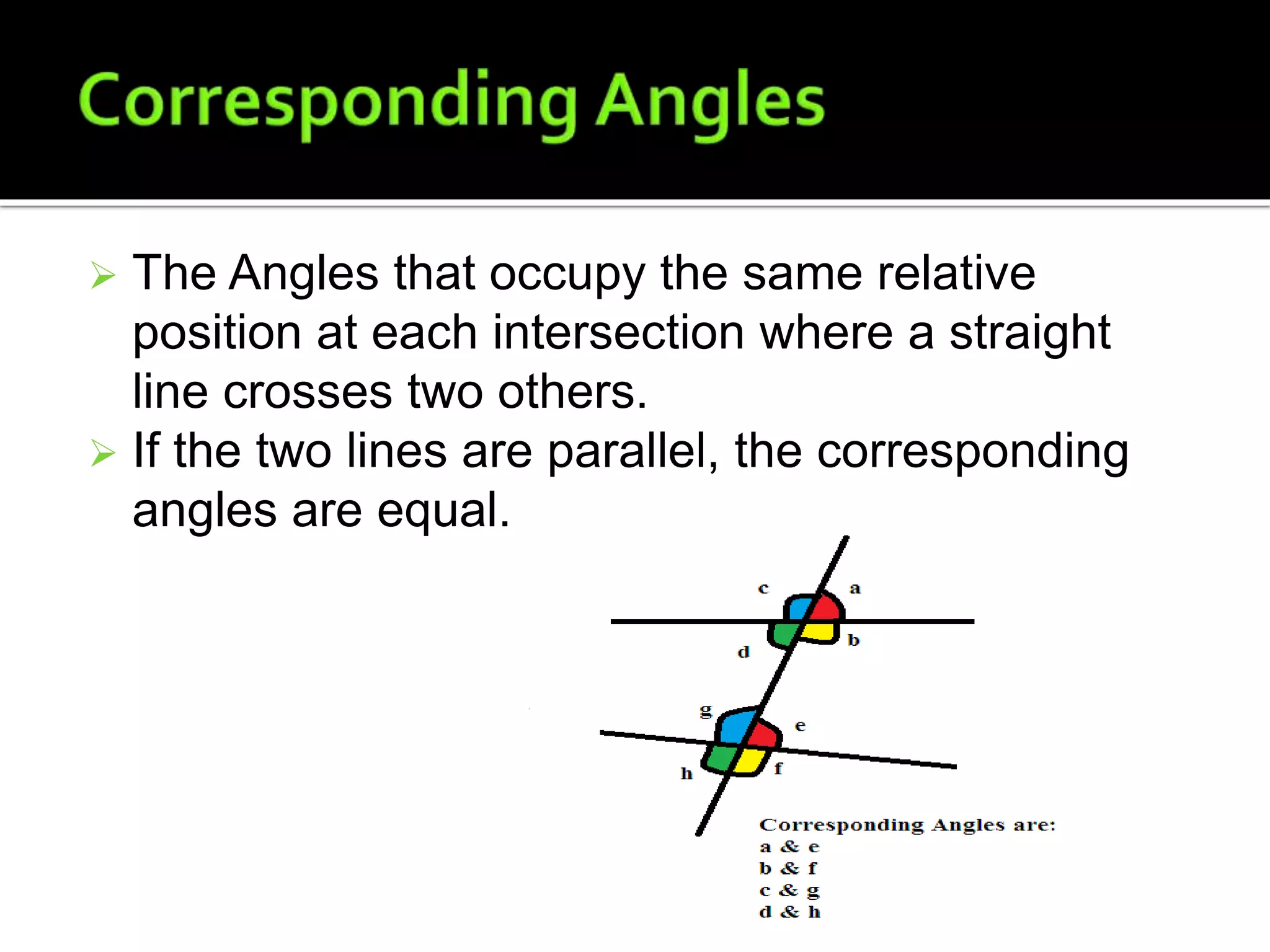
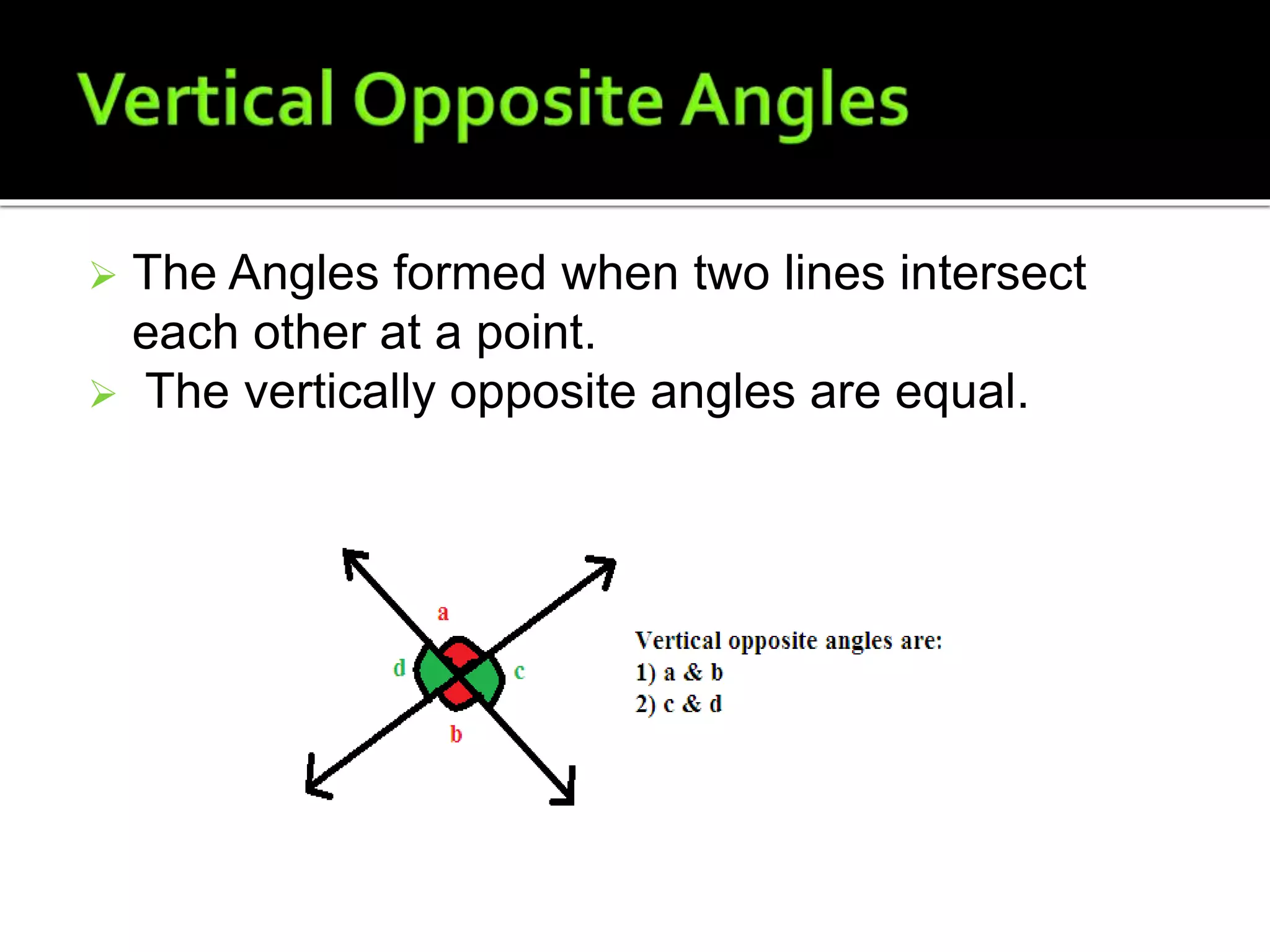
This document defines and provides examples of lines, angles, and the relationships between them. It explains that two points are needed to draw a line, which can be a line segment or ray. Lines can intersect or be parallel. Angles are formed by two rays with a common endpoint, and types of angles include acute, obtuse, right, straight, and reflex. The document also defines complementary angles, supplementary angles, adjacent angles, corresponding angles, vertical opposite angles, alternate interior angles, and alternate exterior angles.


![ There are two types of Lines :
Intersecting Lines
Non-Intersecting Lines [Parallel Lines]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/linesangles-170102064056/75/Lines-amp-angles-5-2048.jpg)